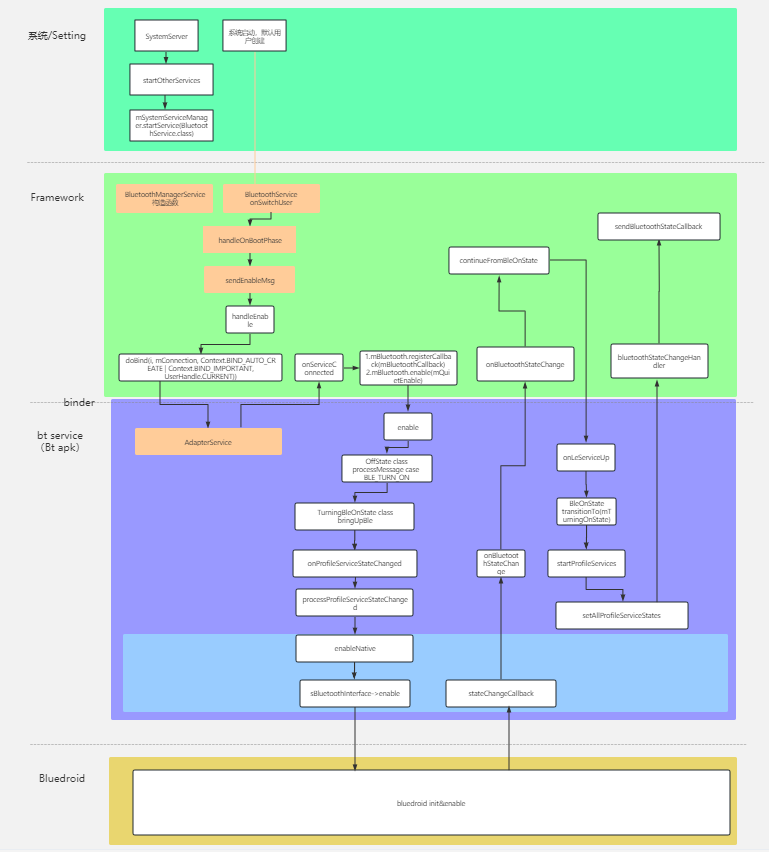
Android蓝牙使能流程图(Android Bluetooth enable) -- java & jni层
目前蓝牙协议栈本身的架构就很复杂,而且大部分都是用C/C++编写,对于蓝牙协议栈工程师硬啃可能啃的动,但是Android上层又用java编写,又加了很多binder,jn机制,并且伴有Android本身apk的一些特性在里面,让蓝牙工程师苦不堪言,所以本文秉着大道至简的目的,给你们来介绍下android上层,包括framework,service的enable流程,让你们有一些概念,抛砖引玉下!
在介绍Android enable流程之前,我们首先来看下Android的流程图

以上图示是android8以上的,主要跟Android8之前的架构在于Bluetooth stack跟vendor层之间增加一层HIDL,主要是抽象硬件层的作用
OK,回归主题,我们来看下Android的enable流程,首先上一张架构图

另外声明下:我们做了一些列的蓝牙教程(包括视频)。我们会以连载的方式持续更新,内容如下:
本专栏文章我们会以连载的方式持续更新,本专栏计划更新内容如下:

第一篇:蓝牙综合介绍 ,主要介绍蓝牙的一些概念,产生背景,发展轨迹,市面蓝牙介绍,以及蓝牙开发板介绍。
第二篇:Transport层介绍,主要介绍蓝牙协议栈跟蓝牙芯片之前的硬件传输协议,比如基于UART的H4,H5,BCSP,基于USB的H2等
第三篇:传统蓝牙controller介绍,主要介绍传统蓝牙芯片的介绍,包括射频层(RF),基带层(baseband),链路管理层(LMP)等
第四篇:传统蓝牙host介绍,主要介绍传统蓝牙的协议栈,比如HCI,L2CAP,SDP,RFCOMM,HFP,SPP,HID,AVDTP,AVCTP,A2DP,AVRCP,OBEX,PBAP,MAP等等一系列的协议吧。
第五篇:低功耗蓝牙controller介绍,主要介绍低功耗蓝牙芯片,包括物理层(PHY),链路层(LL)
第六篇:低功耗蓝牙host介绍,低功耗蓝牙协议栈的介绍,包括HCI,L2CAP,ATT,GATT,SM等
第七篇:蓝牙芯片介绍,主要介绍一些蓝牙芯片的初始化流程,基于HCI vendor command的扩展
第八篇:附录,主要介绍以上常用名词的介绍以及一些特殊流程的介绍等。
另外,开发板如下所示,对于想学习蓝牙协议栈的最好人手一套。以便更好的学习蓝牙协议栈,相信我,学完这一套视频你将拥有修改任何协议栈的能力(比如Linux下的bluez,Android下的bluedroid)。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
蓝牙视频教程(跟韦东山老师合作):https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?spm=a1z10.5-c-s.w4002-22329603914.10.77201fc98qgCWh&id=679276693032
蓝牙交流扣扣群:970324688
蓝牙学习目录:一篇文章足够你学习蓝牙技术,提供史上最全的蓝牙技术(传统蓝牙/低功耗蓝牙)文章总结,文档下载总结(2020/12/11更新)_Wireless_Link的博客-CSDN博客_蓝牙eir
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
步骤1:开机会启动SystemServer类的main函数
在Android系统启动过程中,SystemServer是第一个被启动的进程。当Android设备被开机后,内核会创建一个名为init的进程,init进程会启动Zygote进程,Zygote进程会启动SystemServer进程。因此,SystemServer是整个Android系统启动的核心进程,它负责初始化并启动大部分系统服务和应用程序,是整个Android系统的主要启动入口。
具体来说,SystemServer主要完成以下几个任务:
启动和初始化系统服务:SystemServer会启动和初始化大部分系统服务,例如ActivityManagerService、WindowManagerService、PackageManagerService、PowerManagerService等等。这些服务会在启动过程中被创建并注册到系统服务中心,供其他应用程序和服务调用。
启动和初始化核心应用程序:SystemServer会启动和初始化Android系统中的核心应用程序,例如SystemUI、Settings等等。这些应用程序会在启动过程中被创建并运行,提供各种用户界面和功能。
加载和初始化系统属性:SystemServer会加载和初始化/system/build.prop文件中定义的系统属性,例如设备型号、厂商信息等等。这些属性可以在系统运行时被访问和修改。
启动Adb守护进程:SystemServer会启动Adb守护进程,使得开发者可以通过adb工具来访问设备。
总之,SystemServer是整个Android系统启动过程中的核心进程,负责启动和初始化大部分系统服务和应用程序,为整个系统的运行提供基础支持。SystemServer的启动时间通常在内核启动之后的几秒钟内,具体时间取决于设备的硬件性能和系统配置。
/**
* The main entry point from zygote.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}SystemServer().run();执行startOtherServices(t);
然后startOtherServices(t);执行如下代码,开启Bluetooth service类
private void startOtherServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
...
if (mFactoryTestMode == FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
Slog.i(TAG, "No Bluetooth Service (factory test)");
} else if (!context.getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature
(PackageManager.FEATURE_BLUETOOTH)) {
Slog.i(TAG, "No Bluetooth Service (Bluetooth Hardware Not Present)");
} else {
t.traceBegin("StartBluetoothService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(BluetoothService.class);
t.traceEnd();
}
...
}步骤2:BluetoothService构造函数中执行创建BluetoothManagerService
mBluetoothManagerService = new BluetoothManagerService(context);
BluetoothManagerService(Context context) {
Slog.e(TAG, "new BluetoothManagerService");
// BluetoothManagerService的私有类,主要用于处理一些message
mHandler = new BluetoothHandler(IoThread.get().getLooper());
mContext = context;
mWirelessConsentRequired = context.getResources()
.getBoolean(com.android.internal.R.bool.config_wirelessConsentRequired);
mCrashes = 0;
mBluetooth = null;
mBluetoothBinder = null;
mBluetoothGatt = null;
mBinding = false;
mUnbinding = false;
mEnable = false;
mState = BluetoothAdapter.STATE_OFF;
mQuietEnableExternal = false;
mEnableExternal = false;
mAddress = null;
mName = null;
mErrorRecoveryRetryCounter = 0;
mContentResolver = context.getContentResolver();
// Observe BLE scan only mode settings change.
registerForBleScanModeChange();
mCallbacks = new RemoteCallbackList<IBluetoothManagerCallback>();
mStateChangeCallbacks = new RemoteCallbackList<IBluetoothStateChangeCallback>();
mIsHearingAidProfileSupported = context.getResources()
.getBoolean(com.android.internal.R.bool.config_hearing_aid_profile_supported);
// TODO: We need a more generic way to initialize the persist keys of FeatureFlagUtils
String value = SystemProperties.get(FeatureFlagUtils.PERSIST_PREFIX + FeatureFlagUtils.HEARING_AID_SETTINGS);
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(value)) {
boolean isHearingAidEnabled = Boolean.parseBoolean(value);
Log.v(TAG, "set feature flag HEARING_AID_SETTINGS to " + isHearingAidEnabled);
FeatureFlagUtils.setEnabled(context, FeatureFlagUtils.HEARING_AID_SETTINGS, isHearingAidEnabled);
if (isHearingAidEnabled && !mIsHearingAidProfileSupported) {
// Overwrite to enable support by FeatureFlag
mIsHearingAidProfileSupported = true;
}
}
IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter();
filter.addAction(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_LOCAL_NAME_CHANGED);
filter.addAction(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_BLUETOOTH_ADDRESS_CHANGED);
filter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_SETTING_RESTORED);
filter.setPriority(IntentFilter.SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY);
mContext.registerReceiver(mReceiver, filter);
loadStoredNameAndAddress();
if (isBluetoothPersistedStateOn()) {
if (DBG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Startup: Bluetooth persisted state is ON.");
}
mEnableExternal = true;
}
String airplaneModeRadios =
Settings.Global.getString(mContentResolver, Settings.Global.AIRPLANE_MODE_RADIOS);
if (airplaneModeRadios == null || airplaneModeRadios.contains(
Settings.Global.RADIO_BLUETOOTH)) {
mBluetoothAirplaneModeListener = new BluetoothAirplaneModeListener(
this, IoThread.get().getLooper(), context);
}
int systemUiUid = -1;
// Check if device is configured with no home screen, which implies no SystemUI.
boolean noHome = mContext.getResources().getBoolean(R.bool.config_noHomeScreen);
if (!noHome) {
PackageManagerInternal pm = LocalServices.getService(PackageManagerInternal.class);
systemUiUid = pm.getPackageUid(pm.getSystemUiServiceComponent().getPackageName(),
MATCH_SYSTEM_ONLY, USER_SYSTEM);
}
if (systemUiUid >= 0) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Detected SystemUiUid: " + Integer.toString(systemUiUid));
} else {
// Some platforms, such as wearables do not have a system ui.
Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to resolve SystemUI's UID.");
}
mSystemUiUid = systemUiUid;
}步骤3:启动默认用户调用的方法处理
public void onSwitchUser(int userHandle) {
if (!mInitialized) {
initialize();
} else {
mBluetoothManagerService.handleOnSwitchUser(userHandle);
}
}onSwitchUser 是 Android 框架中的一个回调方法,用于在用户切换时接收通知。当有多个用户在同一个设备上使用时,可以使用此方法来执行一些特定于用户的操作,例如切换到其它用户时保存当前用户的状态并加载新用户的数据。
在 Android 系统中,只有在设备启用多用户功能并启用多个用户帐户时才会调用此方法。在单用户设备上,该方法不会被调用。
当一个用户从其它用户切换到当前用户时,系统会调用 onSwitchUser 方法。
当设备启动时,如果已经启用了多用户功能,则系统会自动创建一个默认的用户,并在该用户的环境下启动应用程序。此时,onSwitchUser 方法也会被调用,此时传递给方法的 userId 参数为默认用户的 ID。
备注:该方法已经在 Android 12 中被标记为过时。因此,在新的应用程序中,应该避免使用该方法,而应该考虑使用更现代的 Android 架构组件或 API 来实现多用户管理和数据保护。
private void initialize() {
if (!mInitialized) {
mBluetoothManagerService.handleOnBootPhase();
mInitialized = true;
}
}public void handleOnBootPhase() {
...
final boolean isSafeMode = mContext.getPackageManager().isSafeMode();
if (mEnableExternal && isBluetoothPersistedStateOnBluetooth() && !isSafeMode) {
if (DBG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Auto-enabling Bluetooth.");
}
//调用
sendEnableMsg(mQuietEnableExternal,
BluetoothProtoEnums.ENABLE_DISABLE_REASON_SYSTEM_BOOT,
mContext.getPackageName());
}
....
}步骤4:BluetoothManagerService.java处理enable
private void sendEnableMsg(boolean quietMode, int reason, String packageName) {
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(MESSAGE_ENABLE, quietMode ? 1 : 0, 0));
addActiveLog(reason, packageName, true);
mLastEnabledTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
}public void handleMessage(Message msg)
{
switch (msg.what)
{
case MESSAGE_ENABLE:
handleEnable(mQuietEnable);
break;
}
}private void handleEnable(boolean quietMode)
{
...
Intent i = new Intent(IBluetooth.class.getName());
if (!doBind(i, mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE | Context.BIND_IMPORTANT,
UserHandle.CURRENT)) {
mHandler.removeMessages(MESSAGE_TIMEOUT_BIND);
} else {
mBinding = true;
}
...
}bond后会调用这个函数onServiceConnected
private class BluetoothServiceConnection implements ServiceConnection {
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder service) {
String name = componentName.getClassName();
if (DBG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "BluetoothServiceConnection: " + name);
}
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(MESSAGE_BLUETOOTH_SERVICE_CONNECTED);
if (name.equals("com.android.bluetooth.btservice.AdapterService")) {
msg.arg1 = SERVICE_IBLUETOOTH;
} else if (name.equals("com.android.bluetooth.gatt.GattService")) {
msg.arg1 = SERVICE_IBLUETOOTHGATT;
} else {
Slog.e(TAG, "Unknown service connected: " + name);
return;
}
msg.obj = service;
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName) {
// Called if we unexpectedly disconnect.
String name = componentName.getClassName();
if (DBG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "BluetoothServiceConnection, disconnected: " + name);
}
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(MESSAGE_BLUETOOTH_SERVICE_DISCONNECTED);
if (name.equals("com.android.bluetooth.btservice.AdapterService")) {
msg.arg1 = SERVICE_IBLUETOOTH;
} else if (name.equals("com.android.bluetooth.gatt.GattService")) {
msg.arg1 = SERVICE_IBLUETOOTHGATT;
} else {
Slog.e(TAG, "Unknown service disconnected: " + name);
return;
}
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
}public void handleMessage(Message msg)
{
switch (msg.what)
{
case MESSAGE_BLUETOOTH_SERVICE_CONNECTED:
...
mBluetooth.registerCallback(mBluetoothCallback);
...
sendBluetoothServiceUpCallback();
...
mBluetooth.enable(mQuietEnable);
break;
}
}步骤5:AdapterService.java处理enable
注意在里面还有一个AdapterServiceBinder的类,不是这个类下面的enable
public synchronized boolean enable(boolean quietMode) {
// Enforce the user restriction for disallowing Bluetooth if it was set.
if (mUserManager.hasUserRestriction(UserManager.DISALLOW_BLUETOOTH, UserHandle.SYSTEM)) {
debugLog("enable() called when Bluetooth was disallowed");
return false;
}
Log.e(TAG, "AdapterService enable");
debugLog("enable() - Enable called with quiet mode status = " + quietMode);
mQuietmode = quietMode;
mAdapterStateMachine.sendMessage(AdapterState.BLE_TURN_ON);
return true;
}这个会触发status machine,会调用到OffState中processMessage
public boolean processMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case BLE_TURN_ON:
transitionTo(mTurningBleOnState);
break;
default:
infoLog("Unhandled message - " + messageString(msg.what));
return false;
}
return true;
}然后进入到TurningBleOnState类中的enter
public void enter() {
super.enter();
sendMessageDelayed(BLE_START_TIMEOUT, BLE_START_TIMEOUT_DELAY);
mAdapterService.bringUpBle();
}void bringUpBle() {
...
//Start Gatt service
setProfileServiceState(GattService.class, BluetoothAdapter.STATE_ON);
}开启gattservice服务
另外,ProfileService的状态改变会触发AdapterService的onProfileServiceStateChanged
public void onProfileServiceStateChanged(ProfileService profile, int state) {
if (state != BluetoothAdapter.STATE_ON && state != BluetoothAdapter.STATE_OFF) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(BluetoothAdapter.nameForState(state));
}
Message m = mHandler.obtainMessage(MESSAGE_PROFILE_SERVICE_STATE_CHANGED);
m.obj = profile;
m.arg1 = state;
mHandler.sendMessage(m);
}private void processProfileServiceStateChanged(ProfileService profile, int state) {
switch (state) {
case BluetoothAdapter.STATE_ON:
if (!mRegisteredProfiles.contains(profile)) {
Log.e(TAG, profile.getName() + " not registered (STATE_ON).");
return;
}
if (mRunningProfiles.contains(profile)) {
Log.e(TAG, profile.getName() + " already running.");
return;
}
mRunningProfiles.add(profile);
if (GattService.class.getSimpleName().equals(profile.getName())) {
Log.e(TAG, "processProfileServiceStateChanged enableNative");
// 这个地方就是调用libjni.so的方法,通过jni native调用
enableNative();
} else if (mRegisteredProfiles.size() == Config.getSupportedProfiles().length
&& mRegisteredProfiles.size() == mRunningProfiles.size()) {
mAdapterProperties.onBluetoothReady();
updateUuids();
setBluetoothClassFromConfig();
initProfileServices();
getAdapterPropertyNative(AbstractionLayer.BT_PROPERTY_LOCAL_IO_CAPS);
getAdapterPropertyNative(AbstractionLayer.BT_PROPERTY_LOCAL_IO_CAPS_BLE);
mAdapterStateMachine.sendMessage(AdapterState.BREDR_STARTED);
}
break;
default:
Log.e(TAG, "Unhandled profile state: " + state);
}
}NOTED:能够直接调用到libbluetooth_jni.so的原因是AdapterApp 类在启动的时候加载了
public class AdapterApp extends Application
{
private static final String TAG = "BluetoothAdapterApp";
private static final boolean DBG = false;
//For Debugging only
private static int sRefCount = 0;
static {
if (DBG) {
Log.d(TAG, "Loading JNI Library");
}
System.loadLibrary("bluetooth_jni");
}
...
}然后这个动作会触发com_android_bluetooth_btservice_adapterService.cpp中的
jint JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM* jvm, void* reserved) {
JNIEnv* e;
int status;
ALOGE("Bluetooth Adapter Service : loading JNI\n");
ALOGV("Bluetooth Adapter Service : loading JNI\n");
// Check JNI version
if (jvm->GetEnv((void**)&e, JNI_VERSION_1_6)) {
ALOGE("JNI version mismatch error");
return JNI_ERR;
}
status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_btservice_AdapterService(e);
if (status < 0) {
ALOGE("jni adapter service registration failure, status: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
status =
android::register_com_android_bluetooth_btservice_BluetoothKeystore(e);
if (status < 0) {
ALOGE("jni BluetoothKeyStore registration failure: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_hfp(e);
if (status < 0) {
ALOGE("jni hfp registration failure, status: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_hfpclient(e);
if (status < 0) {
ALOGE("jni hfp client registration failure, status: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_a2dp(e);
if (status < 0) {
ALOGE("jni a2dp source registration failure: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_a2dp_sink(e);
if (status < 0) {
ALOGE("jni a2dp sink registration failure: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_avrcp_target(e);
if (status < 0) {
ALOGE("jni new avrcp target registration failure: %d", status);
}
status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_avrcp_controller(e);
if (status < 0) {
ALOGE("jni avrcp controller registration failure: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_hid_host(e);
if (status < 0) {
ALOGE("jni hid registration failure: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_hid_device(e);
if (status < 0) {
ALOGE("jni hidd registration failure: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_pan(e);
if (status < 0) {
ALOGE("jni pan registration failure: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_gatt(e);
if (status < 0) {
ALOGE("jni gatt registration failure: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_sdp(e);
if (status < 0) {
ALOGE("jni sdp registration failure: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
status = android::register_com_android_bluetooth_hearing_aid(e);
if (status < 0) {
ALOGE("jni hearing aid registration failure: %d", status);
return JNI_ERR;
}
return JNI_VERSION_1_6;
}
步骤6:bluetooth jni的enableNative处理
static jboolean enableNative(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj) {
ALOGV("%s", __func__);
if (!sBluetoothInterface) return JNI_FALSE;
int ret = sBluetoothInterface->enable();
return (ret == BT_STATUS_SUCCESS || ret == BT_STATUS_DONE) ? JNI_TRUE
: JNI_FALSE;
}其中sBluetoothInterface 是hal接口,定义如下:
typedef struct {
/** set to sizeof(bt_interface_t) */
size_t size;
/**
* Opens the interface and provides the callback routines
* to the implemenation of this interface.
* The |is_atv| flag indicates whether the local device is an Android TV
*/
int (*init)(bt_callbacks_t* callbacks, bool is_atv);
/** Enable Bluetooth. */
int (*enable)(bool guest_mode);
/** Disable Bluetooth. */
int (*disable)(void);
/** Closes the interface. */
void (*cleanup)(void);
/** Get all Bluetooth Adapter properties at init */
int (*get_adapter_properties)(void);
/** Get Bluetooth Adapter property of 'type' */
int (*get_adapter_property)(bt_property_type_t type);
/** Set Bluetooth Adapter property of 'type' */
/* Based on the type, val shall be one of
* RawAddress or bt_bdname_t or bt_scanmode_t etc
*/
int (*set_adapter_property)(const bt_property_t *property);
/** Get all Remote Device properties */
int (*get_remote_device_properties)(RawAddress *remote_addr);
/** Get Remote Device property of 'type' */
int (*get_remote_device_property)(RawAddress *remote_addr,
bt_property_type_t type);
/** Set Remote Device property of 'type' */
int (*set_remote_device_property)(RawAddress *remote_addr,
const bt_property_t *property);
/** Get Remote Device's service record for the given UUID */
int (*get_remote_service_record)(const RawAddress& remote_addr,
const bluetooth::Uuid& uuid);
/** Start SDP to get remote services */
int (*get_remote_services)(RawAddress *remote_addr);
/** Start Discovery */
int (*start_discovery)(void);
/** Cancel Discovery */
int (*cancel_discovery)(void);
/** Create Bluetooth Bonding */
int (*create_bond)(const RawAddress *bd_addr, int transport);
/** Create Bluetooth Bond using out of band data */
int (*create_bond_out_of_band)(const RawAddress *bd_addr, int transport,
const bt_out_of_band_data_t *oob_data);
/** Remove Bond */
int (*remove_bond)(const RawAddress *bd_addr);
/** Cancel Bond */
int (*cancel_bond)(const RawAddress *bd_addr);
/**
* Get the connection status for a given remote device.
* return value of 0 means the device is not connected,
* non-zero return status indicates an active connection.
*/
int (*get_connection_state)(const RawAddress *bd_addr);
/** BT Legacy PinKey Reply */
/** If accept==FALSE, then pin_len and pin_code shall be 0x0 */
int (*pin_reply)(const RawAddress *bd_addr, uint8_t accept,
uint8_t pin_len, bt_pin_code_t *pin_code);
/** BT SSP Reply - Just Works, Numeric Comparison and Passkey
* passkey shall be zero for BT_SSP_VARIANT_PASSKEY_COMPARISON &
* BT_SSP_VARIANT_CONSENT
* For BT_SSP_VARIANT_PASSKEY_ENTRY, if accept==FALSE, then passkey
* shall be zero */
int (*ssp_reply)(const RawAddress *bd_addr, bt_ssp_variant_t variant,
uint8_t accept, uint32_t passkey);
/** Get Bluetooth profile interface */
const void* (*get_profile_interface) (const char *profile_id);
/** Bluetooth Test Mode APIs - Bluetooth must be enabled for these APIs */
/* Configure DUT Mode - Use this mode to enter/exit DUT mode */
int (*dut_mode_configure)(uint8_t enable);
/* Send any test HCI (vendor-specific) command to the controller. Must be in DUT Mode */
int (*dut_mode_send)(uint16_t opcode, uint8_t *buf, uint8_t len);
/** BLE Test Mode APIs */
/* opcode MUST be one of: LE_Receiver_Test, LE_Transmitter_Test, LE_Test_End */
int (*le_test_mode)(uint16_t opcode, uint8_t *buf, uint8_t len);
/** Sets the OS call-out functions that bluedroid needs for alarms and wake locks.
* This should be called immediately after a successful |init|.
*/
int (*set_os_callouts)(bt_os_callouts_t *callouts);
/** Read Energy info details - return value indicates BT_STATUS_SUCCESS or BT_STATUS_NOT_READY
* Success indicates that the VSC command was sent to controller
*/
int (*read_energy_info)();
/**
* Native support for dumpsys function
* Function is synchronous and |fd| is owned by caller.
* |arguments| are arguments which may affect the output, encoded as
* UTF-8 strings.
*/
void (*dump)(int fd, const char **arguments);
/**
* Clear /data/misc/bt_config.conf and erase all stored connections
*/
int (*config_clear)(void);
/**
* Clear (reset) the dynamic portion of the device interoperability database.
*/
void (*interop_database_clear)(void);
/**
* Add a new device interoperability workaround for a remote device whose
* first |len| bytes of the its device address match |addr|.
* NOTE: |feature| has to match an item defined in interop_feature_t (interop.h).
*/
void (*interop_database_add)(uint16_t feature, const RawAddress *addr, size_t len);
} bt_interface_t;这个enable是调用libbluetooth.so中的enable,也就是bluedroid bluetooth.cc或者android8之前的bluetooth.c
static int enable() {
if (!interface_ready()) return BT_STATUS_NOT_READY;
stack_manager_get_interface()->start_up_stack_async();
return BT_STATUS_SUCCESS;
}然后就是走bluedroid流程了,host的初始化流程可以看我协议栈的其他文章
步骤7:底层bluedroid enable成功后回调处理
bluedroid底层enable跟controller交互成功后,调用这个函数,通过HAL_CBACK回调到bt service apk的jni
static void event_signal_stack_up(UNUSED_ATTR void* context) {
// Notify BTIF connect queue that we've brought up the stack. It's
// now time to dispatch all the pending profile connect requests.
btif_queue_connect_next();
HAL_CBACK(bt_hal_cbacks, adapter_state_changed_cb, BT_STATE_ON);
}思考:为什么能调用到callback呢?
是因为adapterService 服务启动的时候调用到onCreate方法,里面有
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
debugLog("onCreate()");
...
// 调用jni的方法
initNative(isGuest(), isNiapMode(), configCompareResult, isAtvDevice);
...
}static bool initNative(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj, jboolean isGuest,
jboolean isNiapMode, int configCompareResult,
jboolean isAtvDevice) {
ALOGV("%s", __func__);
// 注册jni的callback到bluedroid,bluedroid有回调的时候回调用到sBluetoothCallbacks
int ret = sBluetoothInterface->init(
&sBluetoothCallbacks, isGuest == JNI_TRUE ? 1 : 0,
isNiapMode == JNI_TRUE ? 1 : 0, configCompareResult,
isAtvDevice == JNI_TRUE ? 1 : 0);
if (ret != BT_STATUS_SUCCESS) {
ALOGE("Error while setting the callbacks: %d\n", ret);
sBluetoothInterface = NULL;
return JNI_FALSE;
}
}好了,回归会提,如果bluedroid enable成功后,会调用到sBluetoothCallbacks的adapter_state_change_callback函数
static void adapter_state_change_callback(bt_state_t status) {
ALOGE("Bluetooth adapter_state_change_callback:%d\n",status);
CallbackEnv sCallbackEnv(__func__);
if (!sCallbackEnv.valid()) return;
ALOGV("%s: Status is: %d", __func__, status);
// 通过jni的回调方法调用到AdapterService的stateChangeCallback
sCallbackEnv->CallVoidMethod(sJniCallbacksObj, method_stateChangeCallback,
(jint)status);
}步骤8:bt service的处理enable成功后的回调过程
void stateChangeCallback(int status) {
Log.e(TAG, "stateChangeCallback:"+status);
if (status == AbstractionLayer.BT_STATE_OFF) {
debugLog("stateChangeCallback: disableNative() completed");
mAdapterStateMachine.sendMessage(AdapterState.BLE_STOPPED);
} else if (status == AbstractionLayer.BT_STATE_ON) {
mAdapterStateMachine.sendMessage(AdapterState.BLE_STARTED);
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "Incorrect status " + status + " in stateChangeCallback");
}
}此时进入这个类中的processMessage处理
public boolean processMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case BLE_STARTED:
transitionTo(mBleOnState);
break;
case BLE_START_TIMEOUT:
errorLog(messageString(msg.what));
transitionTo(mTurningBleOffState);
break;
default:
infoLog("Unhandled message - " + messageString(msg.what));
return false;
}
return true;
}迁徙到mBleOnState状态,然后处理,另外状态概念,会触发AdapterService.java中的updateAdapterState
void updateAdapterState(int prevState, int newState) {
mAdapterProperties.setState(newState);
invalidateBluetoothGetStateCache();
if (mCallbacks != null) {
int n = mCallbacks.beginBroadcast();
debugLog("updateAdapterState() - Broadcasting state " + BluetoothAdapter.nameForState(
newState) + " to " + n + " receivers.");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
try {
mCallbacks.getBroadcastItem(i).onBluetoothStateChange(prevState, newState);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
debugLog("updateAdapterState() - Callback #" + i + " failed (" + e + ")");
}
}
mCallbacks.finishBroadcast();
}
....
}private final IBluetoothCallback mBluetoothCallback = new IBluetoothCallback.Stub() {
@Override
public void onBluetoothStateChange(int prevState, int newState) throws RemoteException {
Message msg =
mHandler.obtainMessage(MESSAGE_BLUETOOTH_STATE_CHANGE, prevState, newState);
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
};case处理
case MESSAGE_BLUETOOTH_STATE_CHANGE: {
....
bluetoothStateChangeHandler(prevState, newState);
break;
}private void bluetoothStateChangeHandler(int prevState, int newState) {
if (newState == BluetoothAdapter.STATE_BLE_ON || newState == BluetoothAdapter.STATE_OFF) {
.......
continueFromBleOnState();
}
}private void continueFromBleOnState() {
...
mBluetooth.onLeServiceUp();
...
}public void onLeServiceUp() {
AdapterService service = getService();
if (service == null || !callerIsSystemOrActiveUser(TAG, "onLeServiceUp")) {
return;
}
enforceBluetoothPrivilegedPermission(service);
service.mAdapterStateMachine.sendMessage(AdapterState.USER_TURN_ON);
}private class BleOnState extends BaseAdapterState {
@Override
int getStateValue() {
return BluetoothAdapter.STATE_BLE_ON;
}
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case USER_TURN_ON:
transitionTo(mTurningOnState);
break;
case BLE_TURN_OFF:
transitionTo(mTurningBleOffState);
break;
default:
infoLog("Unhandled message - " + messageString(msg.what));
return false;
}
return true;
}
}然后进入到TurningOnState class的enter处理
public void enter() {
super.enter();
sendMessageDelayed(BREDR_START_TIMEOUT, BREDR_START_TIMEOUT_DELAY);
mAdapterService.startProfileServices();
}步骤9:开启所有profile的service
void startProfileServices() {
...
setAllProfileServiceStates(supportedProfileServices, BluetoothAdapter.STATE_ON);
}private static final ProfileConfig[] PROFILE_SERVICES_AND_FLAGS = {
new ProfileConfig(HeadsetService.class, R.bool.profile_supported_hs_hfp,
(1 << BluetoothProfile.HEADSET)),
new ProfileConfig(A2dpService.class, R.bool.profile_supported_a2dp,
(1 << BluetoothProfile.A2DP)),
new ProfileConfig(A2dpSinkService.class, R.bool.profile_supported_a2dp_sink,
(1 << BluetoothProfile.A2DP_SINK)),
new ProfileConfig(HidHostService.class, R.bool.profile_supported_hid_host,
(1 << BluetoothProfile.HID_HOST)),
new ProfileConfig(PanService.class, R.bool.profile_supported_pan,
(1 << BluetoothProfile.PAN)),
new ProfileConfig(GattService.class, R.bool.profile_supported_gatt,
(1 << BluetoothProfile.GATT)),
new ProfileConfig(BluetoothMapService.class, R.bool.profile_supported_map,
(1 << BluetoothProfile.MAP)),
new ProfileConfig(HeadsetClientService.class, R.bool.profile_supported_hfpclient,
(1 << BluetoothProfile.HEADSET_CLIENT)),
new ProfileConfig(AvrcpTargetService.class, R.bool.profile_supported_avrcp_target,
(1 << BluetoothProfile.AVRCP)),
new ProfileConfig(AvrcpControllerService.class,
R.bool.profile_supported_avrcp_controller,
(1 << BluetoothProfile.AVRCP_CONTROLLER)),
new ProfileConfig(SapService.class, R.bool.profile_supported_sap,
(1 << BluetoothProfile.SAP)),
new ProfileConfig(PbapClientService.class, R.bool.profile_supported_pbapclient,
(1 << BluetoothProfile.PBAP_CLIENT)),
new ProfileConfig(MapClientService.class, R.bool.profile_supported_mapmce,
(1 << BluetoothProfile.MAP_CLIENT)),
new ProfileConfig(HidDeviceService.class, R.bool.profile_supported_hid_device,
(1 << BluetoothProfile.HID_DEVICE)),
new ProfileConfig(BluetoothOppService.class, R.bool.profile_supported_opp,
(1 << BluetoothProfile.OPP)),
new ProfileConfig(BluetoothPbapService.class, R.bool.profile_supported_pbap,
(1 << BluetoothProfile.PBAP)),
new ProfileConfig(HearingAidService.class,
com.android.internal.R.bool.config_hearing_aid_profile_supported,
(1 << BluetoothProfile.HEARING_AID))
};因为我们之前在前面说过,开启成功后就会调用profileService change的消息,所以如下
private void processProfileServiceStateChanged(ProfileService profile, int state) {
switch (state) {
case BluetoothAdapter.STATE_ON:
........
if (GattService.class.getSimpleName().equals(profile.getName())) {
enableNative();
} else if (mRegisteredProfiles.size() == Config.getSupportedProfiles().length
&& mRegisteredProfiles.size() == mRunningProfiles.size()) { //所有ProfileService都启动完毕
.......
mAdapterStateMachine.sendMessage(AdapterState.BREDR_STARTED);
}
break;public boolean processMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case BREDR_STARTED:
transitionTo(mOnState);
break;
}
return true;
}private void bluetoothStateChangeHandler(int prevState, int newState) {
...
sendBluetoothStateCallback(isUp); //广播发出数据
sendBleStateChanged(prevState, newState);
...
}
开放原子开发者工作坊旨在鼓励更多人参与开源活动,与志同道合的开发者们相互交流开发经验、分享开发心得、获取前沿技术趋势。工作坊有多种形式的开发者活动,如meetup、训练营等,主打技术交流,干货满满,真诚地邀请各位开发者共同参与!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献42条内容
已为社区贡献42条内容





所有评论(0)