x264源代码简单分析:宏块分析(Analysis)部分-帧间宏块(Inter)
本文记录x264的 x264_slice_write()函数中调用的x264_macroblock_analyse()的源代码。x264_macroblock_analyse()对应着x264中的分析模块。分析模块主要完成了下面2个方面的功能:(1)对于帧内宏块,分析帧内预测模式(2)对于帧间宏块,进行运动估计,分析帧间预测模式上一篇文章记录了帧内宏块预测模式的分析,本文继续记录帧间宏块预测模式的
=====================================================
H.264源代码分析文章列表:
【编码 - x264】
x264源代码简单分析:x264命令行工具(x264.exe)
x264源代码简单分析:x264_slice_write()
x264源代码简单分析:宏块分析(Analysis)部分-帧内宏块(Intra)
x264源代码简单分析:宏块分析(Analysis)部分-帧间宏块(Inter)
x264源代码简单分析:熵编码(Entropy Encoding)部分
【解码 - libavcodec H.264 解码器】
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:解析器(Parser)部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:解码器主干部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:熵解码(EntropyDecoding)部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:宏块解码(Decode)部分-帧内宏块(Intra)
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:宏块解码(Decode)部分-帧间宏块(Inter)
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:环路滤波(Loop Filter)部分
=====================================================
本文记录x264的 x264_slice_write()函数中调用的x264_macroblock_analyse()的源代码。x264_macroblock_analyse()对应着x264中的分析模块。分析模块主要完成了下面2个方面的功能:
(1)对于帧内宏块,分析帧内预测模式上一篇文章记录了帧内宏块预测模式的分析,本文继续记录帧间宏块预测模式的分析。
(2)对于帧间宏块,进行运动估计,分析帧间预测模式
函数调用关系图
宏块分析(Analysis)部分的源代码在整个x264中的位置如下图所示。
宏块分析(Analysis)部分的函数调用关系如下图所示。
从图中可以看出,分析模块的x264_macroblock_analyse()调用了如下函数(只列举了几个有代表性的函数):
x264_mb_analyse_init():Analysis模块初始化。
x264_mb_analyse_intra():Intra宏块帧内预测模式分析。
x264_macroblock_probe_pskip():分析是否是skip模式。
x264_mb_analyse_inter_p16x16():P16x16宏块帧间预测模式分析。
x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x8():P8x8宏块帧间预测模式分析。
x264_mb_analyse_inter_p16x8():P16x8宏块帧间预测模式分析。
x264_mb_analyse_inter_b16x16():B16x16宏块帧间预测模式分析。
x264_mb_analyse_inter_b8x8():B8x8宏块帧间预测模式分析。
x264_mb_analyse_inter_b16x8():B16x8宏块帧间预测模式分析。
上一篇文章已经分析了帧内宏块(Intra宏块)的分析函数x264_mb_analyse_intra()。本文重点分析帧间宏块(Inter宏块)的分析函数x264_mb_analyse_inter_p16x16 ()。并简单对比分析x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x8(),x264_mb_analyse_inter_p16x8()等几个针对不同尺寸帧间宏块的预测函数。
x264_slice_write()
x264_slice_write()是x264项目的核心,它完成了编码了一个Slice的工作。有关该函数的分析可以参考文章《 x264源代码简单分析:x264_slice_write()》。x264_macroblock_analyse()
x264_macroblock_analyse()用于分析宏块的预测模式。该函数的定义位于encoder\analyse.c,如下所示。/****************************************************************************
* 分析-帧内预测模式选择、帧间运动估计等
*
* 注释和处理:雷霄骅
* http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020
* leixiaohua1020@126.com
****************************************************************************/
void x264_macroblock_analyse( x264_t *h )
{
x264_mb_analysis_t analysis;
int i_cost = COST_MAX;
//通过码率控制方法,获取本宏块QP
h->mb.i_qp = x264_ratecontrol_mb_qp( h );
/* If the QP of this MB is within 1 of the previous MB, code the same QP as the previous MB,
* to lower the bit cost of the qp_delta. Don't do this if QPRD is enabled. */
if( h->param.rc.i_aq_mode && h->param.analyse.i_subpel_refine < 10 )
h->mb.i_qp = abs(h->mb.i_qp - h->mb.i_last_qp) == 1 ? h->mb.i_last_qp : h->mb.i_qp;
if( h->param.analyse.b_mb_info )
h->fdec->effective_qp[h->mb.i_mb_xy] = h->mb.i_qp; /* Store the real analysis QP. */
//初始化
x264_mb_analyse_init( h, &analysis, h->mb.i_qp );
/*--------------------------- Do the analysis ---------------------------*/
//I帧:只使用帧内预测,分别计算亮度16x16(4种)和4x4(9种)所有模式的代价值,选出代价最小的模式
//P帧:计算帧内模式和帧间模式( P Slice允许有Intra宏块和P宏块;同理B帧也支持Intra宏块)。
//对P帧的每一种分割进行帧间预测,得到最佳的运动矢量及最佳匹配块。
//帧间预测过程:选出最佳矢量——>找到最佳的整像素点——>找到最佳的二分之一像素点——>找到最佳的1/4像素点
//然后取代价最小的为最佳MV和分割方式
//最后从帧内模式和帧间模式中选择代价比较小的方式(有可能没有找到很好的匹配块,这时候就直接使用帧内预测而不是帧间预测)。
if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_I )
{
//I slice
//通过一系列帧内预测模式(16x16的4种,4x4的9种)代价的计算得出代价最小的最优模式
intra_analysis:
if( analysis.i_mbrd )
x264_mb_init_fenc_cache( h, analysis.i_mbrd >= 2 );
//帧内预测分析
//从16×16的SAD,4个8×8的SAD和,16个4×4SAD中选出最优方式
x264_mb_analyse_intra( h, &analysis, COST_MAX );
if( analysis.i_mbrd )
x264_intra_rd( h, &analysis, COST_MAX );
//分析结果都存储在analysis结构体中
//开销
i_cost = analysis.i_satd_i16x16;
h->mb.i_type = I_16x16;
//如果I4x4或者I8x8开销更小的话就拷贝
//copy if little
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_satd_i4x4, h->mb.i_type, I_4x4 );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_satd_i8x8, h->mb.i_type, I_8x8 );
//画面极其特殊的时候,才有可能用到PCM
if( analysis.i_satd_pcm < i_cost )
h->mb.i_type = I_PCM;
else if( analysis.i_mbrd >= 2 )
x264_intra_rd_refine( h, &analysis );
}
else if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_P )
{
//P slice
int b_skip = 0;
h->mc.prefetch_ref( h->mb.pic.p_fref[0][0][h->mb.i_mb_x&3], h->mb.pic.i_stride[0], 0 );
analysis.b_try_skip = 0;
if( analysis.b_force_intra )
{
if( !h->param.analyse.b_psy )
{
x264_mb_analyse_init_qp( h, &analysis, X264_MAX( h->mb.i_qp - h->mb.ip_offset, h->param.rc.i_qp_min ) );
goto intra_analysis;
}
}
else
{
/* Special fast-skip logic using information from mb_info. */
if( h->fdec->mb_info && (h->fdec->mb_info[h->mb.i_mb_xy]&X264_MBINFO_CONSTANT) )
{
if( !SLICE_MBAFF && (h->fdec->i_frame - h->fref[0][0]->i_frame) == 1 && !h->sh.b_weighted_pred &&
h->fref[0][0]->effective_qp[h->mb.i_mb_xy] <= h->mb.i_qp )
{
h->mb.i_partition = D_16x16;
/* Use the P-SKIP MV if we can... */
if( !M32(h->mb.cache.pskip_mv) )
{
b_skip = 1;
h->mb.i_type = P_SKIP;
}
/* Otherwise, just force a 16x16 block. */
else
{
h->mb.i_type = P_L0;
analysis.l0.me16x16.i_ref = 0;
M32( analysis.l0.me16x16.mv ) = 0;
}
goto skip_analysis;
}
/* Reset the information accordingly */
else if( h->param.analyse.b_mb_info_update )
h->fdec->mb_info[h->mb.i_mb_xy] &= ~X264_MBINFO_CONSTANT;
}
int skip_invalid = h->i_thread_frames > 1 && h->mb.cache.pskip_mv[1] > h->mb.mv_max_spel[1];
/* If the current macroblock is off the frame, just skip it. */
if( HAVE_INTERLACED && !MB_INTERLACED && h->mb.i_mb_y * 16 >= h->param.i_height && !skip_invalid )
b_skip = 1;
/* Fast P_SKIP detection */
else if( h->param.analyse.b_fast_pskip )
{
if( skip_invalid )
// FIXME don't need to check this if the reference frame is done
{}
else if( h->param.analyse.i_subpel_refine >= 3 )
analysis.b_try_skip = 1;
else if( h->mb.i_mb_type_left[0] == P_SKIP ||
h->mb.i_mb_type_top == P_SKIP ||
h->mb.i_mb_type_topleft == P_SKIP ||
h->mb.i_mb_type_topright == P_SKIP )
b_skip = x264_macroblock_probe_pskip( h );//检查是否是Skip类型
}
}
h->mc.prefetch_ref( h->mb.pic.p_fref[0][0][h->mb.i_mb_x&3], h->mb.pic.i_stride[0], 1 );
if( b_skip )
{
h->mb.i_type = P_SKIP;
h->mb.i_partition = D_16x16;
assert( h->mb.cache.pskip_mv[1] <= h->mb.mv_max_spel[1] || h->i_thread_frames == 1 );
skip_analysis:
/* Set up MVs for future predictors */
for( int i = 0; i < h->mb.pic.i_fref[0]; i++ )
M32( h->mb.mvr[0][i][h->mb.i_mb_xy] ) = 0;
}
else
{
const unsigned int flags = h->param.analyse.inter;
int i_type;
int i_partition;
int i_satd_inter, i_satd_intra;
x264_mb_analyse_load_costs( h, &analysis );
/*
* 16x16 帧间预测宏块分析-P
*
* +--------+--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* + + +
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+--------+
*
*/
x264_mb_analyse_inter_p16x16( h, &analysis );
if( h->mb.i_type == P_SKIP )
{
for( int i = 1; i < h->mb.pic.i_fref[0]; i++ )
M32( h->mb.mvr[0][i][h->mb.i_mb_xy] ) = 0;
return;
}
if( flags & X264_ANALYSE_PSUB16x16 )
{
if( h->param.analyse.b_mixed_references )
x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x8_mixed_ref( h, &analysis );
else{
/*
* 8x8帧间预测宏块分析-P
* +--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+
*/
x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x8( h, &analysis );
}
}
/* Select best inter mode */
i_type = P_L0;
i_partition = D_16x16;
i_cost = analysis.l0.me16x16.cost;
//如果8x8的代价值小于16x16
//则进行8x8子块分割的处理
//处理的数据源自于l0
if( ( flags & X264_ANALYSE_PSUB16x16 ) && (!analysis.b_early_terminate ||
analysis.l0.i_cost8x8 < analysis.l0.me16x16.cost) )
{
i_type = P_8x8;
i_partition = D_8x8;
i_cost = analysis.l0.i_cost8x8;
/* Do sub 8x8 */
if( flags & X264_ANALYSE_PSUB8x8 )
{
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{
//8x8块的子块的分析
/*
* 4x4
* +----+----+
* | | |
* +----+----+
* | | |
* +----+----+
*
*/
x264_mb_analyse_inter_p4x4( h, &analysis, i );
int i_thresh8x4 = analysis.l0.me4x4[i][1].cost_mv + analysis.l0.me4x4[i][2].cost_mv;
//如果4x4小于8x8
//则再分析8x4,4x8的代价
if( !analysis.b_early_terminate || analysis.l0.i_cost4x4[i] < analysis.l0.me8x8[i].cost + i_thresh8x4 )
{
int i_cost8x8 = analysis.l0.i_cost4x4[i];
h->mb.i_sub_partition[i] = D_L0_4x4;
/*
* 8x4
* +----+----+
* | |
* +----+----+
* | |
* +----+----+
*
*/
//如果8x4小于8x8
x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x4( h, &analysis, i );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost8x8, analysis.l0.i_cost8x4[i],
h->mb.i_sub_partition[i], D_L0_8x4 );
/*
* 4x8
* +----+----+
* | | |
* + + +
* | | |
* +----+----+
*
*/
//如果4x8小于8x8
x264_mb_analyse_inter_p4x8( h, &analysis, i );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost8x8, analysis.l0.i_cost4x8[i],
h->mb.i_sub_partition[i], D_L0_4x8 );
i_cost += i_cost8x8 - analysis.l0.me8x8[i].cost;
}
x264_mb_cache_mv_p8x8( h, &analysis, i );
}
analysis.l0.i_cost8x8 = i_cost;
}
}
/* Now do 16x8/8x16 */
int i_thresh16x8 = analysis.l0.me8x8[1].cost_mv + analysis.l0.me8x8[2].cost_mv;
//前提要求8x8的代价值小于16x16
if( ( flags & X264_ANALYSE_PSUB16x16 ) && (!analysis.b_early_terminate ||
analysis.l0.i_cost8x8 < analysis.l0.me16x16.cost + i_thresh16x8) )
{
int i_avg_mv_ref_cost = (analysis.l0.me8x8[2].cost_mv + analysis.l0.me8x8[2].i_ref_cost
+ analysis.l0.me8x8[3].cost_mv + analysis.l0.me8x8[3].i_ref_cost + 1) >> 1;
analysis.i_cost_est16x8[1] = analysis.i_satd8x8[0][2] + analysis.i_satd8x8[0][3] + i_avg_mv_ref_cost;
/*
* 16x8 宏块划分
*
* +--------+--------+
* | | |
* | | |
* | | |
* +--------+--------+
*
*/
x264_mb_analyse_inter_p16x8( h, &analysis, i_cost );
COPY3_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.l0.i_cost16x8, i_type, P_L0, i_partition, D_16x8 );
i_avg_mv_ref_cost = (analysis.l0.me8x8[1].cost_mv + analysis.l0.me8x8[1].i_ref_cost
+ analysis.l0.me8x8[3].cost_mv + analysis.l0.me8x8[3].i_ref_cost + 1) >> 1;
analysis.i_cost_est8x16[1] = analysis.i_satd8x8[0][1] + analysis.i_satd8x8[0][3] + i_avg_mv_ref_cost;
/*
* 8x16 宏块划分
*
* +--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+
*
*/
x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x16( h, &analysis, i_cost );
COPY3_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.l0.i_cost8x16, i_type, P_L0, i_partition, D_8x16 );
}
h->mb.i_partition = i_partition;
/* refine qpel */
//亚像素精度搜索
//FIXME mb_type costs?
if( analysis.i_mbrd || !h->mb.i_subpel_refine )
{
/* refine later */
}
else if( i_partition == D_16x16 )
{
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l0.me16x16 );
i_cost = analysis.l0.me16x16.cost;
}
else if( i_partition == D_16x8 )
{
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l0.me16x8[0] );
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l0.me16x8[1] );
i_cost = analysis.l0.me16x8[0].cost + analysis.l0.me16x8[1].cost;
}
else if( i_partition == D_8x16 )
{
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l0.me8x16[0] );
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l0.me8x16[1] );
i_cost = analysis.l0.me8x16[0].cost + analysis.l0.me8x16[1].cost;
}
else if( i_partition == D_8x8 )
{
i_cost = 0;
for( int i8x8 = 0; i8x8 < 4; i8x8++ )
{
switch( h->mb.i_sub_partition[i8x8] )
{
case D_L0_8x8:
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l0.me8x8[i8x8] );
i_cost += analysis.l0.me8x8[i8x8].cost;
break;
case D_L0_8x4:
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l0.me8x4[i8x8][0] );
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l0.me8x4[i8x8][1] );
i_cost += analysis.l0.me8x4[i8x8][0].cost +
analysis.l0.me8x4[i8x8][1].cost;
break;
case D_L0_4x8:
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l0.me4x8[i8x8][0] );
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l0.me4x8[i8x8][1] );
i_cost += analysis.l0.me4x8[i8x8][0].cost +
analysis.l0.me4x8[i8x8][1].cost;
break;
case D_L0_4x4:
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l0.me4x4[i8x8][0] );
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l0.me4x4[i8x8][1] );
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l0.me4x4[i8x8][2] );
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l0.me4x4[i8x8][3] );
i_cost += analysis.l0.me4x4[i8x8][0].cost +
analysis.l0.me4x4[i8x8][1].cost +
analysis.l0.me4x4[i8x8][2].cost +
analysis.l0.me4x4[i8x8][3].cost;
break;
default:
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_ERROR, "internal error (!8x8 && !4x4)\n" );
break;
}
}
}
if( h->mb.b_chroma_me )
{
if( CHROMA444 )
{
x264_mb_analyse_intra( h, &analysis, i_cost );
x264_mb_analyse_intra_chroma( h, &analysis );
}
else
{
x264_mb_analyse_intra_chroma( h, &analysis );
x264_mb_analyse_intra( h, &analysis, i_cost - analysis.i_satd_chroma );
}
analysis.i_satd_i16x16 += analysis.i_satd_chroma;
analysis.i_satd_i8x8 += analysis.i_satd_chroma;
analysis.i_satd_i4x4 += analysis.i_satd_chroma;
}
else
x264_mb_analyse_intra( h, &analysis, i_cost );//P Slice中也允许有Intra宏块,所以也要进行分析
i_satd_inter = i_cost;
i_satd_intra = X264_MIN3( analysis.i_satd_i16x16,
analysis.i_satd_i8x8,
analysis.i_satd_i4x4 );
if( analysis.i_mbrd )
{
x264_mb_analyse_p_rd( h, &analysis, X264_MIN(i_satd_inter, i_satd_intra) );
i_type = P_L0;
i_partition = D_16x16;
i_cost = analysis.l0.i_rd16x16;
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.l0.i_cost16x8, i_partition, D_16x8 );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.l0.i_cost8x16, i_partition, D_8x16 );
COPY3_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.l0.i_cost8x8, i_partition, D_8x8, i_type, P_8x8 );
h->mb.i_type = i_type;
h->mb.i_partition = i_partition;
if( i_cost < COST_MAX )
x264_mb_analyse_transform_rd( h, &analysis, &i_satd_inter, &i_cost );
x264_intra_rd( h, &analysis, i_satd_inter * 5/4 + 1 );
}
//获取最小的代价
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_satd_i16x16, i_type, I_16x16 );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_satd_i8x8, i_type, I_8x8 );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_satd_i4x4, i_type, I_4x4 );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_satd_pcm, i_type, I_PCM );
h->mb.i_type = i_type;
if( analysis.b_force_intra && !IS_INTRA(i_type) )
{
/* Intra masking: copy fdec to fenc and re-encode the block as intra in order to make it appear as if
* it was an inter block. */
x264_analyse_update_cache( h, &analysis );
x264_macroblock_encode( h );
for( int p = 0; p < (CHROMA444 ? 3 : 1); p++ )
h->mc.copy[PIXEL_16x16]( h->mb.pic.p_fenc[p], FENC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fdec[p], FDEC_STRIDE, 16 );
if( !CHROMA444 )
{
int height = 16 >> CHROMA_V_SHIFT;
h->mc.copy[PIXEL_8x8] ( h->mb.pic.p_fenc[1], FENC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1], FDEC_STRIDE, height );
h->mc.copy[PIXEL_8x8] ( h->mb.pic.p_fenc[2], FENC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2], FDEC_STRIDE, height );
}
x264_mb_analyse_init_qp( h, &analysis, X264_MAX( h->mb.i_qp - h->mb.ip_offset, h->param.rc.i_qp_min ) );
goto intra_analysis;
}
if( analysis.i_mbrd >= 2 && h->mb.i_type != I_PCM )
{
if( IS_INTRA( h->mb.i_type ) )
{
x264_intra_rd_refine( h, &analysis );
}
else if( i_partition == D_16x16 )
{
x264_macroblock_cache_ref( h, 0, 0, 4, 4, 0, analysis.l0.me16x16.i_ref );
analysis.l0.me16x16.cost = i_cost;
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me16x16, analysis.i_lambda2, 0, 0 );
}
else if( i_partition == D_16x8 )
{
h->mb.i_sub_partition[0] = h->mb.i_sub_partition[1] =
h->mb.i_sub_partition[2] = h->mb.i_sub_partition[3] = D_L0_8x8;
x264_macroblock_cache_ref( h, 0, 0, 4, 2, 0, analysis.l0.me16x8[0].i_ref );
x264_macroblock_cache_ref( h, 0, 2, 4, 2, 0, analysis.l0.me16x8[1].i_ref );
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me16x8[0], analysis.i_lambda2, 0, 0 );
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me16x8[1], analysis.i_lambda2, 8, 0 );
}
else if( i_partition == D_8x16 )
{
h->mb.i_sub_partition[0] = h->mb.i_sub_partition[1] =
h->mb.i_sub_partition[2] = h->mb.i_sub_partition[3] = D_L0_8x8;
x264_macroblock_cache_ref( h, 0, 0, 2, 4, 0, analysis.l0.me8x16[0].i_ref );
x264_macroblock_cache_ref( h, 2, 0, 2, 4, 0, analysis.l0.me8x16[1].i_ref );
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me8x16[0], analysis.i_lambda2, 0, 0 );
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me8x16[1], analysis.i_lambda2, 4, 0 );
}
else if( i_partition == D_8x8 )
{
x264_analyse_update_cache( h, &analysis );
for( int i8x8 = 0; i8x8 < 4; i8x8++ )
{
if( h->mb.i_sub_partition[i8x8] == D_L0_8x8 )
{
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me8x8[i8x8], analysis.i_lambda2, i8x8*4, 0 );
}
else if( h->mb.i_sub_partition[i8x8] == D_L0_8x4 )
{
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me8x4[i8x8][0], analysis.i_lambda2, i8x8*4+0, 0 );
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me8x4[i8x8][1], analysis.i_lambda2, i8x8*4+2, 0 );
}
else if( h->mb.i_sub_partition[i8x8] == D_L0_4x8 )
{
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me4x8[i8x8][0], analysis.i_lambda2, i8x8*4+0, 0 );
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me4x8[i8x8][1], analysis.i_lambda2, i8x8*4+1, 0 );
}
else if( h->mb.i_sub_partition[i8x8] == D_L0_4x4 )
{
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me4x4[i8x8][0], analysis.i_lambda2, i8x8*4+0, 0 );
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me4x4[i8x8][1], analysis.i_lambda2, i8x8*4+1, 0 );
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me4x4[i8x8][2], analysis.i_lambda2, i8x8*4+2, 0 );
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me4x4[i8x8][3], analysis.i_lambda2, i8x8*4+3, 0 );
}
}
}
}
}
}
else if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B )//B Slice的时候
{
int i_bskip_cost = COST_MAX;
int b_skip = 0;
if( analysis.i_mbrd )
x264_mb_init_fenc_cache( h, analysis.i_mbrd >= 2 );
h->mb.i_type = B_SKIP;
if( h->mb.b_direct_auto_write )
{
/* direct=auto heuristic: prefer whichever mode allows more Skip macroblocks */
for( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ )
{
int b_changed = 1;
h->sh.b_direct_spatial_mv_pred ^= 1;
analysis.b_direct_available = x264_mb_predict_mv_direct16x16( h, i && analysis.b_direct_available ? &b_changed : NULL );
if( analysis.b_direct_available )
{
if( b_changed )
{
x264_mb_mc( h );
b_skip = x264_macroblock_probe_bskip( h );
}
h->stat.frame.i_direct_score[ h->sh.b_direct_spatial_mv_pred ] += b_skip;
}
else
b_skip = 0;
}
}
else
analysis.b_direct_available = x264_mb_predict_mv_direct16x16( h, NULL );
analysis.b_try_skip = 0;
if( analysis.b_direct_available )
{
if( !h->mb.b_direct_auto_write )
x264_mb_mc( h );
/* If the current macroblock is off the frame, just skip it. */
if( HAVE_INTERLACED && !MB_INTERLACED && h->mb.i_mb_y * 16 >= h->param.i_height )
b_skip = 1;
else if( analysis.i_mbrd )
{
i_bskip_cost = ssd_mb( h );
/* 6 = minimum cavlc cost of a non-skipped MB */
b_skip = h->mb.b_skip_mc = i_bskip_cost <= ((6 * analysis.i_lambda2 + 128) >> 8);
}
else if( !h->mb.b_direct_auto_write )
{
/* Conditioning the probe on neighboring block types
* doesn't seem to help speed or quality. */
analysis.b_try_skip = x264_macroblock_probe_bskip( h );
if( h->param.analyse.i_subpel_refine < 3 )
b_skip = analysis.b_try_skip;
}
/* Set up MVs for future predictors */
if( b_skip )
{
for( int i = 0; i < h->mb.pic.i_fref[0]; i++ )
M32( h->mb.mvr[0][i][h->mb.i_mb_xy] ) = 0;
for( int i = 0; i < h->mb.pic.i_fref[1]; i++ )
M32( h->mb.mvr[1][i][h->mb.i_mb_xy] ) = 0;
}
}
if( !b_skip )
{
const unsigned int flags = h->param.analyse.inter;
int i_type;
int i_partition;
int i_satd_inter;
h->mb.b_skip_mc = 0;
h->mb.i_type = B_DIRECT;
x264_mb_analyse_load_costs( h, &analysis );
/* select best inter mode */
/* direct must be first */
if( analysis.b_direct_available )
x264_mb_analyse_inter_direct( h, &analysis );
/*
* 16x16 帧间预测宏块分析-B
*
* +--------+--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* + + +
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+--------+
*
*/
x264_mb_analyse_inter_b16x16( h, &analysis );
if( h->mb.i_type == B_SKIP )
{
for( int i = 1; i < h->mb.pic.i_fref[0]; i++ )
M32( h->mb.mvr[0][i][h->mb.i_mb_xy] ) = 0;
for( int i = 1; i < h->mb.pic.i_fref[1]; i++ )
M32( h->mb.mvr[1][i][h->mb.i_mb_xy] ) = 0;
return;
}
i_type = B_L0_L0;
i_partition = D_16x16;
i_cost = analysis.l0.me16x16.cost;
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.l1.me16x16.cost, i_type, B_L1_L1 );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_cost16x16bi, i_type, B_BI_BI );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_cost16x16direct, i_type, B_DIRECT );
if( analysis.i_mbrd && analysis.b_early_terminate && analysis.i_cost16x16direct <= i_cost * 33/32 )
{
x264_mb_analyse_b_rd( h, &analysis, i_cost );
if( i_bskip_cost < analysis.i_rd16x16direct &&
i_bskip_cost < analysis.i_rd16x16bi &&
i_bskip_cost < analysis.l0.i_rd16x16 &&
i_bskip_cost < analysis.l1.i_rd16x16 )
{
h->mb.i_type = B_SKIP;
x264_analyse_update_cache( h, &analysis );
return;
}
}
if( flags & X264_ANALYSE_BSUB16x16 )
{
/*
* 8x8 帧间预测宏块分析-B
* +--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+
*
*/
if( h->param.analyse.b_mixed_references )
x264_mb_analyse_inter_b8x8_mixed_ref( h, &analysis );
else
x264_mb_analyse_inter_b8x8( h, &analysis );
COPY3_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_cost8x8bi, i_type, B_8x8, i_partition, D_8x8 );
/* Try to estimate the cost of b16x8/b8x16 based on the satd scores of the b8x8 modes */
int i_cost_est16x8bi_total = 0, i_cost_est8x16bi_total = 0;
int i_mb_type, i_partition16x8[2], i_partition8x16[2];
for( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ )
{
int avg_l0_mv_ref_cost, avg_l1_mv_ref_cost;
int i_l0_satd, i_l1_satd, i_bi_satd, i_best_cost;
// 16x8
i_best_cost = COST_MAX;
i_l0_satd = analysis.i_satd8x8[0][i*2] + analysis.i_satd8x8[0][i*2+1];
i_l1_satd = analysis.i_satd8x8[1][i*2] + analysis.i_satd8x8[1][i*2+1];
i_bi_satd = analysis.i_satd8x8[2][i*2] + analysis.i_satd8x8[2][i*2+1];
avg_l0_mv_ref_cost = ( analysis.l0.me8x8[i*2].cost_mv + analysis.l0.me8x8[i*2].i_ref_cost
+ analysis.l0.me8x8[i*2+1].cost_mv + analysis.l0.me8x8[i*2+1].i_ref_cost + 1 ) >> 1;
avg_l1_mv_ref_cost = ( analysis.l1.me8x8[i*2].cost_mv + analysis.l1.me8x8[i*2].i_ref_cost
+ analysis.l1.me8x8[i*2+1].cost_mv + analysis.l1.me8x8[i*2+1].i_ref_cost + 1 ) >> 1;
COPY2_IF_LT( i_best_cost, i_l0_satd + avg_l0_mv_ref_cost, i_partition16x8[i], D_L0_8x8 );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_best_cost, i_l1_satd + avg_l1_mv_ref_cost, i_partition16x8[i], D_L1_8x8 );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_best_cost, i_bi_satd + avg_l0_mv_ref_cost + avg_l1_mv_ref_cost, i_partition16x8[i], D_BI_8x8 );
analysis.i_cost_est16x8[i] = i_best_cost;
// 8x16
i_best_cost = COST_MAX;
i_l0_satd = analysis.i_satd8x8[0][i] + analysis.i_satd8x8[0][i+2];
i_l1_satd = analysis.i_satd8x8[1][i] + analysis.i_satd8x8[1][i+2];
i_bi_satd = analysis.i_satd8x8[2][i] + analysis.i_satd8x8[2][i+2];
avg_l0_mv_ref_cost = ( analysis.l0.me8x8[i].cost_mv + analysis.l0.me8x8[i].i_ref_cost
+ analysis.l0.me8x8[i+2].cost_mv + analysis.l0.me8x8[i+2].i_ref_cost + 1 ) >> 1;
avg_l1_mv_ref_cost = ( analysis.l1.me8x8[i].cost_mv + analysis.l1.me8x8[i].i_ref_cost
+ analysis.l1.me8x8[i+2].cost_mv + analysis.l1.me8x8[i+2].i_ref_cost + 1 ) >> 1;
COPY2_IF_LT( i_best_cost, i_l0_satd + avg_l0_mv_ref_cost, i_partition8x16[i], D_L0_8x8 );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_best_cost, i_l1_satd + avg_l1_mv_ref_cost, i_partition8x16[i], D_L1_8x8 );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_best_cost, i_bi_satd + avg_l0_mv_ref_cost + avg_l1_mv_ref_cost, i_partition8x16[i], D_BI_8x8 );
analysis.i_cost_est8x16[i] = i_best_cost;
}
i_mb_type = B_L0_L0 + (i_partition16x8[0]>>2) * 3 + (i_partition16x8[1]>>2);
analysis.i_cost_est16x8[1] += analysis.i_lambda * i_mb_b16x8_cost_table[i_mb_type];
i_cost_est16x8bi_total = analysis.i_cost_est16x8[0] + analysis.i_cost_est16x8[1];
i_mb_type = B_L0_L0 + (i_partition8x16[0]>>2) * 3 + (i_partition8x16[1]>>2);
analysis.i_cost_est8x16[1] += analysis.i_lambda * i_mb_b16x8_cost_table[i_mb_type];
i_cost_est8x16bi_total = analysis.i_cost_est8x16[0] + analysis.i_cost_est8x16[1];
/* We can gain a little speed by checking the mode with the lowest estimated cost first */
int try_16x8_first = i_cost_est16x8bi_total < i_cost_est8x16bi_total;
if( try_16x8_first && (!analysis.b_early_terminate || i_cost_est16x8bi_total < i_cost) )
{
x264_mb_analyse_inter_b16x8( h, &analysis, i_cost );
COPY3_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_cost16x8bi, i_type, analysis.i_mb_type16x8, i_partition, D_16x8 );
}
if( !analysis.b_early_terminate || i_cost_est8x16bi_total < i_cost )
{
x264_mb_analyse_inter_b8x16( h, &analysis, i_cost );
COPY3_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_cost8x16bi, i_type, analysis.i_mb_type8x16, i_partition, D_8x16 );
}
if( !try_16x8_first && (!analysis.b_early_terminate || i_cost_est16x8bi_total < i_cost) )
{
x264_mb_analyse_inter_b16x8( h, &analysis, i_cost );
COPY3_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_cost16x8bi, i_type, analysis.i_mb_type16x8, i_partition, D_16x8 );
}
}
if( analysis.i_mbrd || !h->mb.i_subpel_refine )
{
/* refine later */
}
/* refine qpel */
else if( i_partition == D_16x16 )
{
analysis.l0.me16x16.cost -= analysis.i_lambda * i_mb_b_cost_table[B_L0_L0];
analysis.l1.me16x16.cost -= analysis.i_lambda * i_mb_b_cost_table[B_L1_L1];
if( i_type == B_L0_L0 )
{
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l0.me16x16 );
i_cost = analysis.l0.me16x16.cost
+ analysis.i_lambda * i_mb_b_cost_table[B_L0_L0];
}
else if( i_type == B_L1_L1 )
{
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l1.me16x16 );
i_cost = analysis.l1.me16x16.cost
+ analysis.i_lambda * i_mb_b_cost_table[B_L1_L1];
}
else if( i_type == B_BI_BI )
{
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l0.bi16x16 );
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l1.bi16x16 );
}
}
else if( i_partition == D_16x8 )
{
for( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ )
{
if( analysis.i_mb_partition16x8[i] != D_L1_8x8 )
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l0.me16x8[i] );
if( analysis.i_mb_partition16x8[i] != D_L0_8x8 )
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l1.me16x8[i] );
}
}
else if( i_partition == D_8x16 )
{
for( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ )
{
if( analysis.i_mb_partition8x16[i] != D_L1_8x8 )
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l0.me8x16[i] );
if( analysis.i_mb_partition8x16[i] != D_L0_8x8 )
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, &analysis.l1.me8x16[i] );
}
}
else if( i_partition == D_8x8 )
{
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{
x264_me_t *m;
int i_part_cost_old;
int i_type_cost;
int i_part_type = h->mb.i_sub_partition[i];
int b_bidir = (i_part_type == D_BI_8x8);
if( i_part_type == D_DIRECT_8x8 )
continue;
if( x264_mb_partition_listX_table[0][i_part_type] )
{
m = &analysis.l0.me8x8[i];
i_part_cost_old = m->cost;
i_type_cost = analysis.i_lambda * i_sub_mb_b_cost_table[D_L0_8x8];
m->cost -= i_type_cost;
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, m );
if( !b_bidir )
analysis.i_cost8x8bi += m->cost + i_type_cost - i_part_cost_old;
}
if( x264_mb_partition_listX_table[1][i_part_type] )
{
m = &analysis.l1.me8x8[i];
i_part_cost_old = m->cost;
i_type_cost = analysis.i_lambda * i_sub_mb_b_cost_table[D_L1_8x8];
m->cost -= i_type_cost;
x264_me_refine_qpel( h, m );
if( !b_bidir )
analysis.i_cost8x8bi += m->cost + i_type_cost - i_part_cost_old;
}
/* TODO: update mvp? */
}
}
i_satd_inter = i_cost;
if( analysis.i_mbrd )
{
x264_mb_analyse_b_rd( h, &analysis, i_satd_inter );
i_type = B_SKIP;
i_cost = i_bskip_cost;
i_partition = D_16x16;
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.l0.i_rd16x16, i_type, B_L0_L0 );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.l1.i_rd16x16, i_type, B_L1_L1 );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_rd16x16bi, i_type, B_BI_BI );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_rd16x16direct, i_type, B_DIRECT );
COPY3_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_rd16x8bi, i_type, analysis.i_mb_type16x8, i_partition, D_16x8 );
COPY3_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_rd8x16bi, i_type, analysis.i_mb_type8x16, i_partition, D_8x16 );
COPY3_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_rd8x8bi, i_type, B_8x8, i_partition, D_8x8 );
h->mb.i_type = i_type;
h->mb.i_partition = i_partition;
}
if( h->mb.b_chroma_me )
{
if( CHROMA444 )
{
x264_mb_analyse_intra( h, &analysis, i_satd_inter );
x264_mb_analyse_intra_chroma( h, &analysis );
}
else
{
x264_mb_analyse_intra_chroma( h, &analysis );
x264_mb_analyse_intra( h, &analysis, i_satd_inter - analysis.i_satd_chroma );
}
analysis.i_satd_i16x16 += analysis.i_satd_chroma;
analysis.i_satd_i8x8 += analysis.i_satd_chroma;
analysis.i_satd_i4x4 += analysis.i_satd_chroma;
}
else
x264_mb_analyse_intra( h, &analysis, i_satd_inter );
if( analysis.i_mbrd )
{
x264_mb_analyse_transform_rd( h, &analysis, &i_satd_inter, &i_cost );
x264_intra_rd( h, &analysis, i_satd_inter * 17/16 + 1 );
}
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_satd_i16x16, i_type, I_16x16 );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_satd_i8x8, i_type, I_8x8 );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_satd_i4x4, i_type, I_4x4 );
COPY2_IF_LT( i_cost, analysis.i_satd_pcm, i_type, I_PCM );
h->mb.i_type = i_type;
h->mb.i_partition = i_partition;
if( analysis.i_mbrd >= 2 && IS_INTRA( i_type ) && i_type != I_PCM )
x264_intra_rd_refine( h, &analysis );
if( h->mb.i_subpel_refine >= 5 )
x264_refine_bidir( h, &analysis );
if( analysis.i_mbrd >= 2 && i_type > B_DIRECT && i_type < B_SKIP )
{
int i_biweight;
x264_analyse_update_cache( h, &analysis );
if( i_partition == D_16x16 )
{
if( i_type == B_L0_L0 )
{
analysis.l0.me16x16.cost = i_cost;
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me16x16, analysis.i_lambda2, 0, 0 );
}
else if( i_type == B_L1_L1 )
{
analysis.l1.me16x16.cost = i_cost;
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l1.me16x16, analysis.i_lambda2, 0, 1 );
}
else if( i_type == B_BI_BI )
{
i_biweight = h->mb.bipred_weight[analysis.l0.bi16x16.i_ref][analysis.l1.bi16x16.i_ref];
x264_me_refine_bidir_rd( h, &analysis.l0.bi16x16, &analysis.l1.bi16x16, i_biweight, 0, analysis.i_lambda2 );
}
}
else if( i_partition == D_16x8 )
{
for( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ )
{
h->mb.i_sub_partition[i*2] = h->mb.i_sub_partition[i*2+1] = analysis.i_mb_partition16x8[i];
if( analysis.i_mb_partition16x8[i] == D_L0_8x8 )
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me16x8[i], analysis.i_lambda2, i*8, 0 );
else if( analysis.i_mb_partition16x8[i] == D_L1_8x8 )
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l1.me16x8[i], analysis.i_lambda2, i*8, 1 );
else if( analysis.i_mb_partition16x8[i] == D_BI_8x8 )
{
i_biweight = h->mb.bipred_weight[analysis.l0.me16x8[i].i_ref][analysis.l1.me16x8[i].i_ref];
x264_me_refine_bidir_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me16x8[i], &analysis.l1.me16x8[i], i_biweight, i*2, analysis.i_lambda2 );
}
}
}
else if( i_partition == D_8x16 )
{
for( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ )
{
h->mb.i_sub_partition[i] = h->mb.i_sub_partition[i+2] = analysis.i_mb_partition8x16[i];
if( analysis.i_mb_partition8x16[i] == D_L0_8x8 )
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me8x16[i], analysis.i_lambda2, i*4, 0 );
else if( analysis.i_mb_partition8x16[i] == D_L1_8x8 )
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l1.me8x16[i], analysis.i_lambda2, i*4, 1 );
else if( analysis.i_mb_partition8x16[i] == D_BI_8x8 )
{
i_biweight = h->mb.bipred_weight[analysis.l0.me8x16[i].i_ref][analysis.l1.me8x16[i].i_ref];
x264_me_refine_bidir_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me8x16[i], &analysis.l1.me8x16[i], i_biweight, i, analysis.i_lambda2 );
}
}
}
else if( i_partition == D_8x8 )
{
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{
if( h->mb.i_sub_partition[i] == D_L0_8x8 )
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me8x8[i], analysis.i_lambda2, i*4, 0 );
else if( h->mb.i_sub_partition[i] == D_L1_8x8 )
x264_me_refine_qpel_rd( h, &analysis.l1.me8x8[i], analysis.i_lambda2, i*4, 1 );
else if( h->mb.i_sub_partition[i] == D_BI_8x8 )
{
i_biweight = h->mb.bipred_weight[analysis.l0.me8x8[i].i_ref][analysis.l1.me8x8[i].i_ref];
x264_me_refine_bidir_rd( h, &analysis.l0.me8x8[i], &analysis.l1.me8x8[i], i_biweight, i, analysis.i_lambda2 );
}
}
}
}
}
}
x264_analyse_update_cache( h, &analysis );
/* In rare cases we can end up qpel-RDing our way back to a larger partition size
* without realizing it. Check for this and account for it if necessary. */
if( analysis.i_mbrd >= 2 )
{
/* Don't bother with bipred or 8x8-and-below, the odds are incredibly low. */
static const uint8_t check_mv_lists[X264_MBTYPE_MAX] = {[P_L0]=1, [B_L0_L0]=1, [B_L1_L1]=2};
int list = check_mv_lists[h->mb.i_type] - 1;
if( list >= 0 && h->mb.i_partition != D_16x16 &&
M32( &h->mb.cache.mv[list][x264_scan8[0]] ) == M32( &h->mb.cache.mv[list][x264_scan8[12]] ) &&
h->mb.cache.ref[list][x264_scan8[0]] == h->mb.cache.ref[list][x264_scan8[12]] )
h->mb.i_partition = D_16x16;
}
if( !analysis.i_mbrd )
x264_mb_analyse_transform( h );
if( analysis.i_mbrd == 3 && !IS_SKIP(h->mb.i_type) )
x264_mb_analyse_qp_rd( h, &analysis );
h->mb.b_trellis = h->param.analyse.i_trellis;
h->mb.b_noise_reduction = h->mb.b_noise_reduction || (!!h->param.analyse.i_noise_reduction && !IS_INTRA( h->mb.i_type ));
if( !IS_SKIP(h->mb.i_type) && h->mb.i_psy_trellis && h->param.analyse.i_trellis == 1 )
x264_psy_trellis_init( h, 0 );
if( h->mb.b_trellis == 1 || h->mb.b_noise_reduction )
h->mb.i_skip_intra = 0;
}
尽管x264_macroblock_analyse()的源代码比较长,但是它的逻辑比较简单,如下所示:
(1)如果当前是I Slice,调用x264_mb_analyse_intra()进行Intra宏块的帧内预测模式分析。
(2)如果当前是P Slice,则进行下面流程的分析:a)调用x264_macroblock_probe_pskip()分析是否为Skip宏块,如果是的话则不再进行下面分析。b)调用x264_mb_analyse_inter_p16x16()分析P16x16帧间预测的代价。c)调用x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x8()分析P8x8帧间预测的代价。d)如果P8x8代价值小于P16x16,则依次对4个8x8的子宏块分割进行判断:i.调用x264_mb_analyse_inter_p4x4()分析P4x4帧间预测的代价。ii.如果P4x4代价值小于P8x8,则调用 x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x4()和x264_mb_analyse_inter_p4x8()分析P8x4和P4x8帧间预测的代价。e)如果P8x8代价值小于P16x16,调用x264_mb_analyse_inter_p16x8()和x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x16()分析P16x8和P8x16帧间预测的代价。f)此外还要调用x264_mb_analyse_intra(),检查当前宏块作为Intra宏块编码的代价是否小于作为P宏块编码的代价(P Slice中也允许有Intra宏块)。(3)如果当前是B Slice,则进行和P Slice类似的处理。
x264_macroblock_analyse()的流程中出现了多种帧间宏块的划分方式,在这里汇总一下。《H.264标准》中规定,每个16x16的宏块可以划分为16x16,16x8,8x16,8x8四种类型。而如果宏块划分为8x8类型的时候,每个8x8宏块又可以划分为8x8,8x4,4x8,4x4四种小块。它们之间的关系下图所示。

上图中这些子宏块都包含了自己的运动矢量和参考帧序号,并且根据这两个信息获得最终的预测数据。总体说来,大的子宏块适合平坦区域,而小的子宏块适合多细节区域。例如下面这张图是一张没有进行运动补偿的残差帧的宏块分割方式图,可以看出平坦区域使用了较大的16x16分割方式,而细节区域使用了相对较小的宏块分割方式。
x264_mb_analyse_inter_p16x16()
x264_mb_analyse_inter_p16x16()用于分析P16x16宏块的帧间预测方式。该函数的定义位于encoder\analyse.c,如下所示。/*
* 16x16 帧间预测宏块分析
*
* +--------+--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* + + +
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+--------+
*
*/
static void x264_mb_analyse_inter_p16x16( x264_t *h, x264_mb_analysis_t *a )
{
//运动估计相关的信息
//后面的初始化工作主要是对该结构体赋值
x264_me_t m;
int i_mvc;
ALIGNED_4( int16_t mvc[8][2] );
int i_halfpel_thresh = INT_MAX;
int *p_halfpel_thresh = (a->b_early_terminate && h->mb.pic.i_fref[0]>1) ? &i_halfpel_thresh : NULL;
/* 16x16 Search on all ref frame */
//设定像素分块大小
m.i_pixel = PIXEL_16x16;
LOAD_FENC( &m, h->mb.pic.p_fenc, 0, 0 );
a->l0.me16x16.cost = INT_MAX;
//循环搜索所有的参考帧
//i_ref
//mb.pic.i_fref[0]存储了参考帧的个数
for( int i_ref = 0; i_ref < h->mb.pic.i_fref[0]; i_ref++ )
{
m.i_ref_cost = REF_COST( 0, i_ref );
i_halfpel_thresh -= m.i_ref_cost;
/* search with ref */
//加载半像素点的列表
//参考列表的4个分量列表,包括yN(整点像素),yH(1/2水平内插),yV(1/2垂直内插), yHV(1/2斜对角内插)
LOAD_HPELS( &m, h->mb.pic.p_fref[0][i_ref], 0, i_ref, 0, 0 );
LOAD_WPELS( &m, h->mb.pic.p_fref_w[i_ref], 0, i_ref, 0, 0 );
//获得预测的运动矢量MV(通过取中值)
x264_mb_predict_mv_16x16( h, 0, i_ref, m.mvp );
if( h->mb.ref_blind_dupe == i_ref )
{
CP32( m.mv, a->l0.mvc[0][0] );
x264_me_refine_qpel_refdupe( h, &m, p_halfpel_thresh );
}
else
{
x264_mb_predict_mv_ref16x16( h, 0, i_ref, mvc, &i_mvc );
//关键:运动估计(搜索参考帧)
x264_me_search_ref( h, &m, mvc, i_mvc, p_halfpel_thresh );
}
/* save mv for predicting neighbors */
CP32( h->mb.mvr[0][i_ref][h->mb.i_mb_xy], m.mv );
CP32( a->l0.mvc[i_ref][0], m.mv );
/* early termination
* SSD threshold would probably be better than SATD */
if( i_ref == 0
&& a->b_try_skip
&& m.cost-m.cost_mv < 300*a->i_lambda
&& abs(m.mv[0]-h->mb.cache.pskip_mv[0])
+ abs(m.mv[1]-h->mb.cache.pskip_mv[1]) <= 1
&& x264_macroblock_probe_pskip( h ) )
{
h->mb.i_type = P_SKIP;
x264_analyse_update_cache( h, a );
assert( h->mb.cache.pskip_mv[1] <= h->mb.mv_max_spel[1] || h->i_thread_frames == 1 );
return;
}
m.cost += m.i_ref_cost;
i_halfpel_thresh += m.i_ref_cost;
if( m.cost < a->l0.me16x16.cost )
h->mc.memcpy_aligned( &a->l0.me16x16, &m, sizeof(x264_me_t) );
}
x264_macroblock_cache_ref( h, 0, 0, 4, 4, 0, a->l0.me16x16.i_ref );
assert( a->l0.me16x16.mv[1] <= h->mb.mv_max_spel[1] || h->i_thread_frames == 1 );
h->mb.i_type = P_L0;
if( a->i_mbrd )
{
x264_mb_init_fenc_cache( h, a->i_mbrd >= 2 || h->param.analyse.inter & X264_ANALYSE_PSUB8x8 );
if( a->l0.me16x16.i_ref == 0 && M32( a->l0.me16x16.mv ) == M32( h->mb.cache.pskip_mv ) && !a->b_force_intra )
{
h->mb.i_partition = D_16x16;
x264_macroblock_cache_mv_ptr( h, 0, 0, 4, 4, 0, a->l0.me16x16.mv );
a->l0.i_rd16x16 = x264_rd_cost_mb( h, a->i_lambda2 );
if( !(h->mb.i_cbp_luma|h->mb.i_cbp_chroma) )
h->mb.i_type = P_SKIP;
}
}
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_mb_analyse_inter_p16x16()首先初始化了x264_me_t结构体相关的信息,然后调用x264_me_search_ref()进行运动估计,最后统计运动估计的开销。其中x264_me_search_ref()完成了运动搜索的流程,相对比较复杂,是帧间预测的重点。在看x264_me_search_ref()之前,简单记录一下运动搜索相关的知识。
运动搜索(运动估计)知识
运动搜索可以分成两种基本类型:(1)全局搜索算法。该方法是把搜索区域内所有的像素块逐个与当前宏块进行比较,查找具有最小匹配误差的一个像素块为匹配块。这一方法的好处是可以找到最佳的匹配块,坏处是速度太慢。目前全局搜索算法极少使用。在X264中包含以下几种运动搜索方法:(2)快速搜索算法。该方法按照一定的数学规则进行匹配块的搜索。这一方法的好处是速度快,坏处是可能只能得到次最佳的匹配块。
(1)菱形搜索算法(DIA)论文《X264的运动估计算法研究》中曾经评测了几种运动搜索算法的性能。文中采用了“Foreman”(运动剧烈)、“Carphone”(中等运动)、“Claire”(运动较小)几个视频作为实验素材,搜索范围为设置为16,实验的结果如下表所示。
以搜索起点为中心,采用下图所示的小菱形模板(模板半径为1)搜索。计算各点的匹配误差,得到MBD(最小误差)点。如果MBD点在模板中心,则搜索结束,此时的MBD 点就是最优匹配点,对应的像素块就是最佳匹配块;如果MBD点不在模板中心位置,则以现在MBD点为中心点,继续进行小菱形搜索,直至MBD点落在中心点为止。
4x4的像素块采用菱形搜索算法搜索的示意图如下所示。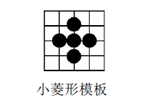
(2)六边形搜索算法(HEX)
该方法采用1个大模板(六边形模板)和2个小模板(小菱形模板和小正方形模板)。具体的搜索步骤如下:
步骤1:以搜索起点为中心,采用图中左边的六边形模板进行搜索。计算区域中心及周围6个点处的匹配误差并比较,如最小MBD 点位于模板中心点,则转至步骤2;否则以上一次的MBD 点作为中心点,以六边形模板为模板进行反复搜索。
步骤2:以上一次的MBD 点为中心点,采用小菱形模板搜索,计算各点的匹配误差,找到MBD 点。然后以MBD点为中心点,采用小正方形模板搜索,得到的MBD点就是最优匹配点。
4x4的像素块采用六边形搜索算法搜索的示意图如下所示。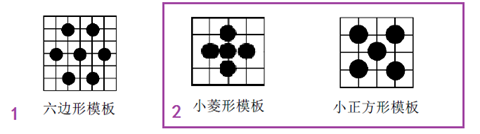
(3)非对称十字型多层次六边形格点搜索算法(UMH)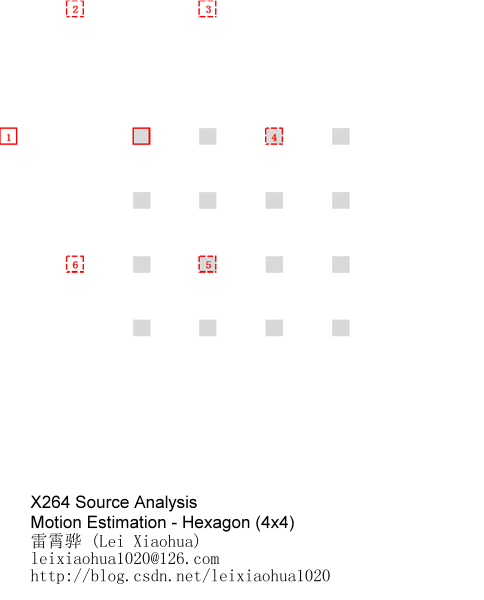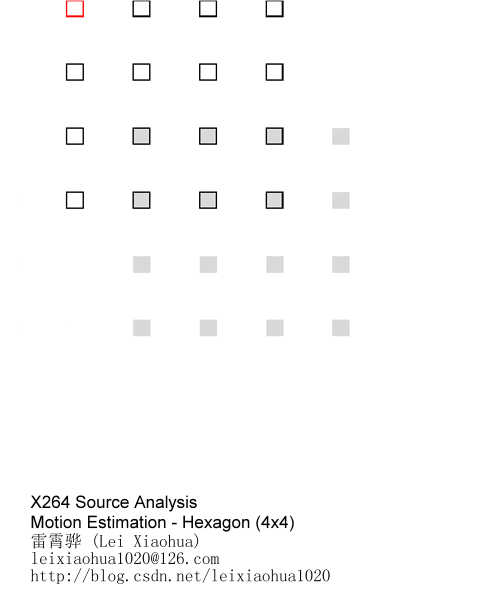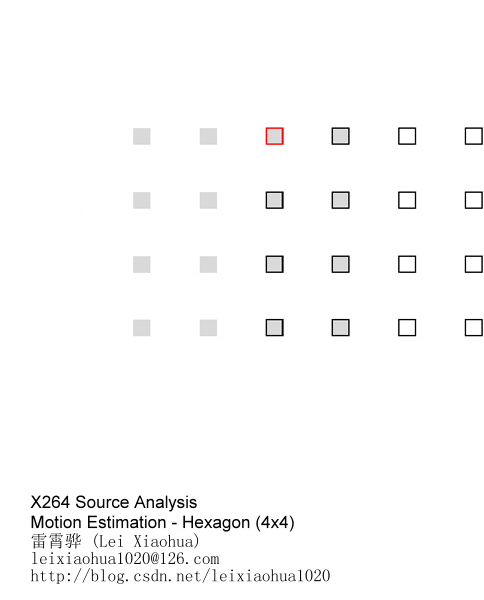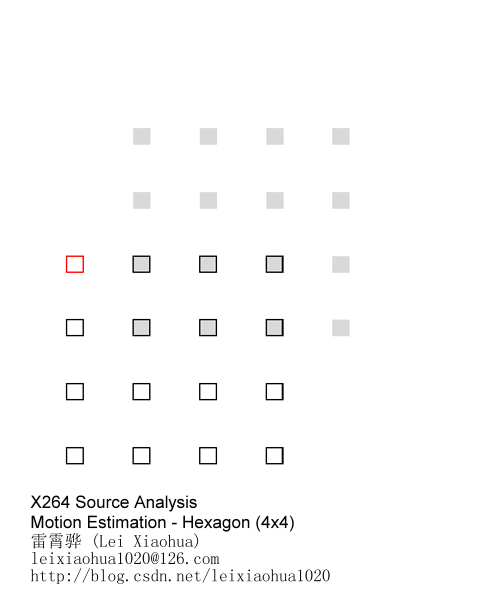
该方法用到了下图所示的多个搜索模板,相对比较复杂,目前还没有仔细研究。记录一下步骤:
步骤0:进行一次小菱形搜索,根据匹配误差值和两个门限值(对于一种尺寸的宏块来说是固定大小的threshold1和threshold2)之间的关系作相应的处理,可能用到中菱形模板或者正八边形模板,也有可能直接跳到步骤1。
步骤1:使用非对称十字模板搜索。“非对称”的原因是一般水平方向运动要比垂直方向运动剧烈,所以将水平方向搜索范围定为W,垂直方向搜索范围定为W/2。
步骤2:使用5x5逐步搜索模板搜索。
步骤3:使用大六边形模板搜索。
步骤4:使用六边形搜索算法找到最优匹配点。
(4)连续消除法(ESA、TESA)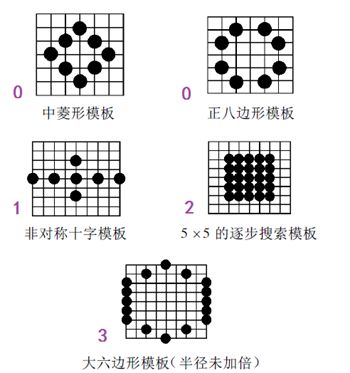
该方法是一种全搜索算法,它对搜索区域内的点进行光栅式搜索,逐一计算并比较。

x264_me_search_ref()
x264_me_search_ref()完成了运动搜索的工作。该函数的定义位于encoder\me.c,如下所示。#define BITS_MVD( mx, my )\
(p_cost_mvx[(mx)<<2] + p_cost_mvy[(my)<<2])
#define COST_MV( mx, my )\
do\
{\
int cost = h->pixf.fpelcmp[i_pixel]( p_fenc, FENC_STRIDE,\
&p_fref_w[(my)*stride+(mx)], stride )\
+ BITS_MVD(mx,my);\
COPY3_IF_LT( bcost, cost, bmx, mx, bmy, my );\
} while(0)
#define COST_MV_HPEL( mx, my, cost )\
do\
{\
intptr_t stride2 = 16;\
pixel *src = h->mc.get_ref( pix, &stride2, m->p_fref, stride, mx, my, bw, bh, &m->weight[0] );\
cost = h->pixf.fpelcmp[i_pixel]( p_fenc, FENC_STRIDE, src, stride2 )\
+ p_cost_mvx[ mx ] + p_cost_mvy[ my ];\
} while(0)
#define COST_MV_X3_DIR( m0x, m0y, m1x, m1y, m2x, m2y, costs )\
{\
pixel *pix_base = p_fref_w + bmx + bmy*stride;\
h->pixf.fpelcmp_x3[i_pixel]( p_fenc,\
pix_base + (m0x) + (m0y)*stride,\
pix_base + (m1x) + (m1y)*stride,\
pix_base + (m2x) + (m2y)*stride,\
stride, costs );\
(costs)[0] += BITS_MVD( bmx+(m0x), bmy+(m0y) );\
(costs)[1] += BITS_MVD( bmx+(m1x), bmy+(m1y) );\
(costs)[2] += BITS_MVD( bmx+(m2x), bmy+(m2y) );\
}
#define COST_MV_X4_DIR( m0x, m0y, m1x, m1y, m2x, m2y, m3x, m3y, costs )\
{\
pixel *pix_base = p_fref_w + bmx + bmy*stride;\
h->pixf.fpelcmp_x4[i_pixel]( p_fenc,\
pix_base + (m0x) + (m0y)*stride,\
pix_base + (m1x) + (m1y)*stride,\
pix_base + (m2x) + (m2y)*stride,\
pix_base + (m3x) + (m3y)*stride,\
stride, costs );\
(costs)[0] += BITS_MVD( bmx+(m0x), bmy+(m0y) );\
(costs)[1] += BITS_MVD( bmx+(m1x), bmy+(m1y) );\
(costs)[2] += BITS_MVD( bmx+(m2x), bmy+(m2y) );\
(costs)[3] += BITS_MVD( bmx+(m3x), bmy+(m3y) );\
}
#define COST_MV_X4( m0x, m0y, m1x, m1y, m2x, m2y, m3x, m3y )\
{\
pixel *pix_base = p_fref_w + omx + omy*stride;\
h->pixf.fpelcmp_x4[i_pixel]( p_fenc,\
pix_base + (m0x) + (m0y)*stride,\
pix_base + (m1x) + (m1y)*stride,\
pix_base + (m2x) + (m2y)*stride,\
pix_base + (m3x) + (m3y)*stride,\
stride, costs );\
costs[0] += BITS_MVD( omx+(m0x), omy+(m0y) );\
costs[1] += BITS_MVD( omx+(m1x), omy+(m1y) );\
costs[2] += BITS_MVD( omx+(m2x), omy+(m2y) );\
costs[3] += BITS_MVD( omx+(m3x), omy+(m3y) );\
COPY3_IF_LT( bcost, costs[0], bmx, omx+(m0x), bmy, omy+(m0y) );\
COPY3_IF_LT( bcost, costs[1], bmx, omx+(m1x), bmy, omy+(m1y) );\
COPY3_IF_LT( bcost, costs[2], bmx, omx+(m2x), bmy, omy+(m2y) );\
COPY3_IF_LT( bcost, costs[3], bmx, omx+(m3x), bmy, omy+(m3y) );\
}
#define COST_MV_X3_ABS( m0x, m0y, m1x, m1y, m2x, m2y )\
{\
h->pixf.fpelcmp_x3[i_pixel]( p_fenc,\
p_fref_w + (m0x) + (m0y)*stride,\
p_fref_w + (m1x) + (m1y)*stride,\
p_fref_w + (m2x) + (m2y)*stride,\
stride, costs );\
costs[0] += p_cost_mvx[(m0x)<<2]; /* no cost_mvy */\
costs[1] += p_cost_mvx[(m1x)<<2];\
costs[2] += p_cost_mvx[(m2x)<<2];\
COPY3_IF_LT( bcost, costs[0], bmx, m0x, bmy, m0y );\
COPY3_IF_LT( bcost, costs[1], bmx, m1x, bmy, m1y );\
COPY3_IF_LT( bcost, costs[2], bmx, m2x, bmy, m2y );\
}
/* 1 */
/* 101 */
/* 1 */
#define DIA1_ITER( mx, my )\
{\
omx = mx; omy = my;\
COST_MV_X4( 0,-1, 0,1, -1,0, 1,0 );\
}
#define CROSS( start, x_max, y_max )\
{\
int i = start;\
if( (x_max) <= X264_MIN(mv_x_max-omx, omx-mv_x_min) )\
for( ; i < (x_max)-2; i+=4 )\
COST_MV_X4( i,0, -i,0, i+2,0, -i-2,0 );\
for( ; i < (x_max); i+=2 )\
{\
if( omx+i <= mv_x_max )\
COST_MV( omx+i, omy );\
if( omx-i >= mv_x_min )\
COST_MV( omx-i, omy );\
}\
i = start;\
if( (y_max) <= X264_MIN(mv_y_max-omy, omy-mv_y_min) )\
for( ; i < (y_max)-2; i+=4 )\
COST_MV_X4( 0,i, 0,-i, 0,i+2, 0,-i-2 );\
for( ; i < (y_max); i+=2 )\
{\
if( omy+i <= mv_y_max )\
COST_MV( omx, omy+i );\
if( omy-i >= mv_y_min )\
COST_MV( omx, omy-i );\
}\
}
#define FPEL(mv) (((mv)+2)>>2) /* Convert subpel MV to fullpel with rounding... */
#define SPEL(mv) ((mv)<<2) /* ... and the reverse. */
#define SPELx2(mv) (SPEL(mv)&0xFFFCFFFC) /* for two packed MVs */
//关键:运动估计(搜索参考帧)
void x264_me_search_ref( x264_t *h, x264_me_t *m, int16_t (*mvc)[2], int i_mvc, int *p_halfpel_thresh )
{
const int bw = x264_pixel_size[m->i_pixel].w;
const int bh = x264_pixel_size[m->i_pixel].h;
const int i_pixel = m->i_pixel;
const int stride = m->i_stride[0];
int i_me_range = h->param.analyse.i_me_range;
int bmx, bmy, bcost = COST_MAX;
int bpred_cost = COST_MAX;
int omx, omy, pmx, pmy;
pixel *p_fenc = m->p_fenc[0];
pixel *p_fref_w = m->p_fref_w;
ALIGNED_ARRAY_N( pixel, pix,[16*16] );
ALIGNED_ARRAY_8( int16_t, mvc_temp,[16],[2] );
ALIGNED_ARRAY_16( int, costs,[16] );
int mv_x_min = h->mb.mv_limit_fpel[0][0];
int mv_y_min = h->mb.mv_limit_fpel[0][1];
int mv_x_max = h->mb.mv_limit_fpel[1][0];
int mv_y_max = h->mb.mv_limit_fpel[1][1];
/* Special version of pack to allow shortcuts in CHECK_MVRANGE */
#define pack16to32_mask2(mx,my) ((mx<<16)|(my&0x7FFF))
uint32_t mv_min = pack16to32_mask2( -mv_x_min, -mv_y_min );
uint32_t mv_max = pack16to32_mask2( mv_x_max, mv_y_max )|0x8000;
uint32_t pmv, bpred_mv = 0;
#define CHECK_MVRANGE(mx,my) (!(((pack16to32_mask2(mx,my) + mv_min) | (mv_max - pack16to32_mask2(mx,my))) & 0x80004000))
const uint16_t *p_cost_mvx = m->p_cost_mv - m->mvp[0];
const uint16_t *p_cost_mvy = m->p_cost_mv - m->mvp[1];
/* Try extra predictors if provided. If subme >= 3, check subpel predictors,
* otherwise round them to fullpel. */
if( h->mb.i_subpel_refine >= 3 )//如果精度为1/4
{
/* Calculate and check the MVP first */
int bpred_mx = x264_clip3( m->mvp[0], SPEL(mv_x_min), SPEL(mv_x_max) );
int bpred_my = x264_clip3( m->mvp[1], SPEL(mv_y_min), SPEL(mv_y_max) );
pmv = pack16to32_mask( bpred_mx, bpred_my );
pmx = FPEL( bpred_mx );
pmy = FPEL( bpred_my );
COST_MV_HPEL( bpred_mx, bpred_my, bpred_cost );
int pmv_cost = bpred_cost;
if( i_mvc > 0 )
{
/* Clip MV candidates and eliminate those equal to zero and pmv. */
int valid_mvcs = x264_predictor_clip( mvc_temp+2, mvc, i_mvc, h->mb.mv_limit_fpel, pmv );
if( valid_mvcs > 0 )
{
int i = 1, cost;
/* We stuff pmv here to branchlessly pick between pmv and the various
* MV candidates. [0] gets skipped in order to maintain alignment for
* x264_predictor_clip. */
M32( mvc_temp[1] ) = pmv;
bpred_cost <<= 4;
do
{
int mx = mvc_temp[i+1][0];
int my = mvc_temp[i+1][1];
COST_MV_HPEL( mx, my, cost );
COPY1_IF_LT( bpred_cost, (cost << 4) + i );
} while( ++i <= valid_mvcs );
bpred_mx = mvc_temp[(bpred_cost&15)+1][0];
bpred_my = mvc_temp[(bpred_cost&15)+1][1];
bpred_cost >>= 4;
}
}
/* Round the best predictor back to fullpel and get the cost, since this is where
* we'll be starting the fullpel motion search. */
//FPEL()宏定义如下
//#define FPEL(mv) (((mv)+2)>>2)
//即把以1/4像素为基本单位的运动矢量转换为以整像素为基本单位(加2是为了四舍五入)
bmx = FPEL( bpred_mx );
bmy = FPEL( bpred_my );
bpred_mv = pack16to32_mask(bpred_mx, bpred_my);
if( bpred_mv&0x00030003 ) /* Only test if the tested predictor is actually subpel... */
COST_MV( bmx, bmy );
else /* Otherwise just copy the cost (we already know it) */
bcost = bpred_cost;
/* Test the zero vector if it hasn't been tested yet. */
if( pmv )
{
if( bmx|bmy ) COST_MV( 0, 0 );
}
/* If a subpel mv candidate was better than the zero vector, the previous
* fullpel check won't have gotten it even if the pmv was zero. So handle
* that possibility here. */
else
{
COPY3_IF_LT( bcost, pmv_cost, bmx, 0, bmy, 0 );
}
}
else
{
/* Calculate and check the fullpel MVP first */
//像素点的坐标(bmx,bmy)
//FPEL()从四分之一像素MV转换为整像素MV
bmx = pmx = x264_clip3( FPEL(m->mvp[0]), mv_x_min, mv_x_max );
bmy = pmy = x264_clip3( FPEL(m->mvp[1]), mv_y_min, mv_y_max );
pmv = pack16to32_mask( bmx, bmy );
/* Because we are rounding the predicted motion vector to fullpel, there will be
* an extra MV cost in 15 out of 16 cases. However, when the predicted MV is
* chosen as the best predictor, it is often the case that the subpel search will
* result in a vector at or next to the predicted motion vector. Therefore, we omit
* the cost of the MV from the rounded MVP to avoid unfairly biasing against use of
* the predicted motion vector.
*
* Disclaimer: this is a post-hoc rationalization for why this hack works. */
bcost = h->pixf.fpelcmp[i_pixel]( p_fenc, FENC_STRIDE, &p_fref_w[bmy*stride+bmx], stride );
if( i_mvc > 0 )
{
/* Like in subme>=3, except we also round the candidates to fullpel. */
int valid_mvcs = x264_predictor_roundclip( mvc_temp+2, mvc, i_mvc, h->mb.mv_limit_fpel, pmv );
if( valid_mvcs > 0 )
{
int i = 1, cost;
M32( mvc_temp[1] ) = pmv;
bcost <<= 4;
do
{
int mx = mvc_temp[i+1][0];
int my = mvc_temp[i+1][1];
cost = h->pixf.fpelcmp[i_pixel]( p_fenc, FENC_STRIDE, &p_fref_w[my*stride+mx], stride ) + BITS_MVD( mx, my );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (cost << 4) + i );
} while( ++i <= valid_mvcs );
bmx = mvc_temp[(bcost&15)+1][0];
bmy = mvc_temp[(bcost&15)+1][1];
bcost >>= 4;
}
}
/* Same as above, except the condition is simpler. */
if( pmv )
COST_MV( 0, 0 );
}
//不同的运动估计算法作不同的处理
switch( h->mb.i_me_method )
{
//钻石(Diamond)搜索
//注意这里是“小钻石”,实际上还有“大钻石”
/*
* x
* x x x
* x
*/
case X264_ME_DIA:
{
/* diamond search, radius 1 */
bcost <<= 4;
//i每次循环减1,
//运动搜索的半径
int i = i_me_range;
//循环
do
{
//COST_MV_X4_DIR()计算4个点的MV开销
//在这里以bmx,bmy为基点在周围进行其四点的cost计算
//周围4个点为(0,-1),(0,1),(-1,0),(1,0)
//每个点的结果存储于costs[]数组
//
//在这里像素比较函数可能是SAD或者SATD,参考mbcmp_init()函数
//
//COST_MV_X4_DIR( 0,-1, 0,1, -1,0, 1,0, costs )宏展开后代码如下所示
/*
* {
pixel *pix_base = p_fref_w + bmx + bmy*stride;
//调用像素比较函数
h->pixf.fpelcmp_x4[i_pixel]( p_fenc,
pix_base + (0) + (-1)*stride, //上
pix_base + (0) + (1)*stride, //下
pix_base + (-1) + (0)*stride, //左
pix_base + (1) + (0)*stride, //右
stride, costs );
//得到4个点的开销,存储到costs[]数组
(costs)[0] += (p_cost_mvx[(bmx+(0))<<2] + p_cost_mvy[(bmy+(-1))<<2]);
(costs)[1] += (p_cost_mvx[(bmx+(0))<<2] + p_cost_mvy[(bmy+(1))<<2]);
(costs)[2] += (p_cost_mvx[(bmx+(-1))<<2] + p_cost_mvy[(bmy+(0))<<2]);
(costs)[3] += (p_cost_mvx[(bmx+(1))<<2] + p_cost_mvy[(bmy+(0))<<2]);
}
*/
/*
* 顺序
* 1
* 3 x 4
* 2
*/
COST_MV_X4_DIR( 0,-1, 0,1, -1,0, 1,0, costs );
//如果小的话,就拷贝至bcost
//COPY1_IF_LT()宏定义如下
//#define COPY1_IF_LT(x,y)\
//if((y)<(x))\
// (x)=(y);
//
//这里左移了4位,加上1个数,可以理解为用于记录哪一个点开销小
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[0]<<4)+1 ); // 1二进制为0001,单看1-2位,“ 1”,对应“上”像素
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[1]<<4)+3 ); // 3二进制为0011,单看1-2位,“-1”,对应“下”像素
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[2]<<4)+4 ); // 4二进制为0100,单看3-4位,“ 1”,对应“左”像素
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[3]<<4)+12 );//12二进制为1100,单看3-4位,“-1”,对应“右”像素
if( !(bcost&15) )//后4位进行检测,如果后4位是0,就是证明所进行比较的4点开销比原点要大,所以不需要继续搜索了
break; //提前结束
//注意右移的时候是区分符号位的
//改变bmx,bmy的值-决定了x和y是加1还是减1
bmx -= (bcost<<28)>>30;//注意不等同于除以4。左移28位后,只剩最后4位。右移30位,只剩3-4位
bmy -= (bcost<<30)>>30;//思路同上,只剩1-2位
bcost &= ~15;
//检查运动搜索范围:mv_min和mv_max
//以及i
} while( --i && CHECK_MVRANGE(bmx, bmy) ); //检查是否越界
//这里右移了4位(之前左移4位)
bcost >>= 4;
break;
}
//六边形(Hexagon)搜索
/*
* x x
*
* x x x
*
* x x
*/
case X264_ME_HEX:
{
me_hex2:
/* hexagon search, radius 2 */
#if 0
for( int i = 0; i < i_me_range/2; i++ )
{
omx = bmx; omy = bmy;
COST_MV( omx-2, omy );
COST_MV( omx-1, omy+2 );
COST_MV( omx+1, omy+2 );
COST_MV( omx+2, omy );
COST_MV( omx+1, omy-2 );
COST_MV( omx-1, omy-2 );
if( bmx == omx && bmy == omy )
break;
if( !CHECK_MVRANGE(bmx, bmy) )
break;
}
#else
/* equivalent to the above, but eliminates duplicate candidates */
/* hexagon */
//一共计算呈六边形分布的6个点
//COST_MV_X3_DIR()计算3个点的MV开销
//3个点为(-2,0),(-1,2),(1,2)
//开销存入costs[]
COST_MV_X3_DIR( -2,0, -1, 2, 1, 2, costs );
//再计算3个点为(2,0),(1,-2),(-1,-2)
COST_MV_X3_DIR( 2,0, 1,-2, -1,-2, costs+4 ); /* +4 for 16-byte alignment */
/*
* 顺序
* 2 3
*
* 1 x 4
*
* 6 5
*/
//这里左移了3位,加上1个数,可以理解为用于记录哪一个点开销小
bcost <<= 3;
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[0]<<3)+2 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[1]<<3)+3 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[2]<<3)+4 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[4]<<3)+5 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[5]<<3)+6 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[6]<<3)+7 );
if( bcost&7 ) //后3位进行检测,如果后3位是0,就是证明所进行比较的6点开销比原点要大,就跳过这一步
{
//int8_t hex2[8][2] = {{-1,-2}, {-2,0}, {-1,2}, {1,2}, {2,0}, {1,-2}, {-1,-2}, {-2,0}};
int dir = (bcost&7)-2;
bmx += hex2[dir+1][0];
bmy += hex2[dir+1][1];
/* half hexagon, not overlapping the previous iteration */
for( int i = (i_me_range>>1) - 1; i > 0 && CHECK_MVRANGE(bmx, bmy); i-- )
{
COST_MV_X3_DIR( hex2[dir+0][0], hex2[dir+0][1],
hex2[dir+1][0], hex2[dir+1][1],
hex2[dir+2][0], hex2[dir+2][1],
costs );
bcost &= ~7;
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[0]<<3)+1 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[1]<<3)+2 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[2]<<3)+3 );
if( !(bcost&7) )
break;
dir += (bcost&7)-2;
dir = mod6m1[dir+1];
bmx += hex2[dir+1][0];
bmy += hex2[dir+1][1];
}
}
bcost >>= 3;
#endif
/* square refine */
//正方形细化
//六边形搜索之后,再进行正方形细化
bcost <<= 4;
/*
* 分两步,标号如下所示:
* 2 1 2
* 1 x 1
* 2 1 2
*/
COST_MV_X4_DIR( 0,-1, 0,1, -1,0, 1,0, costs );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[0]<<4)+1 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[1]<<4)+2 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[2]<<4)+3 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[3]<<4)+4 );
COST_MV_X4_DIR( -1,-1, -1,1, 1,-1, 1,1, costs );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[0]<<4)+5 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[1]<<4)+6 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[2]<<4)+7 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[3]<<4)+8 );
bmx += square1[bcost&15][0];
bmy += square1[bcost&15][1];
bcost >>= 4;
break;
}
//非对称十字多六边形网格(Uneven Multi-Hex)搜索
case X264_ME_UMH:
{
/*
* 主要包含3个步骤
* 第1步:进行混合搜索,包括如下:
* A,非对称十字搜索。
* B,5×5 全搜索。
* C,扩展的多层次六边形(六角形)格点搜索。
* 第2步:以当前最优点为中心,用六边形(六角形)进行搜索,直至最优点在六边型的中点为止。
* 第3步:以当前最优点为中心,用小菱形进行搜索,直至最优点在小菱形的中点为止。
*/
/* Uneven-cross Multi-Hexagon-grid Search
* as in JM, except with different early termination */
static const uint8_t x264_pixel_size_shift[7] = { 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4 };
int ucost1, ucost2;
int cross_start = 1;
/* refine predictors */
ucost1 = bcost;
DIA1_ITER( pmx, pmy );
if( pmx | pmy )
DIA1_ITER( 0, 0 );
if( i_pixel == PIXEL_4x4 )
goto me_hex2;
ucost2 = bcost;
if( (bmx | bmy) && ((bmx-pmx) | (bmy-pmy)) )
DIA1_ITER( bmx, bmy );
if( bcost == ucost2 )
cross_start = 3;
omx = bmx; omy = bmy;
/* early termination */
#define SAD_THRESH(v) ( bcost < ( v >> x264_pixel_size_shift[i_pixel] ) )
if( bcost == ucost2 && SAD_THRESH(2000) )
{
COST_MV_X4( 0,-2, -1,-1, 1,-1, -2,0 );
COST_MV_X4( 2, 0, -1, 1, 1, 1, 0,2 );
if( bcost == ucost1 && SAD_THRESH(500) )
break;
if( bcost == ucost2 )
{
int range = (i_me_range>>1) | 1;
CROSS( 3, range, range );
COST_MV_X4( -1,-2, 1,-2, -2,-1, 2,-1 );
COST_MV_X4( -2, 1, 2, 1, -1, 2, 1, 2 );
if( bcost == ucost2 )
break;
cross_start = range + 2;
}
}
/* adaptive search range */
if( i_mvc )
{
/* range multipliers based on casual inspection of some statistics of
* average distance between current predictor and final mv found by ESA.
* these have not been tuned much by actual encoding. */
static const uint8_t range_mul[4][4] =
{
{ 3, 3, 4, 4 },
{ 3, 4, 4, 4 },
{ 4, 4, 4, 5 },
{ 4, 4, 5, 6 },
};
int mvd;
int sad_ctx, mvd_ctx;
int denom = 1;
if( i_mvc == 1 )
{
if( i_pixel == PIXEL_16x16 )
/* mvc is probably the same as mvp, so the difference isn't meaningful.
* but prediction usually isn't too bad, so just use medium range */
mvd = 25;
else
mvd = abs( m->mvp[0] - mvc[0][0] )
+ abs( m->mvp[1] - mvc[0][1] );
}
else
{
/* calculate the degree of agreement between predictors. */
/* in 16x16, mvc includes all the neighbors used to make mvp,
* so don't count mvp separately. */
denom = i_mvc - 1;
mvd = 0;
if( i_pixel != PIXEL_16x16 )
{
mvd = abs( m->mvp[0] - mvc[0][0] )
+ abs( m->mvp[1] - mvc[0][1] );
denom++;
}
mvd += x264_predictor_difference( mvc, i_mvc );
}
sad_ctx = SAD_THRESH(1000) ? 0
: SAD_THRESH(2000) ? 1
: SAD_THRESH(4000) ? 2 : 3;
mvd_ctx = mvd < 10*denom ? 0
: mvd < 20*denom ? 1
: mvd < 40*denom ? 2 : 3;
i_me_range = i_me_range * range_mul[mvd_ctx][sad_ctx] >> 2;
}
/* FIXME if the above DIA2/OCT2/CROSS found a new mv, it has not updated omx/omy.
* we are still centered on the same place as the DIA2. is this desirable? */
CROSS( cross_start, i_me_range, i_me_range>>1 );
COST_MV_X4( -2,-2, -2,2, 2,-2, 2,2 );
/* hexagon grid */
omx = bmx; omy = bmy;
const uint16_t *p_cost_omvx = p_cost_mvx + omx*4;
const uint16_t *p_cost_omvy = p_cost_mvy + omy*4;
int i = 1;
do
{
static const int8_t hex4[16][2] = {
{ 0,-4}, { 0, 4}, {-2,-3}, { 2,-3},
{-4,-2}, { 4,-2}, {-4,-1}, { 4,-1},
{-4, 0}, { 4, 0}, {-4, 1}, { 4, 1},
{-4, 2}, { 4, 2}, {-2, 3}, { 2, 3},
};
if( 4*i > X264_MIN4( mv_x_max-omx, omx-mv_x_min,
mv_y_max-omy, omy-mv_y_min ) )
{
for( int j = 0; j < 16; j++ )
{
int mx = omx + hex4[j][0]*i;
int my = omy + hex4[j][1]*i;
if( CHECK_MVRANGE(mx, my) )
COST_MV( mx, my );
}
}
else
{
int dir = 0;
pixel *pix_base = p_fref_w + omx + (omy-4*i)*stride;
int dy = i*stride;
#define SADS(k,x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3)\
h->pixf.fpelcmp_x4[i_pixel]( p_fenc,\
pix_base x0*i+(y0-2*k+4)*dy,\
pix_base x1*i+(y1-2*k+4)*dy,\
pix_base x2*i+(y2-2*k+4)*dy,\
pix_base x3*i+(y3-2*k+4)*dy,\
stride, costs+4*k );\
pix_base += 2*dy;
#define ADD_MVCOST(k,x,y) costs[k] += p_cost_omvx[x*4*i] + p_cost_omvy[y*4*i]
#define MIN_MV(k,x,y) COPY2_IF_LT( bcost, costs[k], dir, x*16+(y&15) )
SADS( 0, +0,-4, +0,+4, -2,-3, +2,-3 );
SADS( 1, -4,-2, +4,-2, -4,-1, +4,-1 );
SADS( 2, -4,+0, +4,+0, -4,+1, +4,+1 );
SADS( 3, -4,+2, +4,+2, -2,+3, +2,+3 );
ADD_MVCOST( 0, 0,-4 );
ADD_MVCOST( 1, 0, 4 );
ADD_MVCOST( 2,-2,-3 );
ADD_MVCOST( 3, 2,-3 );
ADD_MVCOST( 4,-4,-2 );
ADD_MVCOST( 5, 4,-2 );
ADD_MVCOST( 6,-4,-1 );
ADD_MVCOST( 7, 4,-1 );
ADD_MVCOST( 8,-4, 0 );
ADD_MVCOST( 9, 4, 0 );
ADD_MVCOST( 10,-4, 1 );
ADD_MVCOST( 11, 4, 1 );
ADD_MVCOST( 12,-4, 2 );
ADD_MVCOST( 13, 4, 2 );
ADD_MVCOST( 14,-2, 3 );
ADD_MVCOST( 15, 2, 3 );
MIN_MV( 0, 0,-4 );
MIN_MV( 1, 0, 4 );
MIN_MV( 2,-2,-3 );
MIN_MV( 3, 2,-3 );
MIN_MV( 4,-4,-2 );
MIN_MV( 5, 4,-2 );
MIN_MV( 6,-4,-1 );
MIN_MV( 7, 4,-1 );
MIN_MV( 8,-4, 0 );
MIN_MV( 9, 4, 0 );
MIN_MV( 10,-4, 1 );
MIN_MV( 11, 4, 1 );
MIN_MV( 12,-4, 2 );
MIN_MV( 13, 4, 2 );
MIN_MV( 14,-2, 3 );
MIN_MV( 15, 2, 3 );
#undef SADS
#undef ADD_MVCOST
#undef MIN_MV
if(dir)
{
bmx = omx + i*(dir>>4);
bmy = omy + i*((dir<<28)>>28);
}
}
} while( ++i <= i_me_range>>2 );
if( bmy <= mv_y_max && bmy >= mv_y_min && bmx <= mv_x_max && bmx >= mv_x_min )
goto me_hex2;
break;
}
//穷尽搜索法(Exhaustive),x264已经取消了这种古老的全搜索法,而是采用下面改进的搜索法
case X264_ME_ESA:
//hadamard全搜索法(Transformed Exhaustive),这个算法和ESA相比主要是在搜索范围上的变化
case X264_ME_TESA:
{
//范围:最小值和最大值
const int min_x = X264_MAX( bmx - i_me_range, mv_x_min );
const int min_y = X264_MAX( bmy - i_me_range, mv_y_min );
const int max_x = X264_MIN( bmx + i_me_range, mv_x_max );
const int max_y = X264_MIN( bmy + i_me_range, mv_y_max );
/* SEA is fastest in multiples of 4 */
const int width = (max_x - min_x + 3) & ~3;
#if 0
/* plain old exhaustive search */
for( int my = min_y; my <= max_y; my++ )
for( int mx = min_x; mx < min_x + width; mx++ )
COST_MV( mx, my );
#else
/* successive elimination by comparing DC before a full SAD,
* because sum(abs(diff)) >= abs(diff(sum)). */
uint16_t *sums_base = m->integral;
ALIGNED_16( static pixel zero[8*FENC_STRIDE] ) = {0};
ALIGNED_ARRAY_16( int, enc_dc,[4] );
int sad_size = i_pixel <= PIXEL_8x8 ? PIXEL_8x8 : PIXEL_4x4;
int delta = x264_pixel_size[sad_size].w;
int16_t *xs = h->scratch_buffer;
int xn;
uint16_t *cost_fpel_mvx = h->cost_mv_fpel[h->mb.i_qp][-m->mvp[0]&3] + (-m->mvp[0]>>2);
h->pixf.sad_x4[sad_size]( zero, p_fenc, p_fenc+delta,
p_fenc+delta*FENC_STRIDE, p_fenc+delta+delta*FENC_STRIDE,
FENC_STRIDE, enc_dc );
if( delta == 4 )
sums_base += stride * (h->fenc->i_lines[0] + PADV*2);
if( i_pixel == PIXEL_16x16 || i_pixel == PIXEL_8x16 || i_pixel == PIXEL_4x8 )
delta *= stride;
if( i_pixel == PIXEL_8x16 || i_pixel == PIXEL_4x8 )
enc_dc[1] = enc_dc[2];
if( h->mb.i_me_method == X264_ME_TESA )
{
// ADS threshold, then SAD threshold, then keep the best few SADs, then SATD
mvsad_t *mvsads = (mvsad_t *)(xs + ((width+31)&~31) + 4);
int nmvsad = 0, limit;
int sad_thresh = i_me_range <= 16 ? 10 : i_me_range <= 24 ? 11 : 12;
int bsad = h->pixf.sad[i_pixel]( p_fenc, FENC_STRIDE, p_fref_w+bmy*stride+bmx, stride )
+ BITS_MVD( bmx, bmy );
for( int my = min_y; my <= max_y; my++ )
{
int i;
int ycost = p_cost_mvy[my<<2];
if( bsad <= ycost )
continue;
bsad -= ycost;
xn = h->pixf.ads[i_pixel]( enc_dc, sums_base + min_x + my * stride, delta,
cost_fpel_mvx+min_x, xs, width, bsad * 17 >> 4 );
for( i = 0; i < xn-2; i += 3 )
{
pixel *ref = p_fref_w+min_x+my*stride;
ALIGNED_ARRAY_16( int, sads,[4] ); /* padded to [4] for asm */
h->pixf.sad_x3[i_pixel]( p_fenc, ref+xs[i], ref+xs[i+1], ref+xs[i+2], stride, sads );
for( int j = 0; j < 3; j++ )
{
int sad = sads[j] + cost_fpel_mvx[xs[i+j]];
if( sad < bsad*sad_thresh>>3 )
{
COPY1_IF_LT( bsad, sad );
mvsads[nmvsad].sad = sad + ycost;
mvsads[nmvsad].mv[0] = min_x+xs[i+j];
mvsads[nmvsad].mv[1] = my;
nmvsad++;
}
}
}
for( ; i < xn; i++ )
{
int mx = min_x+xs[i];
int sad = h->pixf.sad[i_pixel]( p_fenc, FENC_STRIDE, p_fref_w+mx+my*stride, stride )
+ cost_fpel_mvx[xs[i]];
if( sad < bsad*sad_thresh>>3 )
{
COPY1_IF_LT( bsad, sad );
mvsads[nmvsad].sad = sad + ycost;
mvsads[nmvsad].mv[0] = mx;
mvsads[nmvsad].mv[1] = my;
nmvsad++;
}
}
bsad += ycost;
}
limit = i_me_range >> 1;
sad_thresh = bsad*sad_thresh>>3;
while( nmvsad > limit*2 && sad_thresh > bsad )
{
int i;
// halve the range if the domain is too large... eh, close enough
sad_thresh = (sad_thresh + bsad) >> 1;
for( i = 0; i < nmvsad && mvsads[i].sad <= sad_thresh; i++ );
for( int j = i; j < nmvsad; j++ )
{
uint32_t sad;
if( WORD_SIZE == 8 && sizeof(mvsad_t) == 8 )
{
uint64_t mvsad = M64( &mvsads[i] ) = M64( &mvsads[j] );
#if WORDS_BIGENDIAN
mvsad >>= 32;
#endif
sad = mvsad;
}
else
{
sad = mvsads[j].sad;
CP32( mvsads[i].mv, mvsads[j].mv );
mvsads[i].sad = sad;
}
i += (sad - (sad_thresh+1)) >> 31;
}
nmvsad = i;
}
while( nmvsad > limit )
{
int bi = 0;
for( int i = 1; i < nmvsad; i++ )
if( mvsads[i].sad > mvsads[bi].sad )
bi = i;
nmvsad--;
if( sizeof( mvsad_t ) == sizeof( uint64_t ) )
CP64( &mvsads[bi], &mvsads[nmvsad] );
else
mvsads[bi] = mvsads[nmvsad];
}
for( int i = 0; i < nmvsad; i++ )
COST_MV( mvsads[i].mv[0], mvsads[i].mv[1] );
}
else
{
// just ADS and SAD
for( int my = min_y; my <= max_y; my++ )
{
int i;
int ycost = p_cost_mvy[my<<2];
if( bcost <= ycost )
continue;
bcost -= ycost;
xn = h->pixf.ads[i_pixel]( enc_dc, sums_base + min_x + my * stride, delta,
cost_fpel_mvx+min_x, xs, width, bcost );
for( i = 0; i < xn-2; i += 3 )
COST_MV_X3_ABS( min_x+xs[i],my, min_x+xs[i+1],my, min_x+xs[i+2],my );
bcost += ycost;
for( ; i < xn; i++ )
COST_MV( min_x+xs[i], my );
}
}
#endif
}
break;
}
//
//后面的代码与子像素精度的运动搜索有关
//
/* -> qpel mv */
uint32_t bmv = pack16to32_mask(bmx,bmy);
//用于获得子像素精度的运动矢量的值
uint32_t bmv_spel = SPELx2(bmv);
if( h->mb.i_subpel_refine < 3 )
{
m->cost_mv = p_cost_mvx[bmx<<2] + p_cost_mvy[bmy<<2];
m->cost = bcost;
/* compute the real cost */
if( bmv == pmv ) m->cost += m->cost_mv;
M32( m->mv ) = bmv_spel;
}
else
{
M32(m->mv) = bpred_cost < bcost ? bpred_mv : bmv_spel;
m->cost = X264_MIN( bpred_cost, bcost );
}
/* subpel refine */
//子像素精度(1/2,1/4)搜索
if( h->mb.i_subpel_refine >= 2 )
{
int hpel = subpel_iterations[h->mb.i_subpel_refine][2];
int qpel = subpel_iterations[h->mb.i_subpel_refine][3];
refine_subpel( h, m, hpel, qpel, p_halfpel_thresh, 0 );
}
}
#undef COST_MV
从源代码可以看出,x264_me_search_ref()的整像素搜索是在一个很长的switch()语句里面完成的,该switch()语句根据配置的的参数进行相应的运动搜索,如下所示。
switch( h->mb.i_me_method )
{
case X264_ME_DIA:
{
//...
break;
}
case X264_ME_HEX:
{
//...
break;
}
case X264_ME_UMH:
{
//...
break;
}
case X264_ME_ESA:
case X264_ME_TESA:
{
//...
break;
}
}在具体的搜索算法中,包含了一些宏例如“COST_MV_X4_DIR()”,“COST_MV_X3_DIR()”用于完成像素比较。上述宏可以一次性完成多个位置的像素块的比较,其中“X3”代表可以1次完成3个位置的像素块的比较;而“X4” 代表可以1次完成4个位置的像素块的比较。在钻石模板搜索的过程中调用1次COST_MV_X4_DIR()完成了比较,而在六边形搜索的过程中调用2次COST_MV_X3_DIR()完成了比较。
在进行完整像素搜索之后,x264_me_search_ref()会继续调用refine_subpel()完成亚像素精度(半像素,1/4像素)的搜索。再看源代码之前,简单记录一下有关亚像素的知识。
亚像素插值知识
基本知识
简单记录一下亚像素插值的知识。《H.264标准》中规定,运动估计为1/4像素精度。因此在H.264编码和解码的过程中,需要将画面中的像素进行插值——简单地说就是把原先的1个像素点拓展成4x4一共16个点。下图显示了H.264编码和解码过程中像素插值情况。可以看出原先的G点的右下方通过插值的方式产生了a、b、c、d等一共16个点。

(1)半像素内插。这一步通过6抽头滤波器获得5个半像素点。图中半像素内插点为b、m、h、s、j五个点。半像素内插方法是对整像素点进行6 抽头滤波得出,滤波器的权重为(1/32, -5/32, 5/8, 5/8, -5/32, 1/32)。例如b的计算公式为:
(2)线性内插。这一步通过简单的线性内插获得剩余的1/4像素点。
b=round( (E - 5F + 20G + 20H - 5I + J ) / 32)
剩下几个半像素点的计算关系如下:m:由B、D、H、N、S、U计算
h:由A、C、G、M、R、T计算
s:由K、L、M、N、P、Q计算
j:由cc、dd、h、m、ee、ff计算。需要注意j点的运算量比较大,因为cc、dd、ee、ff都需要通过半像素内插方法进行计算。
在获得半像素点之后,就可以通过简单的线性内插获得1/4像素内插点了。1/4像素内插的方式如下图所示。例如图中a点的计算公式如下:
A=round( (G+b)/2 )
在这里有一点需要注意:位于4个角的e、g、p、r四个点并不是通过j点计算计算的,而是通过b、h、s、m四个半像素点计算的。
X264中亚像素的计算方法
X264中,半像素数据是在滤波(Filter)部分的x264_fdec_filter_row()中提前计算出来的,而1/4像素数据则是临时通过半像素数据线性内插得到的。X264中半像素数据
X264中半像素数据在滤波(Filter)部分的x264_fdec_filter_row()中提前计算出来。经过计算之后,半像素点数据存储于x264_frame_t的filter[3][4]中。其中水平半像素点H存储于filter[][1],垂直半像素点V存储于filter[][2],对角线半像素点C存储于filter[][3],而原本整像素点存储于filter[][0]。下图显示了一个4x4图像块经过半像素内插处理后,得到的半像素与整像素点之间的位置关系。

X264中1/4像素数据
X264中1/4像素数据是临时通过半像素点(包括整像素点)线性内插得到的。下图显示了一个4x4图像块进行1/4像素内插的过程。上面一张图中水平半像素点(存储于filter[][1])和垂直半像素点(存储于filter[][2])线性内插后得到了绿色的1/4像素内插点X。下面一张图中整像素点(存储于filter[][0])和垂直半像素点(存储于filter[][2])线性内插后得到了绿色的1/4像素内插点X。

refine_subpel()
refine_subpel()用于进行亚像素的运动搜索。该函数的定义位于encoder\me.c,如下所示。//子像素精度(1/2,1/4)搜索
//hpel_iters 半像素搜索次数 ,qpel_iters 1/4像素搜索次数
static void refine_subpel( x264_t *h, x264_me_t *m, int hpel_iters, int qpel_iters, int *p_halfpel_thresh, int b_refine_qpel )
{
const int bw = x264_pixel_size[m->i_pixel].w;
const int bh = x264_pixel_size[m->i_pixel].h;
const uint16_t *p_cost_mvx = m->p_cost_mv - m->mvp[0];
const uint16_t *p_cost_mvy = m->p_cost_mv - m->mvp[1];
const int i_pixel = m->i_pixel;
const int b_chroma_me = h->mb.b_chroma_me && (i_pixel <= PIXEL_8x8 || CHROMA444);
int chromapix = h->luma2chroma_pixel[i_pixel];
int chroma_v_shift = CHROMA_V_SHIFT;
int mvy_offset = chroma_v_shift & MB_INTERLACED & m->i_ref ? (h->mb.i_mb_y & 1)*4 - 2 : 0;
ALIGNED_ARRAY_N( pixel, pix,[64*18] ); // really 17x17x2, but round up for alignment
ALIGNED_ARRAY_16( int, costs,[4] );
//做完整像素运动搜索之后预测的运动矢量
int bmx = m->mv[0];
int bmy = m->mv[1];
int bcost = m->cost;
int odir = -1, bdir;
/* halfpel diamond search */
//子像素搜索使用钻石法
if( hpel_iters )
{
/* try the subpel component of the predicted mv */
if( h->mb.i_subpel_refine < 3 )
{
int mx = x264_clip3( m->mvp[0], h->mb.mv_min_spel[0]+2, h->mb.mv_max_spel[0]-2 );
int my = x264_clip3( m->mvp[1], h->mb.mv_min_spel[1]+2, h->mb.mv_max_spel[1]-2 );
if( (mx-bmx)|(my-bmy) )
COST_MV_SAD( mx, my );
}
bcost <<= 6;
/*
* 半像素的diamond搜索
* 数字为src{n}中的n
*
* X
*
* 0
*
* X 2 X 3 X
*
* 1
*
* X
*/
for( int i = hpel_iters; i > 0; i-- )
{
int omx = bmx, omy = bmy;
intptr_t stride = 64; // candidates are either all hpel or all qpel, so one stride is enough
pixel *src0, *src1, *src2, *src3;
//得到 omx,omy周围的半像素4个点的地址
//omx和omy以1/4像素为基本单位,+2或者-2取的就是半像素点
src0 = h->mc.get_ref( pix, &stride, m->p_fref, m->i_stride[0], omx, omy-2, bw, bh+1, &m->weight[0] );
src2 = h->mc.get_ref( pix+32, &stride, m->p_fref, m->i_stride[0], omx-2, omy, bw+4, bh, &m->weight[0] );
//src0下面的点
src1 = src0 + stride;//src0为中心点的上方点,src1为中心点的下方点
//src2右边的点
src3 = src2 + 1;//src2为中心点的左侧点,src3为中心点的右侧点
//计算cost
//同时计算4个点,结果存入cost[]
h->pixf.fpelcmp_x4[i_pixel]( m->p_fenc[0], src0, src1, src2, src3, stride, costs );
costs[0] += p_cost_mvx[omx ] + p_cost_mvy[omy-2];
costs[1] += p_cost_mvx[omx ] + p_cost_mvy[omy+2];
costs[2] += p_cost_mvx[omx-2] + p_cost_mvy[omy ];
costs[3] += p_cost_mvx[omx+2] + p_cost_mvy[omy ];
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[0]<<6)+2 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[1]<<6)+6 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[2]<<6)+16 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[3]<<6)+48 );
if( !(bcost&63) )
break;
bmx -= (bcost<<26)>>29;
bmy -= (bcost<<29)>>29;
bcost &= ~63;
}
bcost >>= 6;
}
if( !b_refine_qpel && (h->pixf.mbcmp_unaligned[0] != h->pixf.fpelcmp[0] || b_chroma_me) )
{
bcost = COST_MAX;
COST_MV_SATD( bmx, bmy, -1 );
}
/* early termination when examining multiple reference frames */
if( p_halfpel_thresh )
{
if( (bcost*7)>>3 > *p_halfpel_thresh )
{
m->cost = bcost;
m->mv[0] = bmx;
m->mv[1] = bmy;
// don't need cost_mv
return;
}
else if( bcost < *p_halfpel_thresh )
*p_halfpel_thresh = bcost;
}
/* quarterpel diamond search */
/*
* 1/4像素的搜索
*
* X
*
* 0
* q
* X q 2 q X 3 X
* q
* 1
*
* X
*/
if( h->mb.i_subpel_refine != 1 )
{
bdir = -1;
for( int i = qpel_iters; i > 0; i-- )
{
//判断边界
if( bmy <= h->mb.mv_min_spel[1] || bmy >= h->mb.mv_max_spel[1] || bmx <= h->mb.mv_min_spel[0] || bmx >= h->mb.mv_max_spel[0] )
break;
odir = bdir;
int omx = bmx, omy = bmy;
//依然是Diamond搜索
COST_MV_SATD( omx, omy - 1, 0 );
COST_MV_SATD( omx, omy + 1, 1 );
COST_MV_SATD( omx - 1, omy, 2 );
COST_MV_SATD( omx + 1, omy, 3 );
if( (bmx == omx) & (bmy == omy) )
break;
}
}
/* Special simplified case for subme=1 */
//subme=1的特殊算法?据说效果不好
else if( bmy > h->mb.mv_min_spel[1] && bmy < h->mb.mv_max_spel[1] && bmx > h->mb.mv_min_spel[0] && bmx < h->mb.mv_max_spel[0] )
{
int omx = bmx, omy = bmy;
/* We have to use mc_luma because all strides must be the same to use fpelcmp_x4 */
h->mc.mc_luma( pix , 64, m->p_fref, m->i_stride[0], omx, omy-1, bw, bh, &m->weight[0] );
h->mc.mc_luma( pix+16, 64, m->p_fref, m->i_stride[0], omx, omy+1, bw, bh, &m->weight[0] );
h->mc.mc_luma( pix+32, 64, m->p_fref, m->i_stride[0], omx-1, omy, bw, bh, &m->weight[0] );
h->mc.mc_luma( pix+48, 64, m->p_fref, m->i_stride[0], omx+1, omy, bw, bh, &m->weight[0] );
h->pixf.fpelcmp_x4[i_pixel]( m->p_fenc[0], pix, pix+16, pix+32, pix+48, 64, costs );
costs[0] += p_cost_mvx[omx ] + p_cost_mvy[omy-1];
costs[1] += p_cost_mvx[omx ] + p_cost_mvy[omy+1];
costs[2] += p_cost_mvx[omx-1] + p_cost_mvy[omy ];
costs[3] += p_cost_mvx[omx+1] + p_cost_mvy[omy ];
bcost <<= 4;
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[0]<<4)+1 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[1]<<4)+3 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[2]<<4)+4 );
COPY1_IF_LT( bcost, (costs[3]<<4)+12 );
bmx -= (bcost<<28)>>30;
bmy -= (bcost<<30)>>30;
bcost >>= 4;
}
m->cost = bcost;
m->mv[0] = bmx;
m->mv[1] = bmy;
m->cost_mv = p_cost_mvx[bmx] + p_cost_mvy[bmy];
}
从源代码可以看出,refine_subpel()首先使用小钻石模板(Diamond)查找当前整像素匹配块周围的4个半像素点的匹配块。获取半像素点数据的时候使用了x264_mc_functions_t中的get_ref()函数(后文进行分析)。获取到的src0、src1、src2、src3分别对应当前整像素点上、下、左、右的半像素点。
在查找到半像素点的最小误差点之后,refine_subpel()继续使用小钻石模板查找当前半像素点周围的4个1/4像素点的匹配块。获取1/4像素点数据的时候同样使用了x264_mc_functions_t中的get_ref()函数。
下图显示了一个4x4图像块的运动搜索过程。图中灰色点为整像素点,黄色点为半像素点,绿色点为1/4像素点,红色箭头代表了一次运动搜索过程,蓝色箭头则代表了运动矢量,虚线边缘块则代表了最后的匹配块。
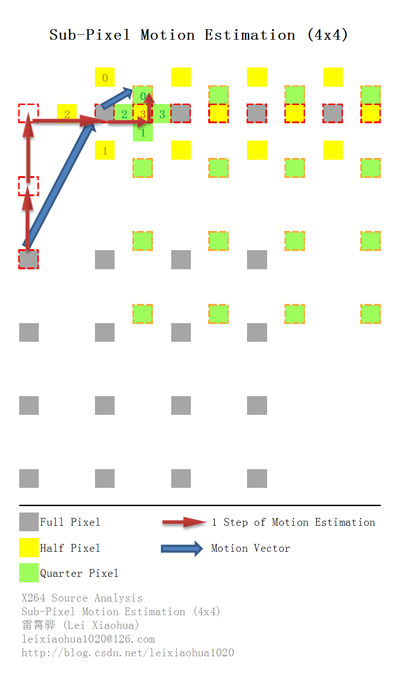
运动估计相关的源代码
运动估计模块的初始化函数是x264_mc_init()。该函数对x264_mc_functions_t结构体中的函数指针进行了赋值。X264运行的过程中只要调用x264_mc_functions_t的函数指针就可以完成相应的功能。
x264_mc_init()
x264_mc_init()用于初始化运动补偿相关的汇编函数。该函数的定义位于common\mc.c,如下所示。//运动补偿
void x264_mc_init( int cpu, x264_mc_functions_t *pf, int cpu_independent )
{
//亮度运动补偿
pf->mc_luma = mc_luma;
//获得匹配块
pf->get_ref = get_ref;
pf->mc_chroma = mc_chroma;
//求平均
pf->avg[PIXEL_16x16]= pixel_avg_16x16;
pf->avg[PIXEL_16x8] = pixel_avg_16x8;
pf->avg[PIXEL_8x16] = pixel_avg_8x16;
pf->avg[PIXEL_8x8] = pixel_avg_8x8;
pf->avg[PIXEL_8x4] = pixel_avg_8x4;
pf->avg[PIXEL_4x16] = pixel_avg_4x16;
pf->avg[PIXEL_4x8] = pixel_avg_4x8;
pf->avg[PIXEL_4x4] = pixel_avg_4x4;
pf->avg[PIXEL_4x2] = pixel_avg_4x2;
pf->avg[PIXEL_2x8] = pixel_avg_2x8;
pf->avg[PIXEL_2x4] = pixel_avg_2x4;
pf->avg[PIXEL_2x2] = pixel_avg_2x2;
//加权相关
pf->weight = x264_mc_weight_wtab;
pf->offsetadd = x264_mc_weight_wtab;
pf->offsetsub = x264_mc_weight_wtab;
pf->weight_cache = x264_weight_cache;
//赋值-只包含了方形的
pf->copy_16x16_unaligned = mc_copy_w16;
pf->copy[PIXEL_16x16] = mc_copy_w16;
pf->copy[PIXEL_8x8] = mc_copy_w8;
pf->copy[PIXEL_4x4] = mc_copy_w4;
pf->store_interleave_chroma = store_interleave_chroma;
pf->load_deinterleave_chroma_fenc = load_deinterleave_chroma_fenc;
pf->load_deinterleave_chroma_fdec = load_deinterleave_chroma_fdec;
//拷贝像素-不论像素块大小
pf->plane_copy = x264_plane_copy_c;
pf->plane_copy_interleave = x264_plane_copy_interleave_c;
pf->plane_copy_deinterleave = x264_plane_copy_deinterleave_c;
pf->plane_copy_deinterleave_rgb = x264_plane_copy_deinterleave_rgb_c;
pf->plane_copy_deinterleave_v210 = x264_plane_copy_deinterleave_v210_c;
//关键:半像素内插
pf->hpel_filter = hpel_filter;
//几个空函数
pf->prefetch_fenc_420 = prefetch_fenc_null;
pf->prefetch_fenc_422 = prefetch_fenc_null;
pf->prefetch_ref = prefetch_ref_null;
pf->memcpy_aligned = memcpy;
pf->memzero_aligned = memzero_aligned;
//降低分辨率-线性内插(不是半像素内插)
pf->frame_init_lowres_core = frame_init_lowres_core;
pf->integral_init4h = integral_init4h;
pf->integral_init8h = integral_init8h;
pf->integral_init4v = integral_init4v;
pf->integral_init8v = integral_init8v;
pf->mbtree_propagate_cost = mbtree_propagate_cost;
pf->mbtree_propagate_list = mbtree_propagate_list;
//各种汇编版本
#if HAVE_MMX
x264_mc_init_mmx( cpu, pf );
#endif
#if HAVE_ALTIVEC
if( cpu&X264_CPU_ALTIVEC )
x264_mc_altivec_init( pf );
#endif
#if HAVE_ARMV6
x264_mc_init_arm( cpu, pf );
#endif
#if ARCH_AARCH64
x264_mc_init_aarch64( cpu, pf );
#endif
if( cpu_independent )
{
pf->mbtree_propagate_cost = mbtree_propagate_cost;
pf->mbtree_propagate_list = mbtree_propagate_list;
}
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_mc_init()中包含了大量的像素内插、拷贝、求平均的函数。这些函数都是用于在H.264编码过程中进行运动估计和运动补偿的。x264_mc_init()的参数x264_mc_functions_t是一个结构体,其中包含了运动补偿函数相关的函数接口。x264_mc_functions_t的定义如下。
typedef struct
{
void (*mc_luma)( pixel *dst, intptr_t i_dst, pixel **src, intptr_t i_src,
int mvx, int mvy, int i_width, int i_height, const x264_weight_t *weight );
/* may round up the dimensions if they're not a power of 2 */
pixel* (*get_ref)( pixel *dst, intptr_t *i_dst, pixel **src, intptr_t i_src,
int mvx, int mvy, int i_width, int i_height, const x264_weight_t *weight );
/* mc_chroma may write up to 2 bytes of garbage to the right of dst,
* so it must be run from left to right. */
void (*mc_chroma)( pixel *dstu, pixel *dstv, intptr_t i_dst, pixel *src, intptr_t i_src,
int mvx, int mvy, int i_width, int i_height );
void (*avg[12])( pixel *dst, intptr_t dst_stride, pixel *src1, intptr_t src1_stride,
pixel *src2, intptr_t src2_stride, int i_weight );
/* only 16x16, 8x8, and 4x4 defined */
void (*copy[7])( pixel *dst, intptr_t dst_stride, pixel *src, intptr_t src_stride, int i_height );
void (*copy_16x16_unaligned)( pixel *dst, intptr_t dst_stride, pixel *src, intptr_t src_stride, int i_height );
void (*store_interleave_chroma)( pixel *dst, intptr_t i_dst, pixel *srcu, pixel *srcv, int height );
void (*load_deinterleave_chroma_fenc)( pixel *dst, pixel *src, intptr_t i_src, int height );
void (*load_deinterleave_chroma_fdec)( pixel *dst, pixel *src, intptr_t i_src, int height );
void (*plane_copy)( pixel *dst, intptr_t i_dst, pixel *src, intptr_t i_src, int w, int h );
void (*plane_copy_interleave)( pixel *dst, intptr_t i_dst, pixel *srcu, intptr_t i_srcu,
pixel *srcv, intptr_t i_srcv, int w, int h );
/* may write up to 15 pixels off the end of each plane */
void (*plane_copy_deinterleave)( pixel *dstu, intptr_t i_dstu, pixel *dstv, intptr_t i_dstv,
pixel *src, intptr_t i_src, int w, int h );
void (*plane_copy_deinterleave_rgb)( pixel *dsta, intptr_t i_dsta, pixel *dstb, intptr_t i_dstb,
pixel *dstc, intptr_t i_dstc, pixel *src, intptr_t i_src, int pw, int w, int h );
void (*plane_copy_deinterleave_v210)( pixel *dsty, intptr_t i_dsty,
pixel *dstc, intptr_t i_dstc,
uint32_t *src, intptr_t i_src, int w, int h );
void (*hpel_filter)( pixel *dsth, pixel *dstv, pixel *dstc, pixel *src,
intptr_t i_stride, int i_width, int i_height, int16_t *buf );
/* prefetch the next few macroblocks of fenc or fdec */
void (*prefetch_fenc) ( pixel *pix_y, intptr_t stride_y, pixel *pix_uv, intptr_t stride_uv, int mb_x );
void (*prefetch_fenc_420)( pixel *pix_y, intptr_t stride_y, pixel *pix_uv, intptr_t stride_uv, int mb_x );
void (*prefetch_fenc_422)( pixel *pix_y, intptr_t stride_y, pixel *pix_uv, intptr_t stride_uv, int mb_x );
/* prefetch the next few macroblocks of a hpel reference frame */
void (*prefetch_ref)( pixel *pix, intptr_t stride, int parity );
void *(*memcpy_aligned)( void *dst, const void *src, size_t n );
void (*memzero_aligned)( void *dst, size_t n );
/* successive elimination prefilter */
void (*integral_init4h)( uint16_t *sum, pixel *pix, intptr_t stride );
void (*integral_init8h)( uint16_t *sum, pixel *pix, intptr_t stride );
void (*integral_init4v)( uint16_t *sum8, uint16_t *sum4, intptr_t stride );
void (*integral_init8v)( uint16_t *sum8, intptr_t stride );
void (*frame_init_lowres_core)( pixel *src0, pixel *dst0, pixel *dsth, pixel *dstv, pixel *dstc,
intptr_t src_stride, intptr_t dst_stride, int width, int height );
weight_fn_t *weight;
weight_fn_t *offsetadd;
weight_fn_t *offsetsub;
void (*weight_cache)( x264_t *, x264_weight_t * );
void (*mbtree_propagate_cost)( int16_t *dst, uint16_t *propagate_in, uint16_t *intra_costs,
uint16_t *inter_costs, uint16_t *inv_qscales, float *fps_factor, int len );
void (*mbtree_propagate_list)( x264_t *h, uint16_t *ref_costs, int16_t (*mvs)[2],
int16_t *propagate_amount, uint16_t *lowres_costs,
int bipred_weight, int mb_y, int len, int list );
} x264_mc_functions_t;
x264_mc_init()的工作就是对x264_mc_functions_t中的函数指针进行赋值。x264_mc_functions_t的成员变量比较多,难以一一分析。下文主要分析其中最重要的两个函数:半像素内插函数hpel_filter()和获取亚像素数据的函数get_ref()。
hpel_filter()
hpel_filter()用于进行半像素插值。该函数的定义位于common\mc.c,如下所示。//半像素插值公式
//b= (E - 5F + 20G + 20H - 5I + J)/32
// x
//d取1,水平滤波器;d取stride,垂直滤波器(这里没有除以32)
#define TAPFILTER(pix, d) ((pix)[x-2*d] + (pix)[x+3*d] - 5*((pix)[x-d] + (pix)[x+2*d]) + 20*((pix)[x] + (pix)[x+d]))
/*
* 半像素插值
* dsth:水平滤波得到的半像素点(aa,bb,b,s,gg,hh)
* dstv:垂直滤波的到的半像素点(cc,dd,h,m,ee,ff)
* dstc:“水平+垂直”滤波得到的位于4个像素中间的半像素点(j)
*
* 半像素插值示意图如下:
*
* A aa B
*
* C bb D
*
* E F G b H I J
*
* cc dd h j m ee ff
*
* K L M s N P Q
*
* R gg S
*
* T hh U
*
* 计算公式如下:
* b=round( (E - 5F + 20G + 20H - 5I + J ) / 32)
*
* 剩下几个半像素点的计算关系如下:
* m:由B、D、H、N、S、U计算
* h:由A、C、G、M、R、T计算
* s:由K、L、M、N、P、Q计算
* j:由cc、dd、h、m、ee、ff计算。需要注意j点的运算量比较大,因为cc、dd、ee、ff都需要通过半像素内插方法进行计算。
*
*/
static void hpel_filter( pixel *dsth, pixel *dstv, pixel *dstc, pixel *src,
intptr_t stride, int width, int height, int16_t *buf )
{
const int pad = (BIT_DEPTH > 9) ? (-10 * PIXEL_MAX) : 0;
/*
* 几种半像素点之间的位置关系
*
* X: 像素点
* H:水平滤波半像素点
* V:垂直滤波半像素点
* C: 中间位置半像素点
*
* X H X X X
*
* V C
*
* X X X X
*
*
*
* X X X X
*
*/
//一行一行处理
for( int y = 0; y < height; y++ )
{
//一个一个点处理
//每个整像素点都对应h,v,c三个半像素点
//v
for( int x = -2; x < width+3; x++ )//(aa,bb,b,s,gg,hh),结果存入buf
{
//垂直滤波半像素点
int v = TAPFILTER(src,stride);
dstv[x] = x264_clip_pixel( (v + 16) >> 5 );
/* transform v for storage in a 16-bit integer */
//这应该是给dstc计算使用的?
buf[x+2] = v + pad;
}
//c
for( int x = 0; x < width; x++ )
dstc[x] = x264_clip_pixel( (TAPFILTER(buf+2,1) - 32*pad + 512) >> 10 );//四个相邻像素中间的半像素点
//h
for( int x = 0; x < width; x++ )
dsth[x] = x264_clip_pixel( (TAPFILTER(src,1) + 16) >> 5 );//水平滤波半像素点
dsth += stride;
dstv += stride;
dstc += stride;
src += stride;
}
}
从源代码可以看出,hpel_filter()中包含了一个宏TAPFILTER()用来完成半像素点像素值的计算。在完成半像素插值工作后,dsth中存储的是经过水平插值后的半像素点,dstv中存储的是经过垂直插值后的半像素点,dstc中存储的是位于4个相邻像素点中间位置的半像素点。这三块内存中的点的位置关系如下图所示(灰色的点是整像素点)。
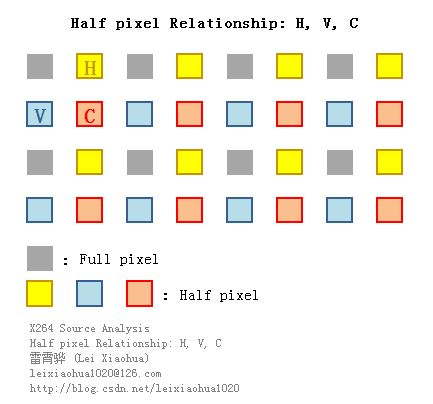
get_ref()
get_ref()用于获取亚像素数据。该函数的定义位于common\mc.c,如下所示。/*
* hpel_ref0[]记录了亚像素点依赖于哪些点。数组元素共有四个取值:0,1,2,3。这四个值分别代表整数像素,水平半像素,垂直半像素,对角线半像素。
* hpel_ref1[]功能是类似的。
* 1/4内插点依赖于2个半像素点,所以才存在这2个数组
*
* 注意对最下1行像素和最右1行像素是需要特殊处理的
*
* hpel_ref0[qpel_idx]表示了第1次半像素内插使用的滤波器。示意如下(矩阵4个角代表4个整像素点)
*
* 0 1 1 1
* 0 1 1 1
* 2 3 3 3
* 0 1 1 1
*
* hpel_ref1[qpel_idx]表示了第2次半像素内插使用的滤波器(只有1/4内插点才需要)。示意如下(矩阵4个角代表4个整像素点)
* 0 0 0 0
* 2 2 3 2
* 2 2 3 2
* 2 2 3 2
*
* 例如
* qpel_idx=5的时候
* hpel_ref0[5]=1,需要进行水平半像素滤波
* hpel_ref1[5]=2,需要进行垂直半像素滤波
* 顺序如下(X代表像素点,数字代表顺序)
* X 1 X
* 3
* 2
*
* X X
*
* qpel_idx=1的时候
* hpel_ref0[5]=1,需要进行水平半像素滤波
* hpel_ref1[5]=0,即直接使用整像素点
* 顺序如下(X代表像素点,数字代表顺序)
* 2 3 1 X
*
*
*
* X X
*
* qpel_idx=4的时候
* hpel_ref0[5]=0,即直接使用整像素点
* hpel_ref1[5]=2,需要进行垂直半像素滤波
* 顺序如下(X代表像素点,数字代表顺序)
* 1 X
* 3
* 2
*
* X X
*/
static const uint8_t hpel_ref0[16] = {0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,2,3,3,3,0,1,1,1};
static const uint8_t hpel_ref1[16] = {0,0,0,0,2,2,3,2,2,2,3,2,2,2,3,2};
//
//获取运动矢量中亚像素的部分的数据
//可以是半像素数据或者1/4像素数据
static pixel *get_ref( pixel *dst, intptr_t *i_dst_stride,
pixel *src[4], intptr_t i_src_stride,
int mvx, int mvy,
int i_width, int i_height, const x264_weight_t *weight )
{
/*
* qpel_idx为hpel_ref0[],hpel_ref1[]的索引值
*
* 运动矢量(mvy,mvx)位置和qpel_idx对应关系如下
* 0pixel | 0p | 1/4p | 1/2p | 3/4p | 1pixel |
* --------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
* 0p | 0<<2+0 | 0<<2+1 | 0<<2+2 | 0<<2+3 | |
* --------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
* 1/4p | 1<<2+0 | 1<<2+1 | 1<<2+2 | 1<<2+3 | |
* --------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
* 1/2p | 2<<2+0 | 2<<2+1 | 2<<2+2 | 2<<2+3 | |
* --------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
* 3/4p | 3<<2+0 | 3<<2+1 | 3<<2+2 | 3<<2+3 | |
* --------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
* 1pixel |
* --------+
* 计算出来后
* 0pixel | 0p | 1/4p | 1/2p | 3/4p | 1pixel |
* --------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
* 0p | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
* --------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
* 1/4p | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
* --------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
* 1/2p | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |
* --------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
* 3/4p | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | |
* --------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
* 1pixel |
* --------+
*
*/
int qpel_idx = ((mvy&3)<<2) + (mvx&3);
//offset是匹配块相对当前宏块的整数偏移量。
int offset = (mvy>>2)*i_src_stride + (mvx>>2);
//src[4]中有4个分量,分别代表:整像素点Full,水平半像素点H,垂直半像素点V,对角线半像素点C的取值(几种半像素点的值已经提前计算出来,而1/4像素点的值则是临时计算)
//注意上述几种半像素点是按照“分量”的方式存储的
//src1[]为选择后的半像素数据
//选择了Full,H,V,C几种“分量”中的1种
pixel *src1 = src[hpel_ref0[qpel_idx]] + offset + ((mvy&3) == 3) * i_src_stride;
//qpel_idx & 5,5是0101, 代表qpel_idx最后1位(对应x分量)为1或者倒数第3位为1(对应y分量)。
//即x或者y中有1/4或者3/4像素点(此时需要1/4像素内插)。
//只有需要1/4内插的点才会qpel_idx & 5!=0。这时候需要通过线性内插获得1/4像素点的值
if( qpel_idx & 5 ) /* qpel interpolation needed */
{
//src2[]为用于内插的数据另一组数据
pixel *src2 = src[hpel_ref1[qpel_idx]] + offset + ((mvx&3) == 3);
//进行1/4像素线性内插
pixel_avg( dst, *i_dst_stride, src1, i_src_stride,
src2, i_src_stride, i_width, i_height );
if( weight->weightfn )
mc_weight( dst, *i_dst_stride, dst, *i_dst_stride, weight, i_width, i_height );
return dst;
}
else if( weight->weightfn )
{
mc_weight( dst, *i_dst_stride, src1, i_src_stride, weight, i_width, i_height );
return dst;
}
else
{
//只需要半像素滤波
*i_dst_stride = i_src_stride;
return src1;
}
}
get_ref()虽然代码简短,但是却不好理解。函数首先取出输入运动矢量亚像素部分(后两位数据),经过计算后赋值给qpel_idx。换句话说qpel_idx记录了运动矢量在亚像素单位上指向的位置,它的取值和像素位置之间的关系如下表所示。
x point | 0p | 1/4p | 1/2p | 3/4p | x+1 point |
0p | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|
1/4p | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|
1/2p | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|
3/4p | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
|
x+stride point |
|
|
|
|
|
接着get_ref()根据qpel_idx从输入图像数据src[4]中取数据。src[4]中[0]存储是整像素数据,[1]存储是水平半像素数据,[2]存储是垂直半像素数据,[3]存储是对角线半像素数据。在取数据的过程中涉及到两个数组hpel_ref0[16]和hpel_ref1[16],这两个数组记录了相应qpel_idx位置应该从哪个半像素点数组中取数据。例如qpel_idx取值为8的时候,应该从垂直半像素数组中取值,因此hpel_ref0[8]=2;而qpel_idx取值为2的时候,应该从水平半像素数组中取值,因此hpel_ref0[2]=1。如果仅仅取半像素点的的话,使用hpel_ref0[16]就足够了,但是如果想要取1/4像素点,就必须使用hpel_ref1[16]。这是因为1/4像素点需要通过2个半像素点线性内插获得,所以hpel_ref1[16]记录了线性内插需要的另一个点是哪个半像素点。例如qpel_idx取值为5的时候,通过垂直半像素点和水平半像素点内插获得该1/4像素点,因此hpel_ref0[5]=1,而hpel_ref1[5]=2;再例如qpel_idx取值为4的时候,通过整像素点和垂直半像素点内插获得该1/4像素点,因此hpel_ref0[4]=0,而hpel_ref1[4]=2。
get_ref()函数通过“qpel_idx & 5”来断定当前运动矢量是否是1/4像素内插点,如果需要的话才会根据hpel_ref1[]加载另一个半像素点的数据并且调用pixel_avg()函数通过线性内插的方式获取该内插点。
下图演示了hpel_ref0[16]和hpel_ref1[16]在获取亚像素数据时候的作用。图中灰色点代表整像素点,黄色点代表半像素点,绿色点代表1/4像素点;左边是一个4x4图像块,其中蓝色箭头标记了1/4像素点需要的两个半像素点(也可能是整像素点);右上方的图将两个像素点之间的图像放大,并且将1/4像素点需要的两个半像素点以数字的方式表示出来;右下方则是将右上方的数字拆开成了两个矩阵,即对应的是hpel_ref0[16]和hpel_ref1[16]。
pixel_avg_wxh()
get_ref()中求1/4像素点的时候调用了一个线性内插函数pixel_avg_wxh()。该函数的定义如下。//像素求平均值
//在这里用于1/4像素内插
static inline void pixel_avg( pixel *dst, intptr_t i_dst_stride,
pixel *src1, intptr_t i_src1_stride,
pixel *src2, intptr_t i_src2_stride, int i_width, int i_height )
{
for( int y = 0; y < i_height; y++ )
{
for( int x = 0; x < i_width; x++ )
dst[x] = ( src1[x] + src2[x] + 1 ) >> 1;
dst += i_dst_stride;
src1 += i_src1_stride;
src2 += i_src2_stride;
}
}至此有关X264帧间预测方面的源代码就基本分析完毕了。前文中以P16x16宏块为例分析的帧间预测的源代码,作为对比下面再看一下P8x8、P16x8、P8x16宏块帧间预测的源代码。实际上这几种宏块的帧间预测的方式是类似的,都调用了x264_me_search_ref()完成了运动搜索的过程,它们的不同主要在于处理的图像块尺寸的不同。
其他划分模式的帧间预测源代码
P8x8宏块帧间预测函数为x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x8();P16x8 宏块帧间预测函数为x264_mb_analyse_inter_p16x8();P8x16宏块帧间预测函数为x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x16()。下面简单扫一眼它们的源代码。x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x8()
x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x8()用于分析P8x8宏块的帧间预测模式,该函数的定义如下。/*
* 8x8帧间预测宏块分析
* +--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+
*/
static void x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x8( x264_t *h, x264_mb_analysis_t *a )
{
/* Duplicate refs are rarely useful in p8x8 due to the high cost of the
* reference frame flags. Thus, if we're not doing mixedrefs, just
* don't bother analysing the dupes. */
const int i_ref = h->mb.ref_blind_dupe == a->l0.me16x16.i_ref ? 0 : a->l0.me16x16.i_ref;
const int i_ref_cost = h->param.b_cabac || i_ref ? REF_COST( 0, i_ref ) : 0;
pixel **p_fenc = h->mb.pic.p_fenc;
int i_mvc;
int16_t (*mvc)[2] = a->l0.mvc[i_ref];
/* XXX Needed for x264_mb_predict_mv */
h->mb.i_partition = D_8x8;
i_mvc = 1;
CP32( mvc[0], a->l0.me16x16.mv );
//处理4个8x8块
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{
x264_me_t *m = &a->l0.me8x8[i];
int x8 = i&1;
int y8 = i>>1;
//设定像素分块大小
m->i_pixel = PIXEL_8x8;
m->i_ref_cost = i_ref_cost;
LOAD_FENC( m, p_fenc, 8*x8, 8*y8 );
LOAD_HPELS( m, h->mb.pic.p_fref[0][i_ref], 0, i_ref, 8*x8, 8*y8 );
LOAD_WPELS( m, h->mb.pic.p_fref_w[i_ref], 0, i_ref, 8*x8, 8*y8 );
x264_mb_predict_mv( h, 0, 4*i, 2, m->mvp );
//调用x264_me_search_ref()
//进行运动估计
x264_me_search( h, m, mvc, i_mvc );
x264_macroblock_cache_mv_ptr( h, 2*x8, 2*y8, 2, 2, 0, m->mv );
CP32( mvc[i_mvc], m->mv );
i_mvc++;
a->i_satd8x8[0][i] = m->cost - m->cost_mv;
/* mb type cost */
m->cost += i_ref_cost;
if( !h->param.b_cabac || (h->param.analyse.inter & X264_ANALYSE_PSUB8x8) )
m->cost += a->i_lambda * i_sub_mb_p_cost_table[D_L0_8x8];
}
//保存开销。4个8x8块开销累加
a->l0.i_cost8x8 = a->l0.me8x8[0].cost + a->l0.me8x8[1].cost +
a->l0.me8x8[2].cost + a->l0.me8x8[3].cost;
/* theoretically this should include 4*ref_cost,
* but 3 seems a better approximation of cabac. */
if( h->param.b_cabac )
a->l0.i_cost8x8 -= i_ref_cost;
h->mb.i_sub_partition[0] = h->mb.i_sub_partition[1] =
h->mb.i_sub_partition[2] = h->mb.i_sub_partition[3] = D_L0_8x8;
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x8()中包含一个4次的for()循环,用于分别处理4个8x8的块。在函数的结尾将4个8x8块的开销累加起来作为该宏块的开销。
x264_mb_analyse_inter_p16x8()
x264_mb_analyse_inter_p16x8()用于分析P16x8宏块的帧间预测模式,该函数的定义如下。/*
* 16x8 宏块划分
*
* +--------+--------+
* | | |
* | | |
* | | |
* +--------+--------+
*
*/
static void x264_mb_analyse_inter_p16x8( x264_t *h, x264_mb_analysis_t *a, int i_best_satd )
{
x264_me_t m;
pixel **p_fenc = h->mb.pic.p_fenc;
ALIGNED_4( int16_t mvc[3][2] );
/* XXX Needed for x264_mb_predict_mv */
h->mb.i_partition = D_16x8;
//轮流处理上下2个块
for( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ )
{
x264_me_t *l0m = &a->l0.me16x8[i];
const int minref = X264_MIN( a->l0.me8x8[2*i].i_ref, a->l0.me8x8[2*i+1].i_ref );
const int maxref = X264_MAX( a->l0.me8x8[2*i].i_ref, a->l0.me8x8[2*i+1].i_ref );
const int ref8[2] = { minref, maxref };
const int i_ref8s = ( ref8[0] == ref8[1] ) ? 1 : 2;
m.i_pixel = PIXEL_16x8;
LOAD_FENC( &m, p_fenc, 0, 8*i );
l0m->cost = INT_MAX;
for( int j = 0; j < i_ref8s; j++ )
{
const int i_ref = ref8[j];
m.i_ref_cost = REF_COST( 0, i_ref );
/* if we skipped the 16x16 predictor, we wouldn't have to copy anything... */
CP32( mvc[0], a->l0.mvc[i_ref][0] );
CP32( mvc[1], a->l0.mvc[i_ref][2*i+1] );
CP32( mvc[2], a->l0.mvc[i_ref][2*i+2] );
LOAD_HPELS( &m, h->mb.pic.p_fref[0][i_ref], 0, i_ref, 0, 8*i );
LOAD_WPELS( &m, h->mb.pic.p_fref_w[i_ref], 0, i_ref, 0, 8*i );
x264_macroblock_cache_ref( h, 0, 2*i, 4, 2, 0, i_ref );
x264_mb_predict_mv( h, 0, 8*i, 4, m.mvp );
/* We can only take this shortcut if the first search was performed on ref0. */
if( h->mb.ref_blind_dupe == i_ref && !ref8[0] )
{
/* We can just leave the MV from the previous ref search. */
x264_me_refine_qpel_refdupe( h, &m, NULL );
}
else
x264_me_search( h, &m, mvc, 3 );//运动搜索
m.cost += m.i_ref_cost;
if( m.cost < l0m->cost )
h->mc.memcpy_aligned( l0m, &m, sizeof(x264_me_t) );
}
/* Early termination based on the current SATD score of partition[0]
plus the estimated SATD score of partition[1] */
if( a->b_early_terminate && (!i && l0m->cost + a->i_cost_est16x8[1] > i_best_satd * (4 + !!a->i_mbrd) / 4) )
{
a->l0.i_cost16x8 = COST_MAX;
return;
}
x264_macroblock_cache_mv_ptr( h, 0, 2*i, 4, 2, 0, l0m->mv );
x264_macroblock_cache_ref( h, 0, 2*i, 4, 2, 0, l0m->i_ref );
}
//2个块的开销相加
a->l0.i_cost16x8 = a->l0.me16x8[0].cost + a->l0.me16x8[1].cost;
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_mb_analyse_inter_p16x8 ()中包含一个2次的for()循环,用于分别处理2个16x8的块。在函数的结尾将2个16x8块的开销累加起来作为该宏块的开销。
x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x16()
x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x16()用于分析P8x16宏块的帧间预测模式,该函数的定义如下。/*
* 8x16 宏块划分
*
* +--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+
*
*/
static void x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x16( x264_t *h, x264_mb_analysis_t *a, int i_best_satd )
{
x264_me_t m;
pixel **p_fenc = h->mb.pic.p_fenc;
ALIGNED_4( int16_t mvc[3][2] );
/* XXX Needed for x264_mb_predict_mv */
h->mb.i_partition = D_8x16;
//轮流处理左右2个块
for( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ )
{
x264_me_t *l0m = &a->l0.me8x16[i];
const int minref = X264_MIN( a->l0.me8x8[i].i_ref, a->l0.me8x8[i+2].i_ref );
const int maxref = X264_MAX( a->l0.me8x8[i].i_ref, a->l0.me8x8[i+2].i_ref );
const int ref8[2] = { minref, maxref };
const int i_ref8s = ( ref8[0] == ref8[1] ) ? 1 : 2;
m.i_pixel = PIXEL_8x16;
LOAD_FENC( &m, p_fenc, 8*i, 0 );
l0m->cost = INT_MAX;
for( int j = 0; j < i_ref8s; j++ )
{
const int i_ref = ref8[j];
m.i_ref_cost = REF_COST( 0, i_ref );
CP32( mvc[0], a->l0.mvc[i_ref][0] );
CP32( mvc[1], a->l0.mvc[i_ref][i+1] );
CP32( mvc[2], a->l0.mvc[i_ref][i+3] );
LOAD_HPELS( &m, h->mb.pic.p_fref[0][i_ref], 0, i_ref, 8*i, 0 );
LOAD_WPELS( &m, h->mb.pic.p_fref_w[i_ref], 0, i_ref, 8*i, 0 );
x264_macroblock_cache_ref( h, 2*i, 0, 2, 4, 0, i_ref );
x264_mb_predict_mv( h, 0, 4*i, 2, m.mvp );
/* We can only take this shortcut if the first search was performed on ref0. */
if( h->mb.ref_blind_dupe == i_ref && !ref8[0] )
{
/* We can just leave the MV from the previous ref search. */
x264_me_refine_qpel_refdupe( h, &m, NULL );
}
else
x264_me_search( h, &m, mvc, 3 );
m.cost += m.i_ref_cost;
if( m.cost < l0m->cost )
h->mc.memcpy_aligned( l0m, &m, sizeof(x264_me_t) );
}
/* Early termination based on the current SATD score of partition[0]
plus the estimated SATD score of partition[1] */
if( a->b_early_terminate && (!i && l0m->cost + a->i_cost_est8x16[1] > i_best_satd * (4 + !!a->i_mbrd) / 4) )
{
a->l0.i_cost8x16 = COST_MAX;
return;
}
x264_macroblock_cache_mv_ptr( h, 2*i, 0, 2, 4, 0, l0m->mv );
x264_macroblock_cache_ref( h, 2*i, 0, 2, 4, 0, l0m->i_ref );
}
//2个块的开销相加
a->l0.i_cost8x16 = a->l0.me8x16[0].cost + a->l0.me8x16[1].cost;
}
从源代码可以看出,x264_mb_analyse_inter_p8x16 ()中包含一个2次的for()循环,用于分别处理2个8x16的块。在函数的结尾将2个8x16块的开销累加起来作为该宏块的开销。
雷霄骅
leixiaohua1020@126.com
http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020

开放原子开发者工作坊旨在鼓励更多人参与开源活动,与志同道合的开发者们相互交流开发经验、分享开发心得、获取前沿技术趋势。工作坊有多种形式的开发者活动,如meetup、训练营等,主打技术交流,干货满满,真诚地邀请各位开发者共同参与!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献25条内容
已为社区贡献25条内容
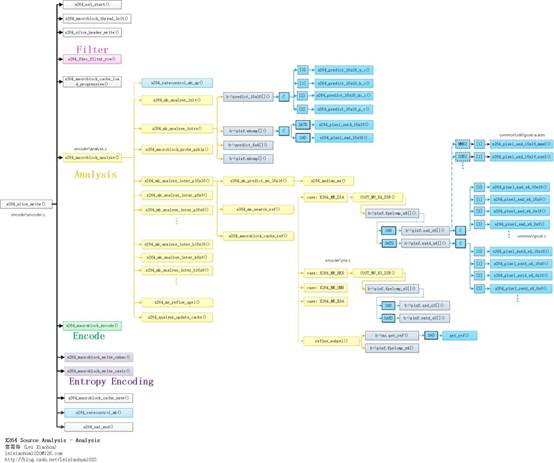

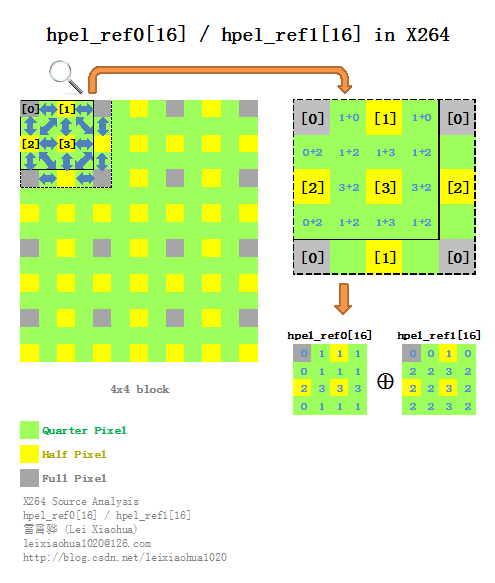





所有评论(0)