加权 KNN 算法的原理与详解
加权kNN,k近邻算法的增强改进版本。近邻算法(k-Nearest Neighbors, kNN)是一种用于分类和回归的非参数方法。它的基本思想是“看邻居”,即通过查找离目标点最近的 K 个数据点,来判断目标点的类别或数值。举个例子,假设有一个训练集,其中有两类点:红色代表类别0,绿色代表类别1。现在有一个白色点,需要确定它的类别。我们选择k=3,计算白色点到所有红色点和绿色点的距离,选取距离最近
加权kNN,k近邻算法的增强改进版本。
加权KNN算法
近邻算法(k-Nearest Neighbors, kNN)是一种用于分类和回归的非参数方法。它的基本思想是“看邻居”,即通过查找离目标点最近的 K 个数据点,来判断目标点的类别或数值。
举个例子,假设有一个训练集,其中有两类点:红色代表类别0,绿色代表类别1。现在有一个白色点,需要确定它的类别。我们选择k=3,计算白色点到所有红色点和绿色点的距离,选取距离最近的3个点。如果这3个点中有2个是绿色,1个是红色,我们就认为白色点属于绿色那一类,即类别1。
但是,KNN算法性能受到超参数k值选择的影响。如果k值过小,算法对离群点会更敏感;如果k值过大,邻域内可能包含过多来自其他类别的点。此外,考虑到一个普遍的认识,即:如果靠近的数据点之间在距离上差异很大,那么其中最靠近的那一个数据点更能可靠地表明对象的类别。 针对这一些情况,加权KNN算法随之诞生。
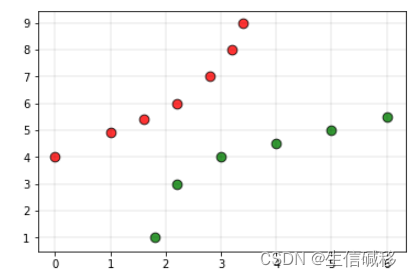
更直观的理解:
假设有以下训练集:

- 红色标签表示类别0的点,绿色标签表示类别1的点。
此时,如果我们将白色点作为查询点(需要预测类别标签的点),并且将上述数据集交给一个基于KNN的分类器,分类器会基于前面提到的最邻近原则将查询点归为类别0。但是,从图中可以明显看出,该点应该更接近类别1的点。为了克服这一缺点,我们就可以使用加权kNN。

在加权kNN中,最近的k个点根据一个称为核函数的函数赋予权重。加权kNN的直觉是,给距离较近的点更多的权重,而给距离较远的点更少的权重。任何值随距离增加而减少的函数都可以用作加权kNN分类器的核函数,其中最简单的函数是反距离函数。
反距离函数是一种常用的加权函数,用于kNN算法中,通过距离的倒数来给近邻点赋予权重。公式如下:
w i = 1 d i w_i = \frac{1}{d_i} wi=di1
其中:
- w i w_i wi是第 i i i 个近邻点的权重。
- d i d_i di 是第 i i i 个近邻点到查询点的距离。
这个函数的直观理解是:距离越近的点,权重越大;距离越远的点,权重越小。这样可以更准确地反映近邻点对查询点的影响。
Python 代码实现如下:
# Python3 program to implement the
# weighted K nearest neighbour algorithm.
import math
def weightedkNN(points,p,k=3):
'''
This function finds classification of p using
weighted k nearest neighbour algorithm. It assumes only two
two classes and returns 0 if p belongs to class 0, else
1 (belongs to class 1).
Parameters -
points : Dictionary of training points having two keys - 0 and 1
Each key have a list of training data points belong to that
p : A tuple ,test data point of form (x,y)
k : number of nearest neighbour to consider, default is 3
'''
distance=[]
for group in points:
for feature in points[group]:
#calculate the euclidean distance of p from training points
euclidean_distance = math.sqrt((feature[0]-p[0])**2 +(feature[1]-p[1])**2)
# Add a tuple of form (distance,group) in the distance list
distance.append((euclidean_distance,group))
# sort the distance list in ascending order
# and select first k distances
distance = sorted(distance)[:k]
freq1 = 0 # weighted sum of group 0
freq2 = 0 # weighted sum of group 1
for d in distance:
if d[1] == 0:
freq1 += (1 / d[0])
elif d[1] == 1:
freq2 += (1 /d[0])
return 0 if freq1>freq2 else 1
# Driver function
def main():
# Dictionary of training points having two keys - 0 and 1
# key 0 have points belong to class 0
# key 1 have points belong to class 1
points = {0:[(0, 4),(1, 4.9),(1.6, 5.4),(2.2, 6),(2.8, 7),(3.2, 8),(3.4, 9)],
1:[(1.8, 1),(2.2, 3),(3, 4),(4, 4.5),(5, 5),(6, 5.5)]}
# query point p(x,y)
p = (2, 4)
# Number of neighbours
k = 5
print("The value classified to query point is: {}".format(weightedkNN(points,p,k)))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
参考链接:
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/weighted-k-nn/

开放原子开发者工作坊旨在鼓励更多人参与开源活动,与志同道合的开发者们相互交流开发经验、分享开发心得、获取前沿技术趋势。工作坊有多种形式的开发者活动,如meetup、训练营等,主打技术交流,干货满满,真诚地邀请各位开发者共同参与!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容





所有评论(0)