路径变量@PathVariable,格式校验:@Validated(Controller上)+ @Pattern + ConstraintViolationException(异常处理)
对API接口中的`路径参数`进行严格的合法性验证是一个重要的环节,以确保请求指向的资源正确无误。在 RESTful API 设计中,通常会通过URL路径中的特定字段来唯一标识资源,例如一个记录的ID。主要的应用场景包括:当需要根据`id`值查询、删除或更新数据库中的一条记录时,必须对传入的`id`参数进行长度和格式的有效性校验。
概述
对API接口中的路径变量进行严格的合法性验证是一个重要的环节,以确保请求指向的资源正确无误。在 RESTful API 设计中,通常会通过URL路径中的特定字段来唯一标识资源,例如一个记录的ID。
主要的应用场景包括:当需要根据id值查询、删除或更新数据库中的一条记录时,必须对传入的id参数进行长度和格式的有效性校验。比如,在执行如下的操作时:
- 通过给定的
id获取一条特定记录; - 根据提供的
id删除一条记录; - 使用指定的
id来修改一条记录的数据;
这些操作的前提都是能够准确地通过id定位到资源。如果接收到的id参数长度不合法(过长或过短),或者格式不符合预期(如应为整数但传入了非数字字符),那么这样的请求理论上不可能找到对应的数据库记录。因此,在服务端接口逻辑处理的最前端,即控制器层(Controller)中实施校验是非常关键的,可以有效拦截这类无效请求,避免不必要的数据库访问操作,同时也能及时返回错误信息,提高系统的稳定性和响应效率。
校验逻辑(有效格式)
在本例中,我们将对删除用户API接口的路径变量——用户ID进行严格格式校验。该接口遵循RESTful设计原则,其中用户ID作为路径变量直接嵌入URL中,用于唯一标识待删除的目标用户。
根据业务规则,此用户ID应当采用雪花算法生成,其标准格式为一个由19位数字组成的字符串。因此,在处理请求之前,我们需要在校验逻辑阶段确保传入的用户ID符合预期的格式要求,即确为一个19位的整数。

核心实现
开启校验,主要包含两个注解:
- 开启校验的注解:
@Validated - 校验格式的注解:
@Pattern
异常统一处理:
ConstraintViolationException
校验不通过会抛出异常 ConstraintViolationException,需要在异常统一处理中,加入对应的处理逻辑,向前端返回适当的响应。
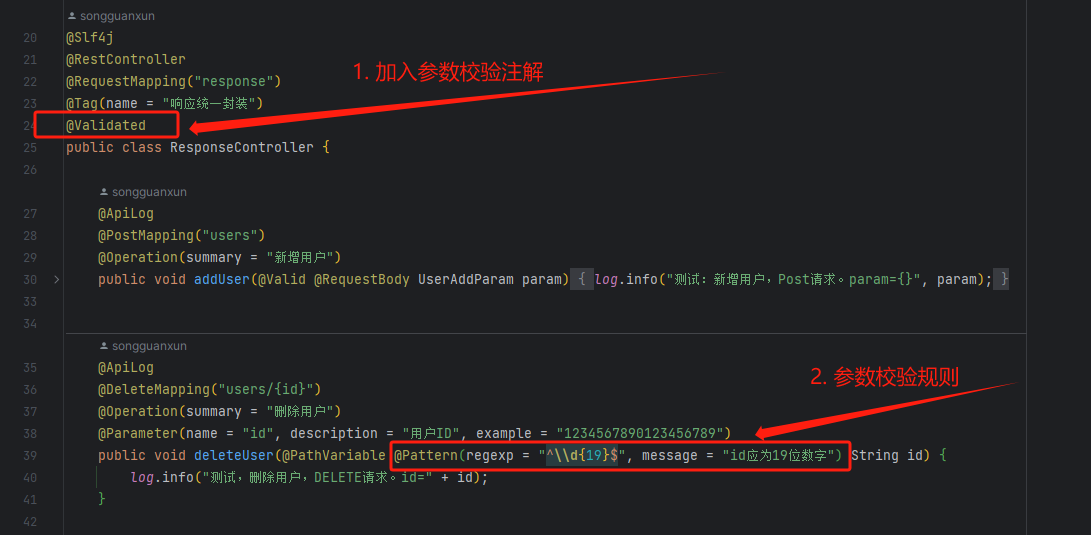
开启校验的注解:@Validated
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("response")
@Tag(name = "响应统一封装")
@Validated
public class ResponseController {
// 接口代码,省略。。。
}
@Validated,是 @Valid 的变体,本例需要对接口方法的参数直接进行校验,所以使用 @Validated(经过测试,使用@Valid无效,不能开启校验)。
@Validated 官方解释如下:
JSR-303的javax.validation.Validity的变体,支持验证组的规范。
可以与Spring MVC处理程序方法参数一起使用。

校验格式的注解:@Pattern
使用位置为:需要校验的路径变量前;
包含的内容有:参数的校验格式 和 校验不通过时的提示语。
@ApiLog
@DeleteMapping("users/{id}")
@Operation(summary = "删除用户")
@Parameter(name = "id", description = "用户ID", example = "1234567890123456789")
public void deleteUser(@PathVariable @Pattern(regexp = "^\\d{19}$", message = "id应为19位数字") String id) {
log.info("测试,删除用户,DELETE请求。id=" + id);
}
异常统一处理:ConstraintViolationException
异常处理代码
/**
* 参数校验异常:直接参数校验。
* <p>
* 此校验适用的接口,需要满足如下条件:
* 1. 需要校验的参数“直接”作为接口方法的参数;
* 2. Controller上添加 @Validated 注解;
* 3. 参数前添加了校验规则注解(比如 @Pattern)。
* <p>
* 示例:删除用户接口
*/
@ExceptionHandler
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public Result<String> handleException(ConstraintViolationException e, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
logInfo(e, handlerMethod);
String userMessage = UserTipGenerator.getUserMessage(e);
String errorMessage = String.format("【参数校验异常】(错误数量:%s):%s", e.getConstraintViolations()
.size(), e.getMessage());
return Result.fail(userMessage, String.valueOf(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value()), errorMessage);
}
异常处理代码图示

不进行异常处理的接口响应

异常统一处理后的接口响应

完整示例代码
接口校验
package com.example.web.response.controller;
import com.example.core.log.annotation.ApiLog;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Operation;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Parameter;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.tags.Tag;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.validation.constraints.Pattern;
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("response")
@Tag(name = "响应统一封装")
@Validated
public class ResponseController {
@ApiLog
@DeleteMapping("users/{id}")
@Operation(summary = "删除用户")
@Parameter(name = "id", description = "用户ID", example = "1234567890123456789")
public void deleteUser(@PathVariable @Pattern(regexp = "^\\d{19}$", message = "id应为19位数字") String id) {
log.info("测试,删除用户,DELETE请求。id=" + id);
}
// 其他接口省略 ...
}
异常统一处理
package com.example.core.advice;
import com.example.core.advice.util.ErrorMessageGenerator;
import com.example.core.advice.util.UserTipGenerator;
import com.example.core.model.BusinessException;
import com.example.core.model.Result;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.validation.BindException;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolationException;
import java.util.List;
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
private final HttpServletRequest request;
public GlobalExceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest request) {
this.request = request;
}
/**
* Get请求,参数校验异常:对象参数校验。
*/
@ExceptionHandler
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public Result<Void> handleException(BindException e, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
logInfo(e, handlerMethod);
List<FieldError> fieldErrors = e.getFieldErrors();
String userMessage = UserTipGenerator.getUserMessage(fieldErrors);
String errorMessageCore = ErrorMessageGenerator.getErrorMessage(fieldErrors);
HttpStatus httpStatus = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
String errorMessage = String.format("【参数校验异常】(错误数量:%s):%s", e.getErrorCount(), errorMessageCore);
return Result.fail(userMessage, String.valueOf(httpStatus.value()), errorMessage);
}
@ExceptionHandler
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public Result<String> handleException(ConstraintViolationException e, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
logInfo(e, handlerMethod);
String userMessage = UserTipGenerator.getUserMessage(e);
HttpStatus httpStatus = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
String errorMessage = String.format("【参数校验异常】(错误数量:%s):%s", e.getConstraintViolations()
.size(), e.getMessage());
return Result.fail(userMessage, String.valueOf(httpStatus.value()), errorMessage);
}
/**
* 业务异常处理
*/
@ExceptionHandler
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public Result<Void> handleException(BusinessException e, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
logInfo(e, handlerMethod);
return Result.fail(e.getUserMessage(), e.getErrorCode(), e.getErrorMessage());
}
private void logInfo(Exception e, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
String message = getLogMessage(e, handlerMethod);
log.info(message, e);
}
private String getLogMessage(Exception e, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) {
String exceptionName = e.getClass()
.getName();
String requestMethod = request.getMethod();
String url = request.getRequestURI();
String className = handlerMethod.getBean()
.getClass()
.getName();
String methodName = handlerMethod.getMethod()
.getName();
return String.format("\n接口:[%s:%s]\n异常名称:[%s]\n出现异常的方法:[%s.%s]\n异常信息:\n%s", requestMethod, url, exceptionName, className, methodName, e.getMessage());
}
}
package com.example.core.advice.util;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolation;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolationException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 用户提示生成器。
*
* @author songguanxun
* @date 2023-8-24
*/
public class UserTipGenerator {
/**
* 获取用户提示(参数校验异常时)
*/
public static String getUserMessage(List<FieldError> errors) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
errors.forEach(error -> {
String defaultMessage = error.getDefaultMessage();
String numberFormatExceptionName = NumberFormatException.class.getName();
if (defaultMessage != null && defaultMessage.contains(numberFormatExceptionName)) {
String message = String.format("数字格式异常,当前输入为:[%s]", error.getRejectedValue());
stringBuilder.append(message)
.append(";");
} else {
stringBuilder.append(defaultMessage)
.append(";");
}
});
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
public static String getUserMessage(ConstraintViolationException e) {
Set<ConstraintViolation<?>> sets = e.getConstraintViolations();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sets)) {
return "";
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sets.forEach(error -> sb.append(error.getMessage())
.append(";"));
return sb.toString();
}
}
校验效果
成功

失败


开放原子开发者工作坊旨在鼓励更多人参与开源活动,与志同道合的开发者们相互交流开发经验、分享开发心得、获取前沿技术趋势。工作坊有多种形式的开发者活动,如meetup、训练营等,主打技术交流,干货满满,真诚地邀请各位开发者共同参与!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献27条内容
已为社区贡献27条内容





所有评论(0)