simplifyEnrichment简化富集分析结果
主要针对富集分析的结果进行简化,并提供了一些强大的可视化函数。GO的条目是冗余的,做一次GO富集分析可以得到几千条term,让人眼花缭乱,可以使用simplify函数去冗余。做的是类似的事情,但是并,把相似性大的条目聚到一起,实现“物以类聚人以群分”的效果,让我们对所有的富集的结果有一个整体的认知。作者开发了一种binary cut但DOSEmeshesReactomePA以上几个函数都是计算相似
simplifyEnrichment主要针对富集分析的结果进行简化,并提供了一些强大的可视化函数。
GO的条目是冗余的,做一次GO富集分析可以得到几千条term,让人眼花缭乱,clusterprofiler可以使用simplify函数去冗余。
simplifyEnrichment做的是类似的事情,但是并不是直接去除冗余,而是对所有的GO条目进行聚类,把相似性大的条目聚到一起,实现“物以类聚人以群分”的效果,让我们对所有的富集的结果有一个整体的认知。
作者开发了一种binary cut的方法,聚类结果比其他方法更好,具体方法细节可以参考作者的paper:simplifyEnrichment: A Bioconductor Package for Clustering and Visualizing Functional Enrichment Results
但simplifyEnrichment不仅可以对GO的term进行聚类,其他的数据也可以,包括:
- 由不同基因集组成的列表
enrichResult对象(也就是clusterProfiler,DOSE,meshes,ReactomePA的ORA结果),看过前面几篇推文的你肯定知道这是什么- KEGG/Reactome/MsigDB的id组成的列表
- gmt文件以及对应的基因集ID
并且作者开发了专门的函数用于对接以上数据:term_similarity_from_enrichResult(), term_similarity_from_KEGG(), term_similarity_from_Reactome(), term_similarity_from_MSigDB()
以上几个函数都是计算相似性矩阵用的,下面会演示什么是相似形矩阵。
simplifyEnrichment的作者即是大名鼎鼎的complexheatmap包的作者。
本期目录:
准备数据
用gse87466这个GEO的数据做演示,下载整理的过程这次就不演示了。数据可以直接在粉丝QQ群下载。
load(file = "G:/easyTCGA_test/gse87466.Rdata")
这是一个炎症性肠病的数据集,一共108个样本,21个normal,87个uc(ulcerative colitis)。
exprSet[1:4,1:4]
## GSM2332098 GSM2332099 GSM2332100
## IGK@ /// IGKC 13.86197 13.76880 13.95740
## 13.95740 13.92619 13.79664
## IGL@ 13.73797 13.61266 13.86197
## IGH@ /// IGHA1 /// IGHA2 /// LOC100126583 13.79664 13.16844 13.76880
## GSM2332101
## IGK@ /// IGKC 13.95740
## 13.86197
## IGL@ 13.76880
## IGH@ /// IGHA1 /// IGHA2 /// LOC100126583 13.73797
group <- factor(group_list,levels = c("normal","UC"))
table(group)
## group
## normal UC
## 21 87
首先对这个数据做下差异分析,也是用easyTCGA包,1行代码即可,基因芯片数据也是支持的,并且它会自动检测需不需要进行log2转换,如果是count矩阵,会自动使用DESeq2、limma、edgeR进行差异分析,如果不是,会自动进行wilcoxon和limma的差异分析:
library(easyTCGA)
diff_res <- diff_analysis(exprset = exprSet
, group = group
, is_count = F # 不是count数据
, logFC_cut = 0 # 可以直接筛选结果
, pvalue_cut = 1
)
## log2 transform not needed
## => Running limma
## => Running wilcoxon test
## => Analysis done.
# limma的结果
diff_limma <- diff_res$deg_limma
# 多个gene symbol的直接删除,方便演示
diff_limma <- diff_limma[!grepl("/",diff_limma$genesymbol),]
head(diff_limma)
## logFC AveExpr t P.Value adj.P.Val B
## SLC6A14 5.024103 9.413107 21.56440 4.104849e-41 8.514279e-37 82.58182
## LOC389023 -3.550396 5.541681 -21.01057 4.054400e-40 4.204818e-36 80.36199
## SLC23A1 -2.473180 5.649224 -17.88487 3.378001e-34 2.335550e-30 67.08748
## DUOX2 4.911030 9.916299 17.37129 3.569259e-33 1.850839e-29 64.78265
## DPP10 -1.910958 3.991413 -16.98863 2.113068e-32 7.304876e-29 63.04259
## TIMP1 2.125930 11.402645 16.88534 3.425860e-32 1.015131e-28 62.56956
## genesymbol
## SLC6A14 SLC6A14
## LOC389023 LOC389023
## SLC23A1 SLC23A1
## DUOX2 DUOX2
## DPP10 DPP10
## TIMP1 TIMP1
因为接下来会同时演示ORA和GSEA两种富集分析,所以我们把筛选后的差异基因用于ORA分析,所有的基因用于GSEA分析。
选取logFC > 1 & adj.P.Val<0.01 的基因作为差异基因进行后续的ORA分析:
deg_genes <- diff_limma[abs(diff_limma$logFC)>1 & diff_limma$adj.P.Val<0.01,]
deg_genes <- deg_genes$genesymbol
length(deg_genes)
## [1] 1192
head(deg_genes)
## [1] "SLC6A14" "LOC389023" "SLC23A1" "DUOX2" "DPP10" "TIMP1"
1192个差异基因等下用于ORA富集分析。
然后准备下GSEA需要的格式。
富集分析最好用ENTREZID进行,关于多种不同的ID,在曾老师的书中都有详细介绍,强烈推荐初学者一定要看:生信初学者基础知识资源推荐。这里的ID转换和GEO的探针注释并不是一回事,初学者要注意。
suppressMessages(library(clusterProfiler))
gene_entrezid <- bitr(geneID = diff_limma$genesymbol
, fromType = "SYMBOL" # 从symbol
, toType = "ENTREZID" # 转成ENTREZID
, OrgDb = "org.Hs.eg.db"
)
##
## 'select()' returned 1:many mapping between keys and columns
gene_entrezid <- merge(gene_entrezid,diff_limma,by.x = "SYMBOL", by.y = "genesymbol")
genelist <- gene_entrezid$logFC
names(genelist) <- gene_entrezid$ENTREZID
genelist <- sort(genelist,decreasing = T)
head(genelist)
## 4314 11254 50506 1673 1116 6279
## 5.123666 5.024103 4.911030 4.608619 4.552790 4.256463
这样GSEA需要的数据也准备好了。
富集分析
富集分析首选clusterProfiler,没有之一!简单,好用!
富集分析最好用ENTREZID进行,但其实不转换也可以进行,富集分析时会给你转换,你只要指定类型即可,这里是因为enrichGO富集分析会借助Org注释包进行,里面含有多种不同的基因ID,它可以自动帮你进行转换,如果没有使用Org注释包的富集分析函数就只能用ENTREZID。
首先进行ORA:
ora_res <- enrichGO(gene = deg_genes,
OrgDb = "org.Hs.eg.db",
keyType = "SYMBOL",#这里指定ID类型
ont = "ALL", # "BP", "MF", "CC"
pvalueCutoff = 0.05,
pAdjustMethod = "BH",
qvalueCutoff = 0.05,
minGSSize = 10,# 最少的基因数量
maxGSSize = 500, # 最大的基因数量
readable = T # 把ENTREZID转换为SYMBOL
)
class(ora_res)
## [1] "enrichResult"
## attr(,"package")
## [1] "DOSE"
这个结果是一个enrichResult对象,
下面进行GSEA富集分析:
gsea_res <- gseGO(gene = genelist,
OrgDb = "org.Hs.eg.db",
keyType = "ENTREZID",
ont = "ALL",
pvalueCutoff = 0.05,
pAdjustMethod = "BH",
minGSSize = 10,
maxGSSize = 500
)
## preparing geneSet collections...
## GSEA analysis...
## leading edge analysis...
## done...
class(gsea_res)
## [1] "gseaResult"
## attr(,"package")
## [1] "DOSE"
这个结果是gseaResult对象。
有了这两个结果,我们就可以演示simplifyEnrichment的用法了。
基本用法
我们就以GO ORA和GO GSEA的富集结果为例进行演示,其他类型数据的使用方法也是基本一样的。
simplifyEnrichment使用起来非常简单,主要就是两步:
- 第一步,计算相似性矩阵
- 第二步,根据相似性矩阵进行聚类
你需要提供一个由GO-id组成的字符创向量,然后simplifyEnrichment会计算相似性矩阵(clusterprofiler中也有一个函数可以计算相似性矩阵,不知道你还记得吗?),根据相似性矩阵,最终把GO-id聚成几个类别。
library(simplifyEnrichment)
## Loading required package: BiocGenerics
##
## Attaching package: 'BiocGenerics'
## The following objects are masked from 'package:stats':
##
## IQR, mad, sd, var, xtabs
## The following objects are masked from 'package:base':
##
## anyDuplicated, aperm, append, as.data.frame, basename, cbind,
## colnames, dirname, do.call, duplicated, eval, evalq, Filter, Find,
## get, grep, grepl, intersect, is.unsorted, lapply, Map, mapply,
## match, mget, order, paste, pmax, pmax.int, pmin, pmin.int,
## Position, rank, rbind, Reduce, rownames, sapply, setdiff, sort,
## table, tapply, union, unique, unsplit, which.max, which.min
## Loading required package: grid
## ========================================
## simplifyEnrichment version 1.8.0
## Bioconductor page: https://bioconductor.org/packages/simplifyEnrichment/
## Github page: https://github.com/jokergoo/simplifyEnrichment
## Documentation: https://jokergoo.github.io/simplifyEnrichment/
## Examples: https://simplifyenrichment.github.io/
##
## If you use it in published research, please cite:
## Gu, Z. simplifyEnrichment: an R/Bioconductor package for Clustering and
## Visualizing Functional Enrichment Results, Genomics, Proteomics &
## Bioinformatics 2022.
##
## This message can be suppressed by:
## suppressPackageStartupMessages(library(simplifyEnrichment))
## ========================================
GO ORA
我们已经有了GO的富集分析结果,直接从结果中提取GO-id即可。
不过这个富集分析的结果我总是记不住名字,所以把它打印出来:
names(ora_res@result)
## [1] "ONTOLOGY" "ID" "Description" "GeneRatio" "BgRatio"
## [6] "pvalue" "p.adjust" "qvalue" "geneID" "Count"
simplifyEnrichment计算GO的相似性矩阵需要指定ont,所以我们单独提取BP/CC/MF的结果:
# 分别提取GO id
go_id_bp <- ora_res[ora_res$ONTOLOGY == "BP", "ID"]
go_id_cc <- ora_res[ora_res$ONTOLOGY == "CC", "ID"]
go_id_mf <- ora_res[ora_res$ONTOLOGY == "MF", "ID"]
length(go_id_bp);length(go_id_cc);length(go_id_mf)
## [1] 1172
## [1] 44
## [1] 85
head(go_id_bp)
## [1] "GO:0050900" "GO:0097530" "GO:0002237" "GO:0060326" "GO:0030595"
## [6] "GO:0071621"
结果显示BP中竟然有1172个条目,而CC和MF则较少。
下面我们以BP为例进行演示:
# 计算相似性矩阵
mat <- GO_similarity(go_id_bp, ont = "BP", db="org.Hs.eg.db")
# 聚类并画图
df <- simplifyGO(mat, plot = T)
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'binary_cut'... 28 clusters, used 3.037701 secs.
## Perform keywords enrichment for 10 GO lists...
这个图也是基于complexheatmap画出来的,左边是相似性矩阵的可视化,右边的是词云图的注释。1172个条目最终被聚为10个类!
这样我们就可以轻松看出我们的基因大概有哪些功能,不必在1172条结果中迷失了。
返回的df是一个数据框,包含GO_id和cluster:
head(df)
## id cluster
## 1 GO:0050900 1
## 2 GO:0097530 1
## 3 GO:0002237 2
## 4 GO:0060326 1
## 5 GO:0030595 1
## 6 GO:0071621 1
查看每个cluster中有几个term
sort(table(df$cluster))
##
## 18 21 23 24 25 26 27 28 22 9 12 15 16 19 20 10 14 17 7 13
## 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 3 3 3 4 4 4 5 8 10 19 20
## 3 5 6 8 11 2 4 1
## 23 23 25 109 134 137 237 391
如果只是想单纯的对term进行聚类,不要画图,也可以直接使用binary_cut或者cluster_terms(),或者simplifyGO(mat, plot = F)。
# 3选1
binary_cut(mat)
cluster_terms(mat, method = "binary_cut")
simplifyGO(mat, plot = F)
本文开头也说过了,simplifyEnrichment也提供了专门的函数对接不同的数据进行简化,开头提到的几个函数都是用于计算相似形矩阵的,不过简化了你自己提取数据的过程。
比如对于我们这个ora_res,它是enrichResult对象,我们也可以直接用term_similarity_from_enrichResult()计算相似性矩阵,省去自己提取ID的过程。但是还是要注意,simplifyEnrichment计算GO的相似性矩阵需要指定ont!需要手动筛选一下。
# 还记得我们说过多次的富集结果取子集吗?
mat_bp <- ora_res %>%
filter(ONTOLOGY == "BP") %>%
term_similarity_from_enrichResult()
class(mat_bp)
## [1] "matrix" "array"
dim(mat_bp)
## [1] 1172 1172
GO GSEA
gseaResult的结果当然也是可以用的。不过GSEA分析更关心基因在哪些通路中是上调的,哪些是下调的,如果我们一股脑把所有的GO-ID进行简化,可能并不能达到我们的目的,所以我们可以根据上下调把GO-ID分开,分别进行聚类。
这里有用到了之前介绍过的富集分析结果取子集的方法,我们就以上调的为例进行演示:
# 看看一共多少条通路
dim(gsea_res)
## [1] 1568 12
# 选取上调的
gsea_up <- gsea_res %>%
filter(NES > 0)
# 看看上调的有多少
dim(gsea_up)
## [1] 1293 12
接下来就是提取id,计算相似性矩阵,聚类,画图:
ids <- gsea_res %>%
filter(ONTOLOGY == "CC", NES > 0)
ids <- ids[, "ID"]
length(ids)
## [1] 68
head(ids)
## [1] "GO:0009897" "GO:0062023" "GO:0070820" "GO:0005788" "GO:0060205"
## [6] "GO:0031983"
mat_up <- GO_similarity(ids, ont = "CC")
simplifyGO(mat_up)
## Cluster 68 terms by 'binary_cut'... 9 clusters, used 0.06264091 secs.
## Perform keywords enrichment for 9 GO lists...

这样就可以看出,在CC这个ont中,上调的通路主要分为哪几类。
不同方法的比较
该包也提供了对不同聚类方法进行比较的函数,可以通过图形方式展示比较结果。
以下代码展示了8种聚类方法进行比较的结果:
# 8种方法比较
set.seed(123)
compare_clustering_methods(mat)
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'binary_cut'... 28 clusters, used 3.058754 secs.
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'kmeans'... 16 clusters, used 9.841361 secs.
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'pam'... 95 clusters, used 8.713 mins.
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'dynamicTreeCut'... 107 clusters, used 1.75574 secs.
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'apcluster'...
## Error in cluster_terms(mat, me, verbose = verbose) :
## Error : You need to manually install package 'apcluster' from CRAN.
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'hdbscan'...
## Error in cluster_terms(mat, me, verbose = verbose) :
## Error : You need to manually install package 'dbscan' from CRAN.
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'fast_greedy'... 5 clusters, used 0.3842499 secs.
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'louvain'... 6 clusters, used 0.3793299 secs.
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'walktrap'... 7 clusters, used 2.048265 secs.
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'MCL'... 5 clusters, used 10.78715 secs.

上图可以分为3个部分,左上角是相似性矩阵热图以及8种聚类方法的热图,左下角是两两比较的一致性热图(展示不同方法间的一致性,或理解为相关性),右边的3张条形图从上到下依次展示8种方法的Different score,Number of clusters,Block mean
具体解释我们就不说了,感兴趣的可以去官网查看。
如果设置参数plot_type = "heatmap"则会画出8种方法的热图:
set.seed(123)
compare_clustering_methods(mat, plot_type = "heatmap")
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'binary_cut'... 28 clusters, used 3.138706 secs.
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'kmeans'... 16 clusters, used 10.05892 secs.
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'pam'... 95 clusters, used 8.695316 mins.
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'dynamicTreeCut'... 107 clusters, used 2.185381 secs.
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'apcluster'...
## Error in cluster_terms(mat, me, verbose = verbose) :
## Error : You need to manually install package 'apcluster' from CRAN.
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'hdbscan'...
## Error in cluster_terms(mat, me, verbose = verbose) :
## Error : You need to manually install package 'dbscan' from CRAN.
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'fast_greedy'... 5 clusters, used 0.3853619 secs.
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'louvain'... 6 clusters, used 0.3222599 secs.
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'walktrap'... 7 clusters, used 2.039792 secs.
## Cluster 1172 terms by 'MCL'... 5 clusters, used 10.39192 secs.

从结果中可以看出,有的方法聚类数太多,有的方法聚类数太少,或者不能很好的把term聚到一起。binary_cut算是比较好的。(有几个包没装,可以看到它报错了,我们就不冲新运行了,感兴趣的自己运行以下即可)
对多个GO列表进行简化
同时对多组GO-ID进行简化,比如你有8个基因集,同时对这8个基因集做了GO富集分析,得到8个结果,那你就可以同时对这8个结果进行简化。
我觉得这个功能又和clusterprofiler中的compareCluster是绝配,因为compareCluster可以同时对这8个基因集进行各种富集分析!
library(clusterProfiler)
data(gcSample)
str(gcSample)
## List of 8
## $ X1: chr [1:216] "4597" "7111" "5266" "2175" ...
## $ X2: chr [1:805] "23450" "5160" "7126" "26118" ...
## $ X3: chr [1:392] "894" "7057" "22906" "3339" ...
## $ X4: chr [1:838] "5573" "7453" "5245" "23450" ...
## $ X5: chr [1:929] "5982" "7318" "6352" "2101" ...
## $ X6: chr [1:585] "5337" "9295" "4035" "811" ...
## $ X7: chr [1:582] "2621" "2665" "5690" "3608" ...
## $ X8: chr [1:237] "2665" "4735" "1327" "3192" ...
# 进行富集分析
ck <- compareCluster(geneCluster = gcSample, fun = "enrichGO"
,ont = "BP"
,OrgDb = "org.Hs.eg.db"
)
ck
## #
## # Result of Comparing 8 gene clusters
## #
## #.. @fun enrichGO
## #.. @geneClusters List of 8
## $ X1: chr [1:216] "4597" "7111" "5266" "2175" ...
## $ X2: chr [1:805] "23450" "5160" "7126" "26118" ...
## $ X3: chr [1:392] "894" "7057" "22906" "3339" ...
## $ X4: chr [1:838] "5573" "7453" "5245" "23450" ...
## $ X5: chr [1:929] "5982" "7318" "6352" "2101" ...
## $ X6: chr [1:585] "5337" "9295" "4035" "811" ...
## $ X7: chr [1:582] "2621" "2665" "5690" "3608" ...
## $ X8: chr [1:237] "2665" "4735" "1327" "3192" ...
## #...Result 'data.frame': 1062 obs. of 10 variables:
## $ Cluster : Factor w/ 8 levels "X1","X2","X3",..: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ...
## $ ID : chr "GO:0021978" "GO:0061351" "GO:0086005" "GO:1990266" ...
## $ Description: chr "telencephalon regionalization" "neural precursor cell proliferation" "ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential" "neutrophil migration" ...
## $ GeneRatio : chr "4/199" "9/199" "5/199" "8/199" ...
## $ BgRatio : chr "13/18903" "149/18903" "36/18903" "130/18903" ...
## $ pvalue : num 7.91e-06 2.90e-05 3.56e-05 7.11e-05 7.62e-05 ...
## $ p.adjust : num 0.0214 0.0321 0.0321 0.0363 0.0363 ...
## $ qvalue : num 0.0199 0.0299 0.0299 0.0338 0.0338 ...
## $ geneID : chr "5080/9355/2016/2018" "4771/5080/9355/8326/64211/2047/2016/51176/2018" "55800/3757/3752/23630/29119" "6364/5319/2921/2529/3576/2813/6279/6374" ...
## $ Count : int 4 9 5 8 5 7 9 4 3 12 ...
## #.. number of enriched terms found for each gene cluster:
## #.. X1: 10
## #.. X2: 273
## #.. X3: 85
## #.. X4: 94
## #.. X5: 159
## #.. X6: 100
## #.. X7: 156
## #.. X8: 185
## #
## #...Citation
## T Wu, E Hu, S Xu, M Chen, P Guo, Z Dai, T Feng, L Zhou,
## W Tang, L Zhan, X Fu, S Liu, X Bo, and G Yu.
## clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data.
## The Innovation. 2021, 2(3):100141
把这个ck按照genecluster拆分为长度为8的列表,这样每个元素就是一个基因集的富集结果:
go_id_list <- ck@compareClusterResult %>%
split(., .$Cluster)
length(go_id_list)
## [1] 8
# 看看第一个元素是不是第一个genecluster的富集结果
go_id_list[[1]][,1:5]
## Cluster ID
## 1 X1 GO:0021978
## 2 X1 GO:0061351
## 3 X1 GO:0086005
## 4 X1 GO:1990266
## 5 X1 GO:0086091
## 6 X1 GO:0061337
## 7 X1 GO:0021543
## 8 X1 GO:0021871
## 9 X1 GO:0099566
## 10 X1 GO:0060326
## Description GeneRatio
## 1 telencephalon regionalization 4/199
## 2 neural precursor cell proliferation 9/199
## 3 ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential 5/199
## 4 neutrophil migration 8/199
## 5 regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction 5/199
## 6 cardiac conduction 7/199
## 7 pallium development 9/199
## 8 forebrain regionalization 4/199
## 9 regulation of postsynaptic cytosolic calcium ion concentration 3/199
## 10 cell chemotaxis 12/199
## BgRatio
## 1 13/18903
## 2 149/18903
## 3 36/18903
## 4 130/18903
## 5 42/18903
## 6 101/18903
## 7 174/18903
## 8 24/18903
## 9 10/18903
## 10 319/18903
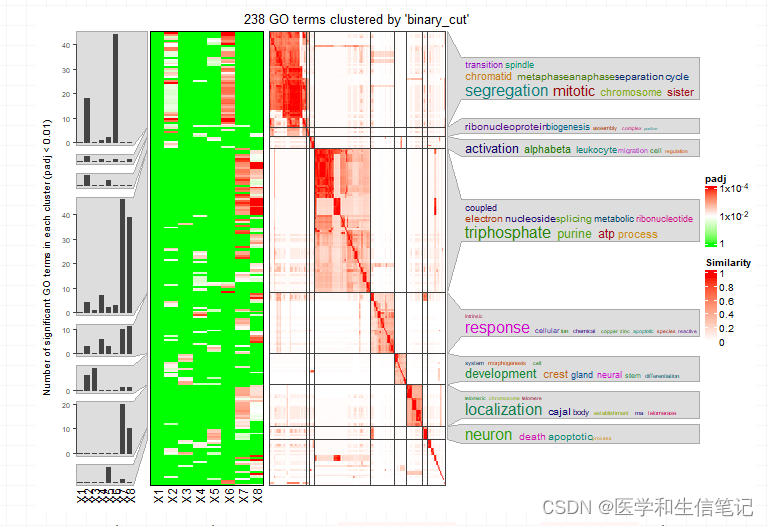
然后这个结果就可以直接提供给simplifyGOFromMultipleLists函数,同时对这8个结果进行简化:
simplifyGOFromMultipleLists(go_id_list,ont = "BP")
## Use column 'ID' as `go_id_column`.
## Use column 'p.adjust' as `padj_column`.
## Loading required namespace: gridtext
## 238/813 GO IDs left for clustering.
## Cluster 238 terms by 'binary_cut'... 22 clusters, used 0.280997 secs.
## Perform keywords enrichment for 8 GO lists...

这个图最左边是8个条形图,每个条形图的横坐标是genecluster,纵坐标是padj<0.01的条目数量;左侧热图的横坐标也是8个genecluster,纵坐标应该是每个条目,颜色表示padj;靠右的热图则是8个相似性矩阵;最右边是词云图注释。
一目了然,非常强大!今天演示的所有图都是complexheatmap画出来的,这么强大的R包,你还不学习起来吗?
- ComplexHeatmap系列1:单个热图
- ComplexHeatmap系列2:热图分割,行列名
- ComplexHeatmap系列3:注释条
- ComplexHeatmap系列4:注释条
- ComplexHeatmap系列5:多个热图拼图
- ComplexHeatmap系列6:图例
- ComplexHeatmap系列07:突变全景图
- ComplexHeatmap系列8(完结篇)
- 韦恩图进阶!complexheatmap包画upset plot
不积跬步无以至千里!

开放原子开发者工作坊旨在鼓励更多人参与开源活动,与志同道合的开发者们相互交流开发经验、分享开发心得、获取前沿技术趋势。工作坊有多种形式的开发者活动,如meetup、训练营等,主打技术交流,干货满满,真诚地邀请各位开发者共同参与!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献38条内容
已为社区贡献38条内容





所有评论(0)