移动应用开发之路 03 Android Studio 6种布局介绍、实战详解
内容主要包括布局介绍和实战两部分。布局介绍简单概括了线性布局、相对布局、帧布局、表格布局、网格布局、约束布局等6种布局的特性。实战包括实践了解布局的属性参数以及完成一个小项目。
学校开了一门移动应用开发课程,我一开始兴趣盎然,但是看到使用的环境是 Java 8 的时候心就凉了一半,在询问老师的意见之后决定使用现在比较常用的Android Studio完成学习,特此记录自学之路。
目录
1. 布局分类
安卓的布局一般分为这几类:
- 线性布局
- 相对布局
- 帧布局
- 表格布局
- 网格布局
- 约束布局
在Android Studio中,创建布局文件时可以直接选布局类型。

1.1. 线性布局(linearlayout)
一般会按照从上到下(垂直布局)或者从左到右(水平布局)的顺序把组件排列至窗口。
1.2. 相对布局(relativelayout)
设置一个参照物,其他的几个组件都是按照跟参照物的相对位置决定自己的位置。
1.3. 帧布局(framlayout)
就一层一层叠到一起,有点像PS里的图层。
1.4. 表格布局(tablelayout)
表格布局适用于那种行列比较有规律性的东西,这个类似于html中的表格布局。
1.5. 网格布局(gridlayout)
类似表格布局,但是不完全一样,更加灵活。
1.6. 约束布局(absolutelayout)
这个是特别特别常用的一种布局,可以用很少量的代码完成比较复杂的功能。
2. 添加布局
我们开发的时候一般使用xml文件设计布局,当然也可用java完成。但是java一般不常用,因为特别麻烦,我们举一个例子,现在我要做下面这个图的效果。

java代码如下,我们发现,每次都要创建一个新布局,写一大堆东西。而且界面代码何逻辑代码一般不放一起。
package com.example.myapplication;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.CollapsibleActionView;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
// Activity: 是一个类,AppCompatActivity也是算是Activity类。类似于一个可视化界面
@Override // 表示这个是重写,只要打开窗口,指定先执行它,所以有点类似于初始化代码
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 创建根布局
LinearLayout ll = new LinearLayout(this);
// 设置宽高
ll.setLayoutParams(new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT));
// 设置背景
ll.setBackgroundColor(Color.BLUE);
// 应用根部局
setContentView(ll);
}
}
我们可以这么操作:
- 创建线性布局文件

- 创建一个线性布局
2.1. 线性布局
2.1.1. 线性布局功能介绍
我们使用一个线性布局,主要是为了验证几个效果。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:padding="100dp">
<!-- match_parent是指适应父容器的大小,就是说外面那个容器多大,这个就多大-->
<!-- 相对的时wrap_content,是指适应包裹内容的大小,就是说里面的东西多大,这个就多大-->
<!-- width何height还可以固定大小,比如200dp,字体大小一般用sp,其他的可以不管-->
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:text="hello world hello world hello world hello world"
android:background="#123456"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:layout_weight="4"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:text="world hello"
android:background="#654321"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:text="world hello"
android:background="#123321"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_gravity="center"/>
<!-- 线性布局有几个需要注意的属性:-->
<!-- 1. orientation: 方向
vertical horizontal-->
<!-- 2. layout_weight: 权重-->
<!-- 3. layout_gravity: 重力-->
</LinearLayout>
设计效果如下:

2.1.2. 线性布局实战演示
因为没有导入相关图标,效果跟想象中还是有差距的,不过图片换了效果应该还是可以的。
chatting_layout.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:background="#333333"
android:paddingLeft="20dp">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="< "
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="30dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="学生管理系统"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="30dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
/>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:layout_weight="0.5"/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:background="#cccccc">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:layout_weight="0.5"/>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:layout_weight="0.5"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="2"/>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:layout_weight="0.5"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
效果如下

2.2. 相对布局
2.2.1. 相对布局特性
使用相对布局的时候注意参照物,有父容器和其他控件(id控制)等选择。
创建一个相对布局xml文件。

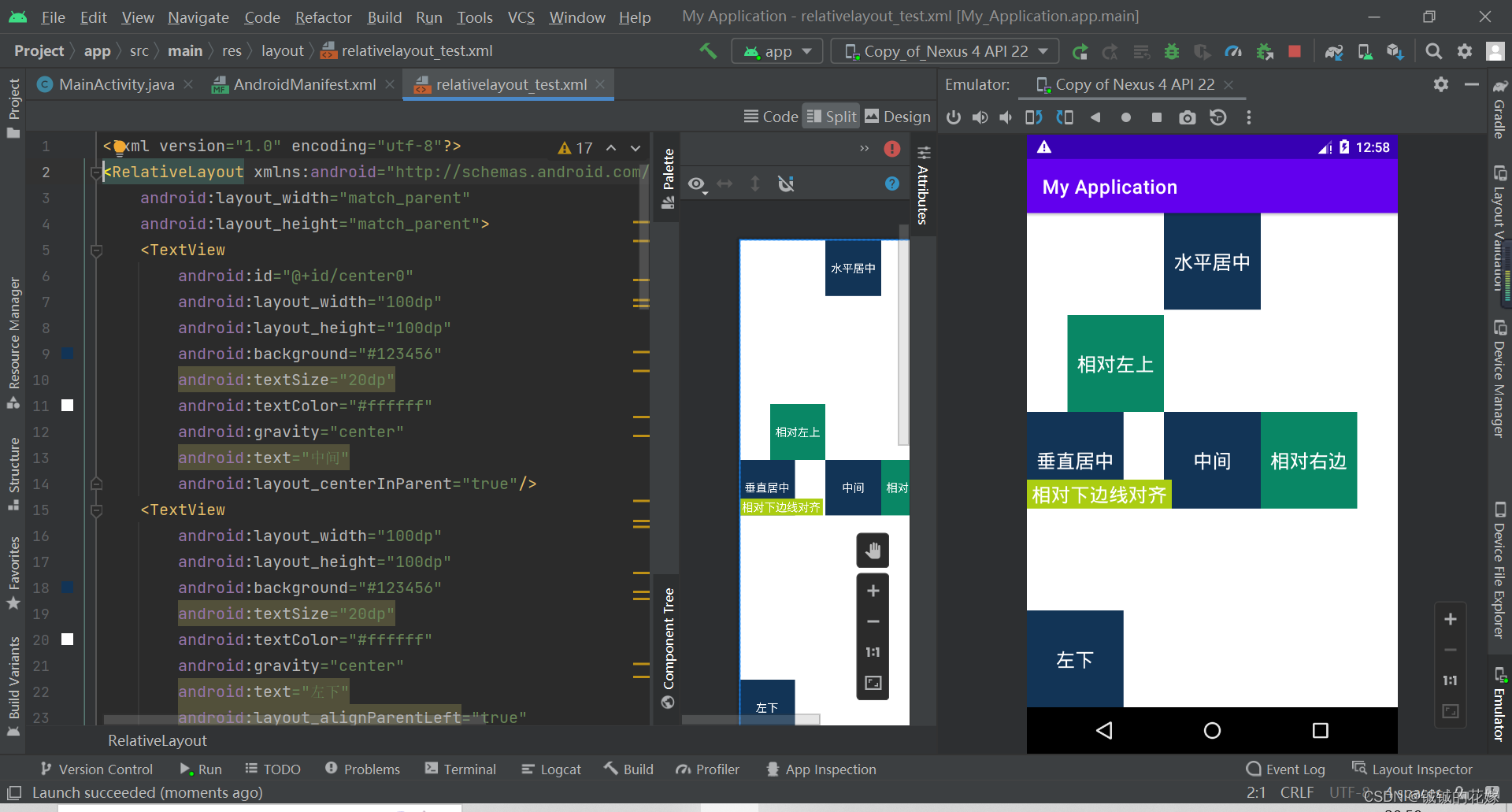
relativelayout_test.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/center0"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="#123456"
android:textSize="20dp"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="中间"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="#123456"
android:textSize="20dp"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="左下"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="#123456"
android:textSize="20dp"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="水平居中"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="#123456"
android:textSize="20dp"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="垂直居中"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="#098765"
android:textSize="20dp"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="相对右边"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/center0"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="#098765"
android:textSize="20dp"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="相对左上"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/center0"
android:layout_above="@+id/center0"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="30dp"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/center0"
android:background="#abcd12"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="相对下边线对齐"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="20dp" />
</RelativeLayout>
效果如下:


开放原子开发者工作坊旨在鼓励更多人参与开源活动,与志同道合的开发者们相互交流开发经验、分享开发心得、获取前沿技术趋势。工作坊有多种形式的开发者活动,如meetup、训练营等,主打技术交流,干货满满,真诚地邀请各位开发者共同参与!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献11条内容
已为社区贡献11条内容





所有评论(0)