Antd Table 分页条件下的动态数据合并单元格
本文介绍 Ant Design Vue 的 a-table 表格组件如何在分页条件下的对动态数据合并单元格。我们希望进行行合并,即将相同日期和相同店铺列的行单元格分别进行行合并。由于数据量可能会很大,因此需要进行分页处理。**在分页情况下,我们进行的行合并其实只需要考虑这一页的记录即可,也就是将这一页的所有记录中相同日期和相同店铺列的行单元格分别进行行合并。**
文章目录
Antd Table 分页条件下的动态数据合并单元格
本文介绍 Ant Design Vue 的 a-table 表格组件 如何在分页条件下的对动态数据合并单元格。
1.表格组件 API
1.1 Table
| 参数 | 说明 | 类型 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| bordered | 是否展示外边框和列边框 | boolean | false |
| columns | 表格列的配置描述 | array | - |
| dataSource | 数据数组 | any[] | |
| pagination | 分页器,参考配置项或 pagination文档,设为 false 时不展示和进行分页 | object |
1.2 事件
| 事件名称 | 说明 | 回调参数 |
|---|---|---|
| change | 分页、排序、筛选变化时触发 | Function(pagination, filters, sorter, { currentDataSource }) |
1.3 Column
列描述数据对象,是 columns 中的一项,Column 使用相同的 API。
| 参数 | 说明 | 类型 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| colSpan | 表头列合并,设置为 0 时,不渲染 | number | |
| dataIndex | 列数据在数据项中对应的 key,支持 a.b.c 的嵌套写法 | string | - |
| title | 列头显示文字 | string|slot | - |
| customRender | 生成复杂数据的渲染函数,参数分别为当前行的值、当前行数据、行索引,@return 里面可以设置表格行/列合并,可参考 demo 表格行/列合并 | Function(text, record, index) {}|slot-scope | - |
1.4 pagination
分页的配置项。
| 参数 | 说明 | 类型 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| position | 指定分页显示的位置 | ‘top’ | ‘bottom’ | ‘both’ | ‘bottom’ |
1.5 表格行/列合并
- 表头只支持列合并,使用 column 里的 colSpan 进行设置。
- 表格支持行/列合并,使用 render 里的单元格属性 colSpan 或者 rowSpan 设值为
0时,设置的表格不会渲染。
2.基础环境搭建
这里我们以 vue2 环境为例进行演示。
创建 vue2 项目:
vue create antd-demo
安装 axios:
npm install axios
安装 ant-design-vue:
# 注意这里需要指定版本,因为最新版本与 vue2 不兼容,是面向 vue3 的
npm i --save ant-design-vue@1.7.2
找到 vue.config.js 文件,将 module.exports 中的配置属性 lintOnSave 的值设置为 false,关闭 eslint 的严格语法检测。
找到 main.js 文件,修改内容如下:
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import Antd from 'ant-design-vue';
// 注意:如果使用的 vue3,则应该引入 reset.css 而不是 antd.css
import 'ant-design-vue/dist/antd.css';
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.use(Antd);
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
3.案例背景
我们将以一个商品采购信息的展示为例。需要注意,在同一天有多条采购记录,在一条采购记录中可能存在对不同店铺的采购。
从后端发送请求获取的 JSON 数据的数据结构是一个数组,包含多个对象。每个对象代表一条的采购记录,包含以下字段:
date:字符串类型,表示记录的日期。storeList:数组类型,包含多个店铺的采购信息。
每个店铺的采购信息是一个对象,包含以下字段:
storeName:字符串类型,表示店铺的名称。productList:数组类型,包含多个商品的采购信息。
每个商品的采购信息是一个对象,包含以下字段:
productName:字符串类型,表示商品的名称。count:整数类型,表示该商品的采购数量。
在商品采购案例中,这个数据格式可以用于记录不同日期、不同店铺和不同商品的采购数量,便于进行库存管理和数据分析。例如,可以通过这个数据格式了解到旗舰店在 2024-10-14 这一天采购了哪些商品,各商品的数量是多少,以及分店 1 在同一天的采购情况。同样,也可以了解到 2024-10-15 这一天的采购情况。
为了简单期间,我们将需要从后端发送请求获取的 JSON 数据直接从本地文件获取,存放在 public 目录下的 data.json 新建文件中。以下示例数据你值得一看,更直观理清这个数据结构。
[
{
"date": "2024-10-14",
"storeList": [
{
"storeName": "旗舰店",
"productList": [
{
"productName": "商品A",
"count": 150
},
{
"productName": "商品B",
"count": 200
},
{
"productName": "商品C",
"count": 250
},
{
"productName": "商品D",
"count": 300
},
{
"productName": "商品E",
"count": 350
}
]
},
{
"storeName": "分店1",
"productList": [
{
"productName": "商品F",
"count": 100
},
{
"productName": "商品G",
"count": 250
},
{
"productName": "商品H",
"count": 200
},
{
"productName": "商品I",
"count": 150
},
{
"productName": "商品J",
"count": 300
}
]
}
]
},
{
"date": "2024-10-15",
"storeList": [
{
"storeName": "旗舰店",
"productList": [
{
"productName": "商品K",
"count": 400
},
{
"productName": "商品L",
"count": 450
},
{
"productName": "商品M",
"count": 500
},
{
"productName": "商品N",
"count": 550
},
{
"productName": "商品O",
"count": 600
}
]
},
{
"storeName": "分店2",
"productList": [
{
"productName": "商品P",
"count": 320
},
{
"productName": "商品Q",
"count": 220
},
{
"productName": "商品R",
"count": 210
},
{
"productName": "商品S",
"count": 120
},
{
"productName": "商品T",
"count": 420
}
]
}
]
},
{
"date": "2024-10-15",
"storeList": [
{
"storeName": "生活小超市",
"productList": [
{
"productName": "商品U",
"count": 400
},
{
"productName": "商品V",
"count": 450
},
{
"productName": "商品W",
"count": 500
}
]
},
{
"storeName": "分店3",
"productList": [
{
"productName": "商品X",
"count": 320
},
{
"productName": "商品Y",
"count": 220
},
{
"productName": "商品Z",
"count": 210
}
]
}
]
}
]
4.需要分析
将采购信息以表格且分页的形式进行展示,进行分页的原因是从后端得到的数据量可能比较大。
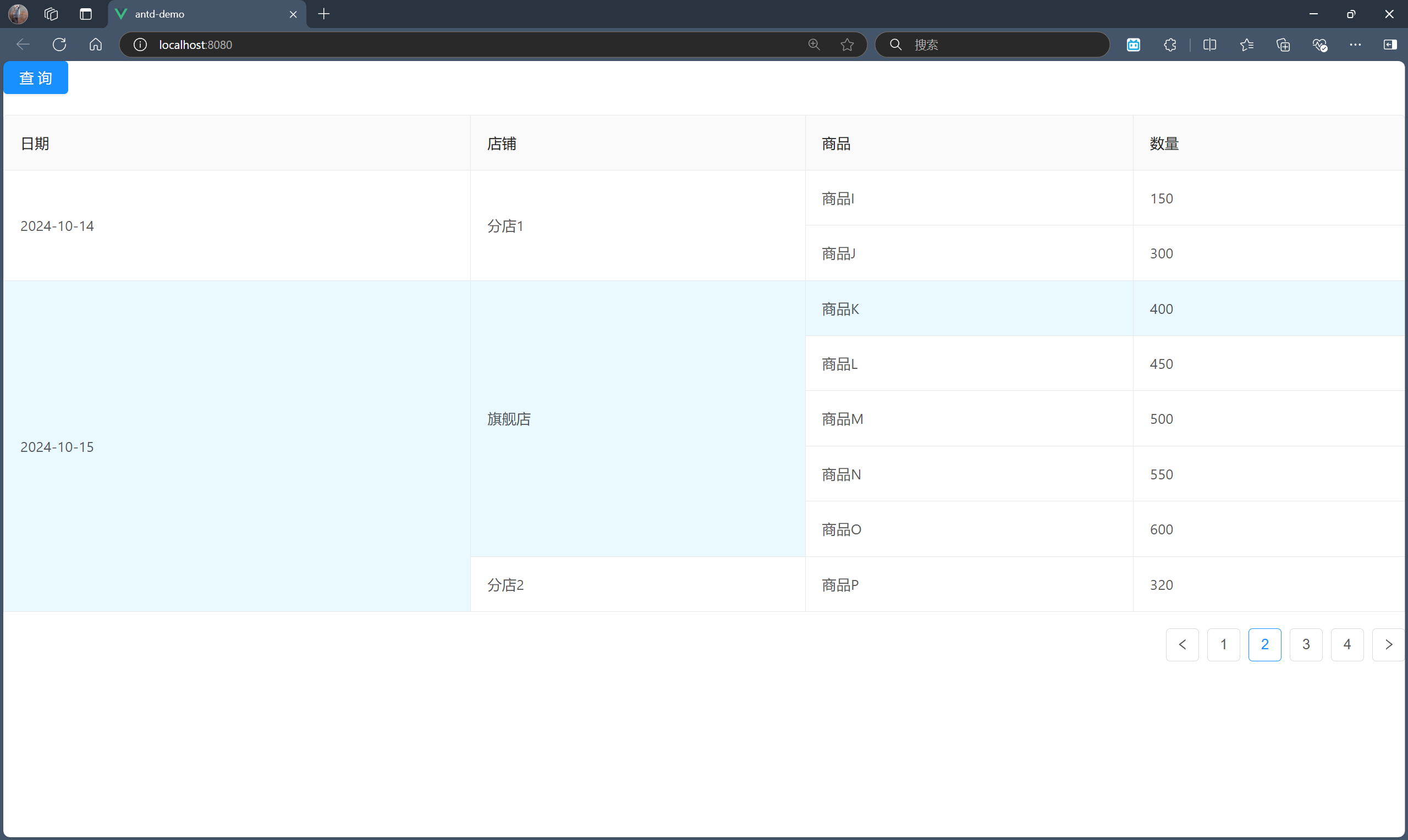
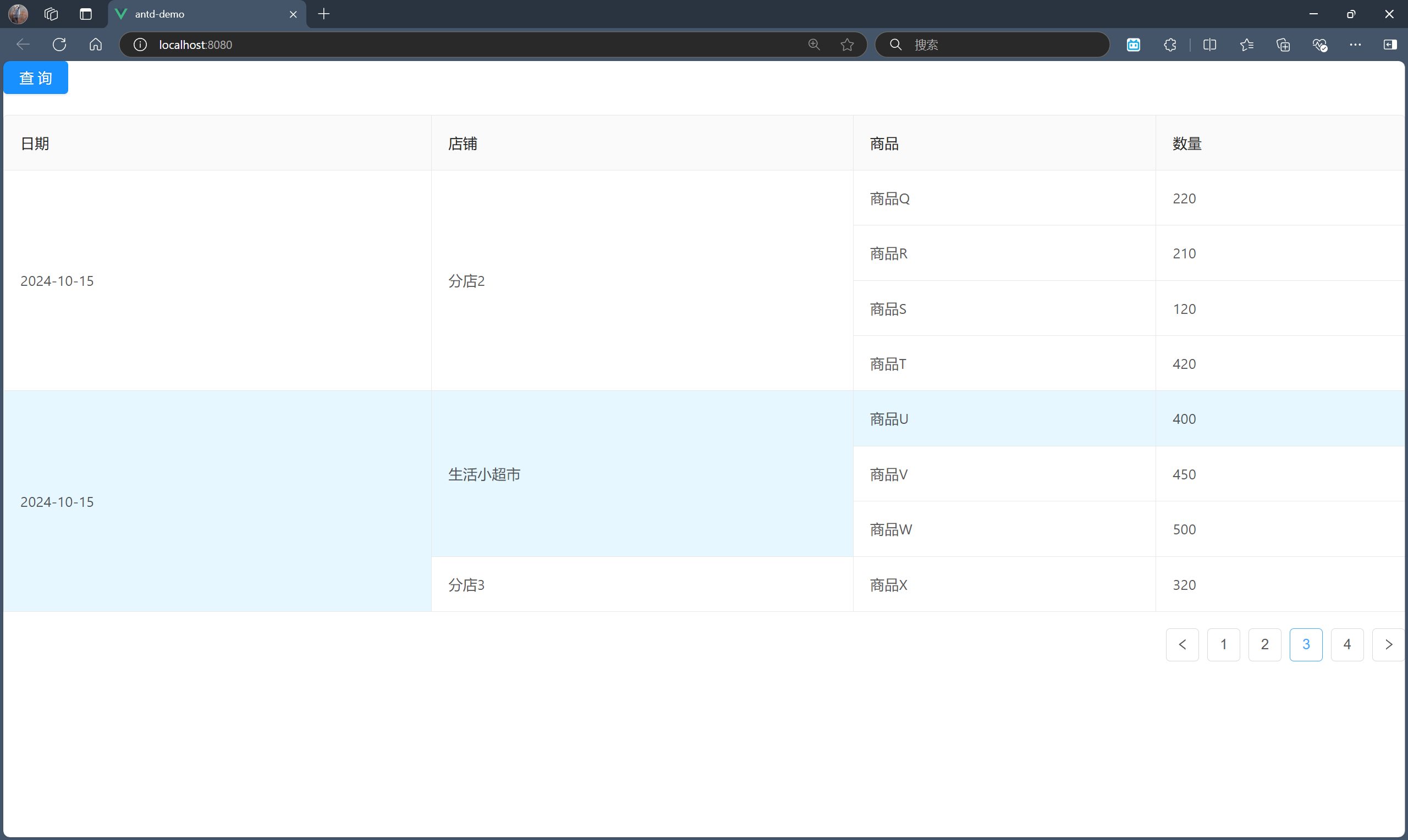
我们希望进行行合并,即将日期列的同一条记录下的行单元格进行合并,将店铺列的同一条记录下的同一店铺的行单元格进行行合并。
在分页情况下,我们其实只需要考虑对这一页的记录进行行合并分析即可。也就是说,将这一页记录的日期列的同一条记录下的行单元格进行合并,将这一页记录的店铺列的同一条记录下的同一店铺的行单元格进行行合并。
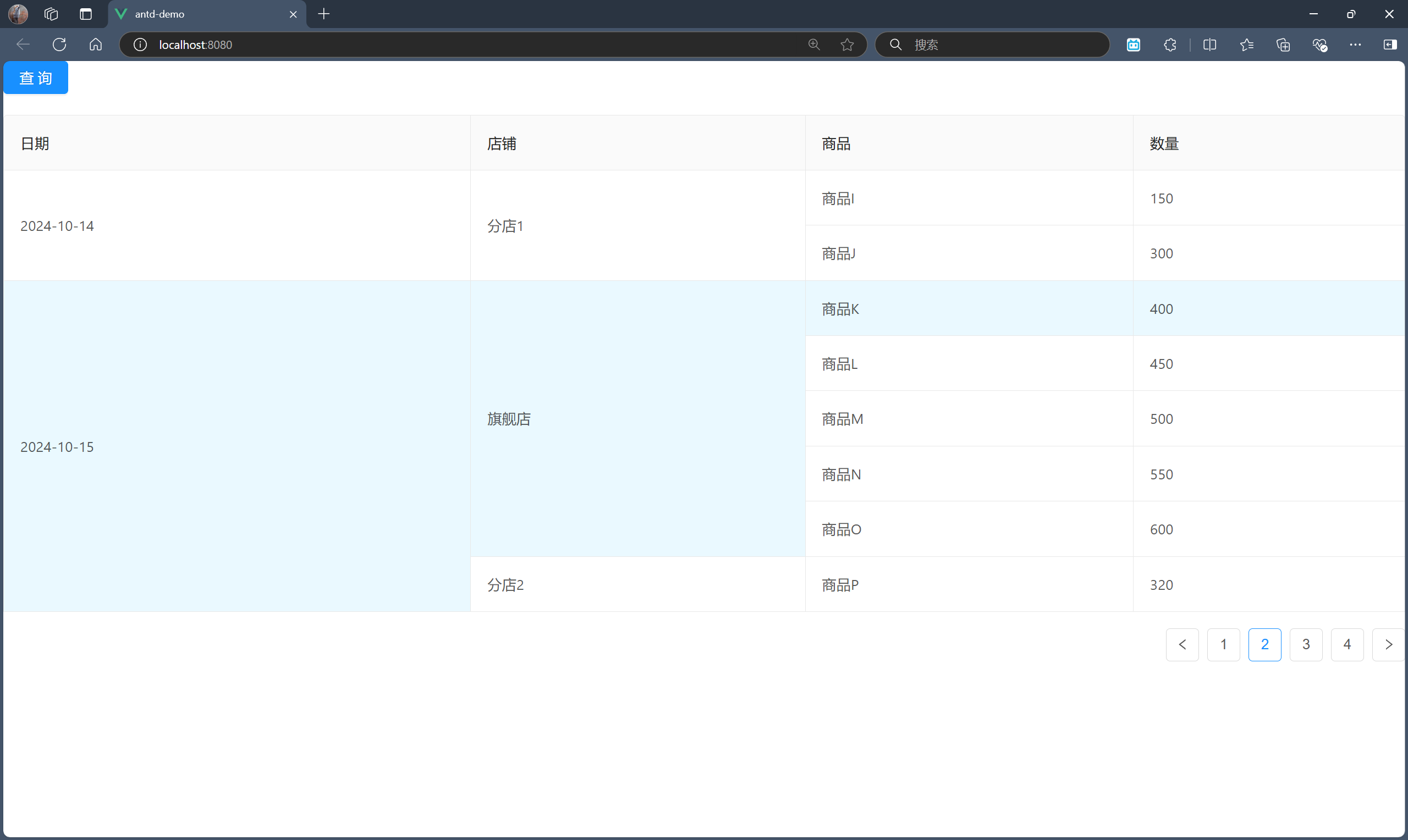
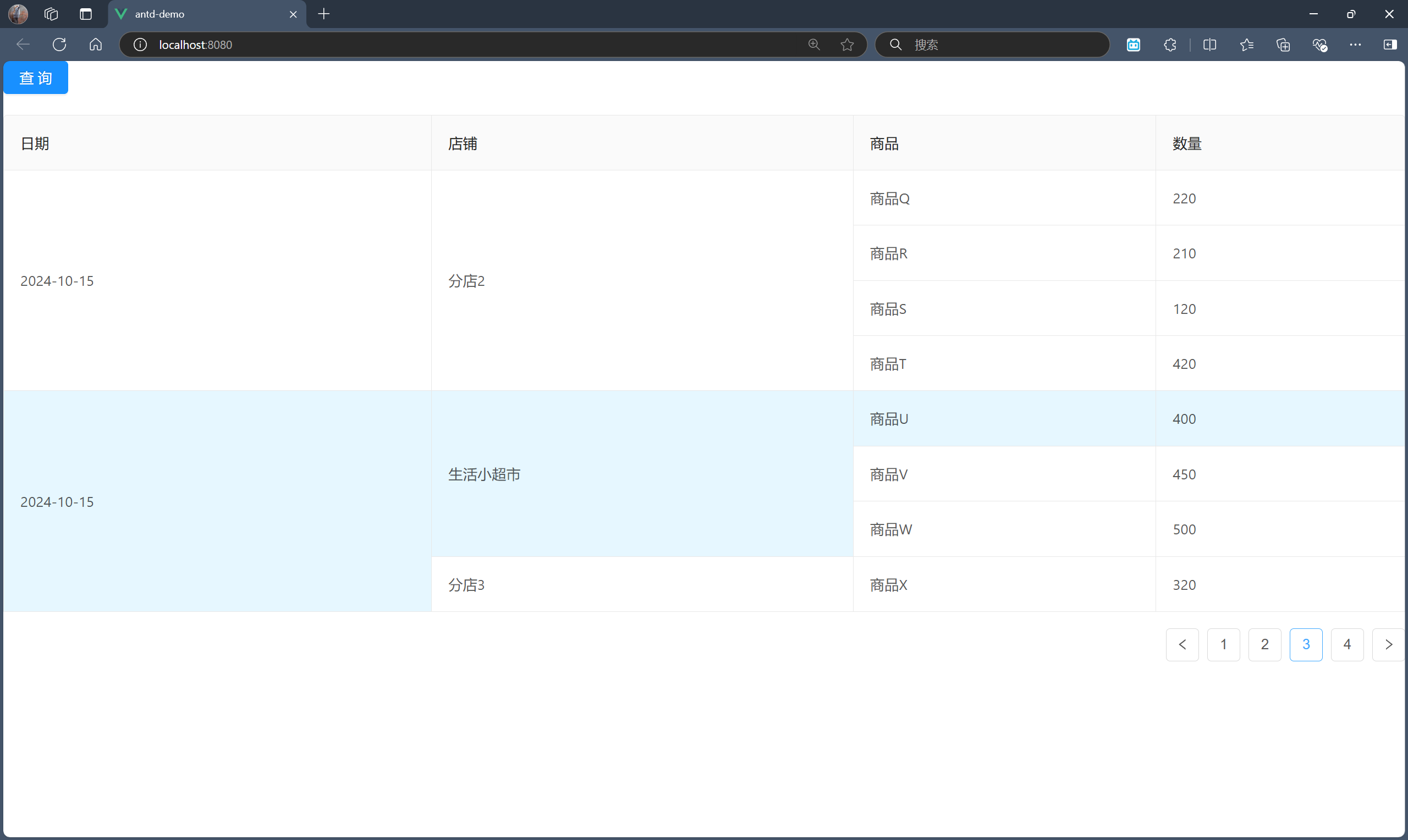
最终效果如下:
5.需求实现
我们接下来所有的代码都是在 App.vue 文件中来实现,就不新建组件了。
步骤一:数据平面化
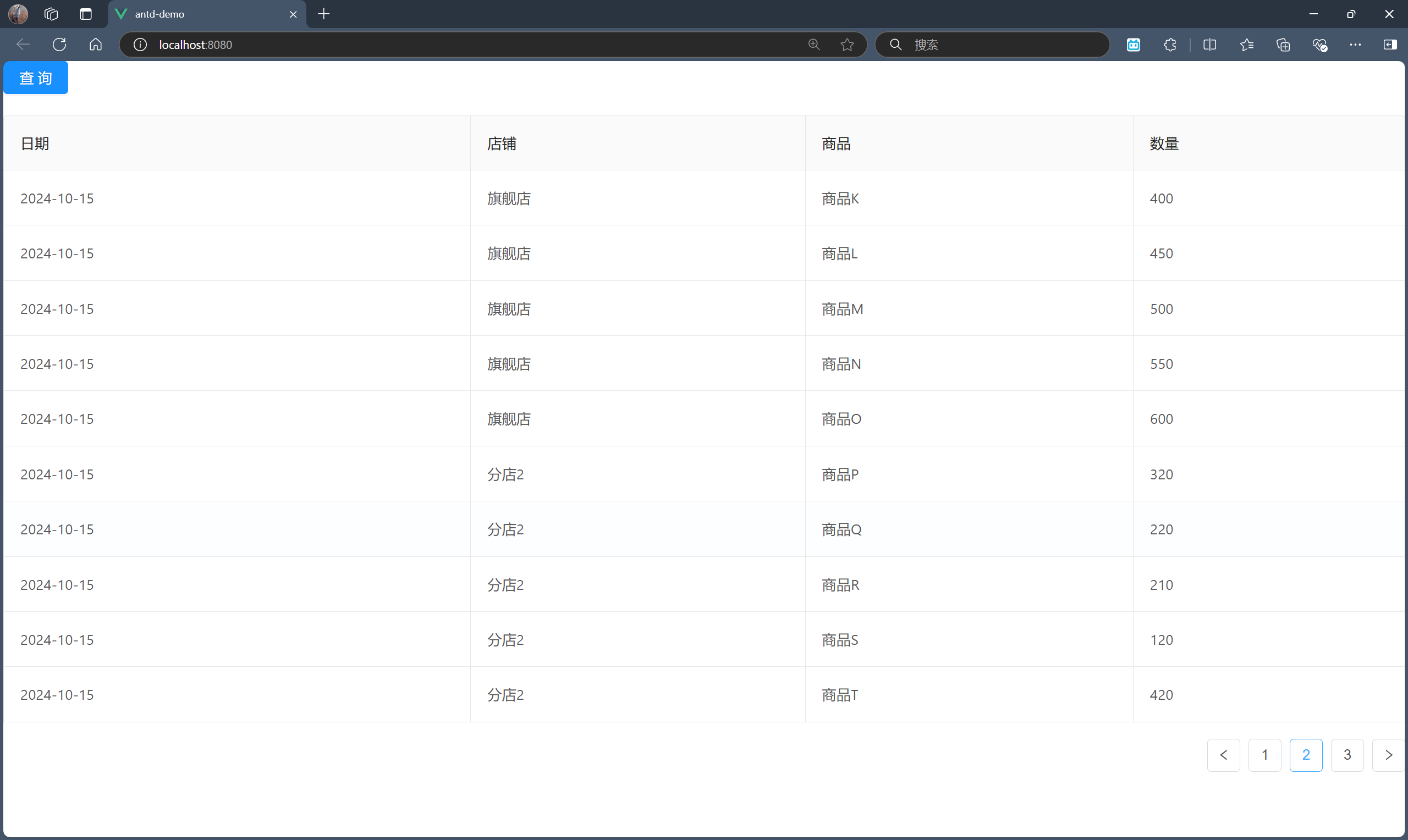
我觉得在一开始,我们需要做的是能将铺平后的每一行先显示出来,铺平是指将从后端请求到的树形结构的数据平面化展开,而不先去考虑如何合并。实现需求的过程应当是从简单到复杂,逐渐完善要求与规则。
过程如下:
- 获取采购商品信息。模拟向后端发送请求,实际是从本地 public/data.json 下拿数据。
- 清空上一次查询保存在本地数据 dataInfo 的数据。
- 将这一次查询到的数据平面化后,加入到 dataInfo 中。并记录好每一层的索引 Id,作为合并标识。
- 将 dataInfo 作为数据源提供给
a-table组件,即设置:data-source="dataInfo"。
<template>
<div>
<a-button type="primary" style="margin-bottom: 20px;" @click="getDataInfo">
查询
</a-button>
<!-- 4.将 dataInfo 作为数据源提供给 `a-table` 组件,即设置 `:data-source="dataInfo"`。 -->
<a-table :columns="columns" :data-source="dataInfo" bordered>
</a-table>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from 'axios';
export default {
data() {
const columns = [
{
title: '日期',
dataIndex: 'dateStr',
customRender: (text, row, index) => {
return {
children: text,
attrs: {
rowSpan: 1,
},
};
},
},
{
title: '店铺',
dataIndex: 'storeName',
customRender: (text, row, index) => {
return {
children: text,
attrs: {
rowSpan: 1,
},
};
},
},
{
title: '商品',
dataIndex: 'productName',
customRender: (text, row, index) => {
return {
children: text,
attrs: {
rowSpan: 1,
},
};
},
},
{
title: '数量',
dataIndex: 'productCount',
customRender: (text, row, index) => {
return {
children: text,
attrs: {
rowSpan: 1,
},
};
},
},
];
return {
columns,
dataInfo: []
};
},
methods: {
// 1.获取采购商品信息
getDataInfo() {
// 模拟向后端发送请求,实际是从本地 public/data.json 下拿数据
axios.get('/data.json')
.then(response => {
let info = response.data;
// 2.清空上一次查询保存在本地数据 dataInfo 的数据。
this.dataInfo = [];
// 3.将这一次查询到的数据「平面化/铺平/展开」后,加入到 dataInfo 中。并记录好每一层的索引 Id,作为合并标识。
info.forEach((record, recordId) => {
record.storeList.forEach((store, storeId) => {
store.productList.forEach((product, productId) => {
let row = {
recordId,
dateStr: record.date,
storeId,
storeName: store.storeName,
productId,
productName: product.productName,
productCount: product.count
}
this.dataInfo.push(row);
})
})
})
console.log("dataInfo", this.dataInfo)
})
.catch(error => {
console.error("Error loading the data.json file:", error);
});
}
}
};
</script>
npm run serve 启动服务,点击“查询”按钮,查看效果。
步骤二:合并日期列的同一记录下的行单元格
在分页情况下,我们其实只需要考虑对这一页的记录进行行合并分析即可。也就是说,将这一页记录的日期列的同一条记录下的行单元格进行合并,将这一页记录的店铺列的同一条记录下的同一店铺的行单元格进行行合并。
同时,考虑到可能有些页我们可能并不会使用到与数据量可能过大,如果一开始就一次性对所有数据的合并行数进行设置,可能会造成不必要的资源浪费,因此我在这里选择「懒加载」的方式,即当用户点击页码时才会触发对应页的合并行数设置。
如果你每次请求获取到的数据并不多,或者几乎所有页用户都需要查询,则可以在一开始就一次性对所有数据设置好行合并数。
🤔 这里面临几个问题需要解决。
第一个问题,当用户点击页码时,如何确认该页的记录有哪些呢?
例如 dataInfo[] 数组中一共有 26 条数据,每页大小为 8 条,那么:
- 第 1 1 1 页对应 dataInfo[] 数组索引应该为 [ 0 , 7 ] [0, 7] [0,7],即 [ 0 , 8 ) [0, 8) [0,8) 的左闭右开区间。
- 第 2 2 2 页对应 dataInfo[] 数组索引应该为 [ 8 , 15 ] [8, 15] [8,15],即 [ 8 , 16 ) [8, 16) [8,16) 的左闭右开区间。
- 第 3 3 3 页对应 dataInfo[] 数组索引应该为 [ 16 , 23 ] [16, 23] [16,23],即 [ 16 , 24 ) [16, 24) [16,24) 的左闭右开区间。
- 第 4 4 4 页对应 dataInfo[] 数组索引应该为 [ 24 , 25 ] [24, 25] [24,25],即 [ 24 , 26 ) [24, 26) [24,26) 的左闭右开区间。
其实我们从上不难看出分页算法的规律,抽象一下数据,假设每页大小为 p a g e S i z e pageSize pageSize,用户当前点击第 c u r r e n t P a g e currentPage currentPage 页,那么对应 dataInfo[] 数组索引应该为 [ ( c u r r e n t P a g e − 1 ) × p a g e S i z e , c u r r e n t P a g e × p a g e S i z e ) [(currentPage - 1) \times pageSize, currentPage \times pageSize) [(currentPage−1)×pageSize,currentPage×pageSize)。
对应 js 代码:
let currentPageList = this.dataInfo.slice((currentPage - 1) * pageSize, currentPage * pageSize);
好的,还有第二个问题,对于本页的 currentPageList[] 数组中的这些数据,如何知道哪些记录应该是有相同日期行?直接通过日期属性 date 进行字符串相等比较吗?其实这在某些场景下可能并不合适,因为后端可能返回多条记录,这些记录的 date 属性值是一样的,也就是说,在同一天有多条采购记录,在采购记录中可能存在对不同店铺的采购。
而在之前步骤一的「数据平面化」中,我特地保留了遍历的 recordId、storeId 与 productId,也就是说,我们可以通过判断 recordId 是否相同来判断是否为同一日期行记录,或者说进行分组。
并且,由于「数据平面化」是串行且顺序遍历得到的,因此相同的 recordId 应当是连续存在的。
好的,所有的疑问解答完毕,接下来就该进行代码编写。
-
data 中添加属性
pagination,用于记录当前的分页状况。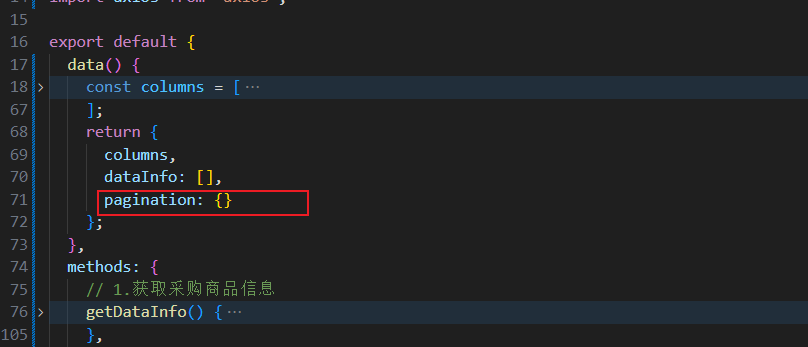
-
添加用户点击页号时的事件方法
handleTableChange// 添加用户点击页号时的事件方法 handleTableChange(pagination, filters, sorter) { // 参数 pagination 与 data 中的 pagination 并不是同一个对象,前者是在传参时创建的新对象 // 因此我们必须更新当前的分页器 this.pagination = pagination; // 用户点击的页号,最小为 1 let currentPage = pagination.current; // 每页大小,即每页最多的记录数 let pageSize = pagination.pageSize; // 获取当前页的数据列表 let currentPageList = this.dataInfo.slice((currentPage - 1) * pageSize, currentPage * 10); // 步骤二:合并日期列的同一记录下的行单元格 // 1.对于每个合并的分组的第一条记录,日期单元格合并行数 rowSpan 应当设置为该分组中的记录数 // 2.对于每个合并的分组的其它记录,日期单元格合并行数 rowSpan 应当设置为 0,表示该单元格不进行渲染 let i = 0; // 注意,为什么不是 i < pageSize 呢?这是由于最后一页的记录数可能不足 pageSize while (i < currentPageList.length) { // 合并分组的第一条记录 let firstRow = currentPageList[i] i++; // 统计该分组的记录数 let groupRecordCount = 1; while (i < currentPageList.length && firstRow.recordId === currentPageList[i].recordId) { groupRecordCount++; // 对应上述注释的第 2 点 currentPageList[i].dateRowSpan = 0; i++; } // 对应上述注释的第 1 点 firstRow.dateRowSpan = groupRecordCount; } } -
在用户点击页号时触发事件方法
handleTableChange,并设置组件的分页器。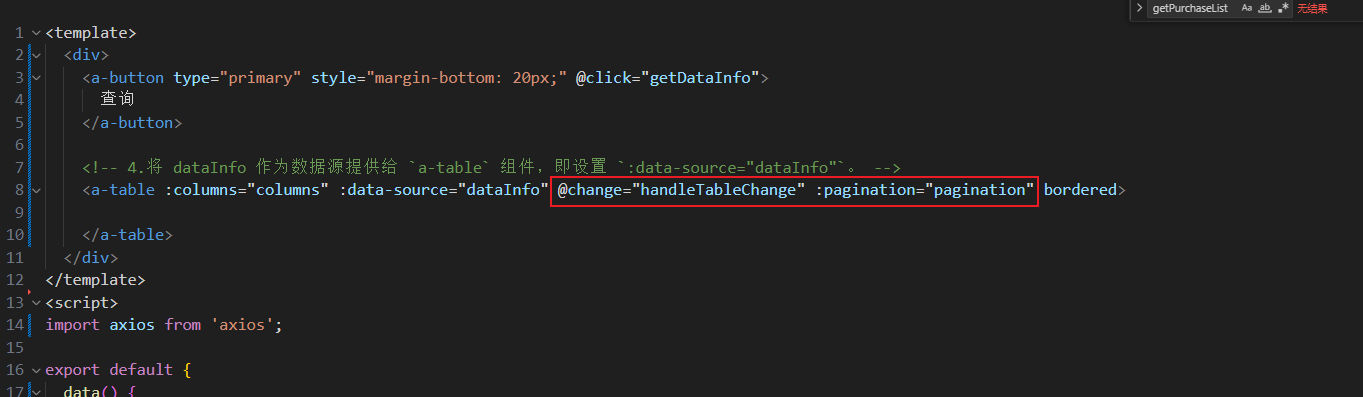
-
在用户点击查询时,数据平面化处理后,为第 1 页设置相同日期的行合并即调用事件方法
handleTableChange。// 并为第 1 页设置相同日期的行合并即调用事件方法 `handleTableChange`。 this.handleTableChange({ current: 1, pageSize: 8 })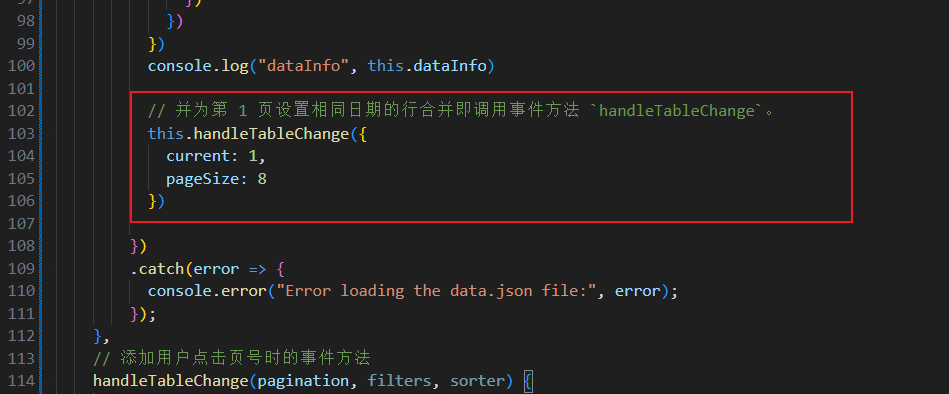
-
修改表格列的配置描述,即修改 columns[] 数组中日期列对象的描述,将
attrs.rowSpan的值设置为row.dateRowSpan。{ title: '日期', dataIndex: 'dateStr', customRender: (text, row, index) => { return { children: text, attrs: { rowSpan: row.dateRowSpan, }, }; }, }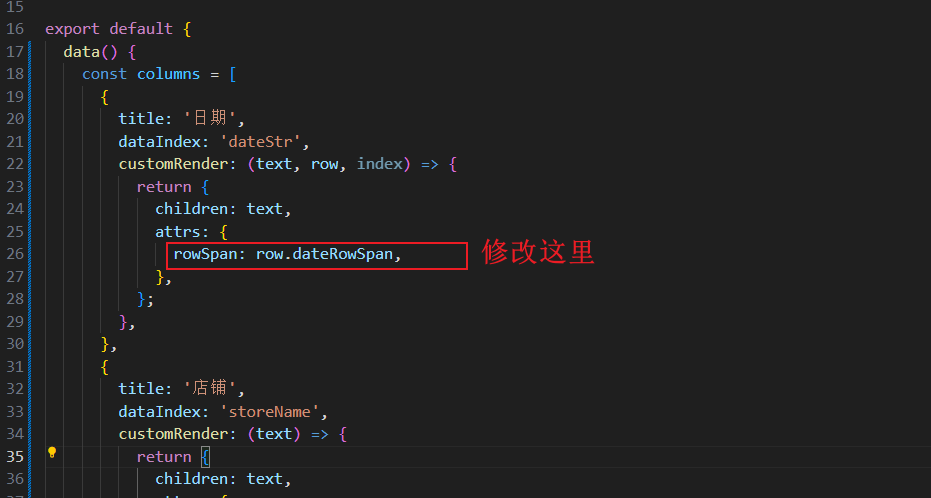
上述修改的完整代码如下:
<template>
<div>
<a-button type="primary" style="margin-bottom: 20px;" @click="getDataInfo">
查询
</a-button>
<!-- 4.将 dataInfo 作为数据源提供给 `a-table` 组件,即设置 `:data-source="dataInfo"`。 -->
<a-table :columns="columns" :data-source="dataInfo" @change="handleTableChange" :pagination="pagination" bordered>
</a-table>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from 'axios';
export default {
data() {
const columns = [
{
title: '日期',
dataIndex: 'dateStr',
customRender: (text, row, index) => {
return {
children: text,
attrs: {
rowSpan: row.dateRowSpan,
},
};
},
},
{
title: '店铺',
dataIndex: 'storeName',
customRender: (text, row, index) => {
return {
children: text,
attrs: {
rowSpan: 1,
},
};
},
},
{
title: '商品',
dataIndex: 'productName',
customRender: (text, row, index) => {
return {
children: text,
attrs: {
rowSpan: 1,
},
};
},
},
{
title: '数量',
dataIndex: 'productCount',
customRender: (text, row, index) => {
return {
children: text,
attrs: {
rowSpan: 1,
},
};
},
},
];
return {
columns,
dataInfo: [],
pagination: {}
};
},
methods: {
// 1.获取采购商品信息
getDataInfo() {
// 模拟向后端发送请求,实际是从本地 public/data.json 下拿数据
axios.get('/data.json')
.then(response => {
let info = response.data;
// 2.清空上一次查询保存在本地数据 dataInfo 的数据。
this.dataInfo = [];
// 3.将这一次查询到的数据「平面化/铺平/展开」后,加入到 dataInfo 中。并记录好每一层的索引 Id,作为合并标识。
info.forEach((record, recordId) => {
record.storeList.forEach((store, storeId) => {
store.productList.forEach((product, productId) => {
let row = {
recordId,
dateStr: record.date,
storeId,
storeName: store.storeName,
productId,
productName: product.productName,
productCount: product.count
}
this.dataInfo.push(row);
})
})
})
// console.log("dataInfo", this.dataInfo)
// 并为第 1 页设置相同日期的行合并即调用事件方法 `handleTableChange`。
this.handleTableChange({
current: 1,
pageSize: 8
})
})
.catch(error => {
console.error("Error loading the data.json file:", error);
});
},
// 添加用户点击页号时的事件方法
handleTableChange(pagination, filters, sorter) {
// 参数 pagination 与 data 中的 pagination 并不是同一个对象,前者是在传参时创建的新对象
// 因此我们必须更新当前的分页器
this.pagination = pagination;
// 用户点击的页号,最小为 1
let currentPage = pagination.current;
// 每页大小,即每页最多的记录数
let pageSize = pagination.pageSize;
// 获取当前页的数据列表
let currentPageList = this.dataInfo.slice((currentPage - 1) * pageSize, currentPage * 10);
// 合并日期列的同一记录下的行单元格
// 1.对于每个合并的分组的第一条记录,日期单元格合并行数 rowSpan 应当设置为该分组中的记录数
// 2.对于每个合并的分组的其它记录,日期单元格合并行数 rowSpan 应当设置为 0,表示该单元格不进行渲染
let i = 0;
// 注意,为什么不是 i < pageSize 呢?这是由于最后一页的记录数可能不足 pageSize
while (i < currentPageList.length) {
// 合并分组的第一条记录
let firstRow = currentPageList[i]
i++;
// 统计该分组的记录数
let groupRecordCount = 1;
while (i < currentPageList.length
&& firstRow.recordId === currentPageList[i].recordId) {
groupRecordCount++;
// 对应上述注释的第 2 点
currentPageList[i].dateRowSpan = 0;
i++;
}
// 对应上述注释的第 1 点
firstRow.dateRowSpan = groupRecordCount;
}
}
}
};
</script>
npm run serve 启动服务,点击“查询”按钮,查看效果。
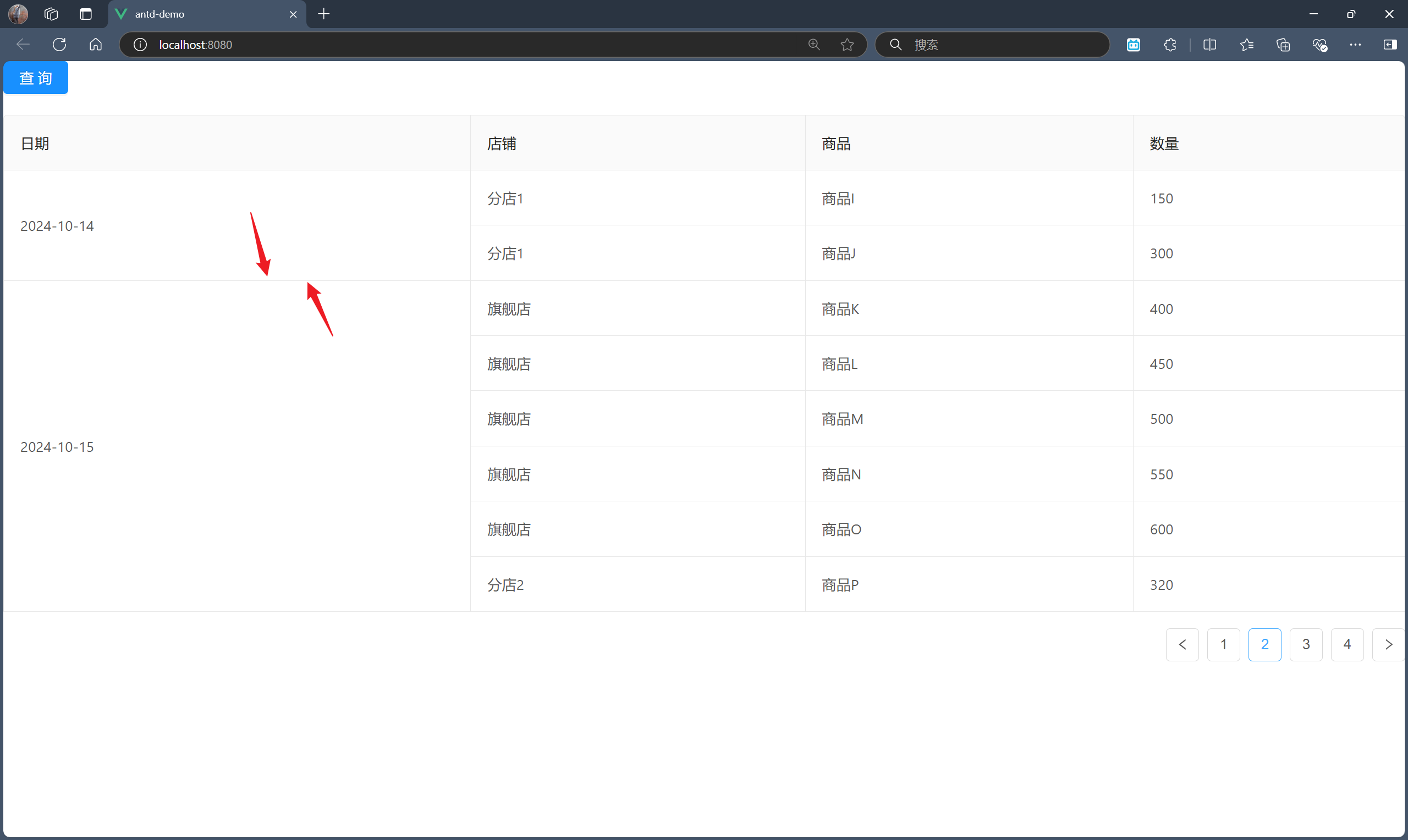
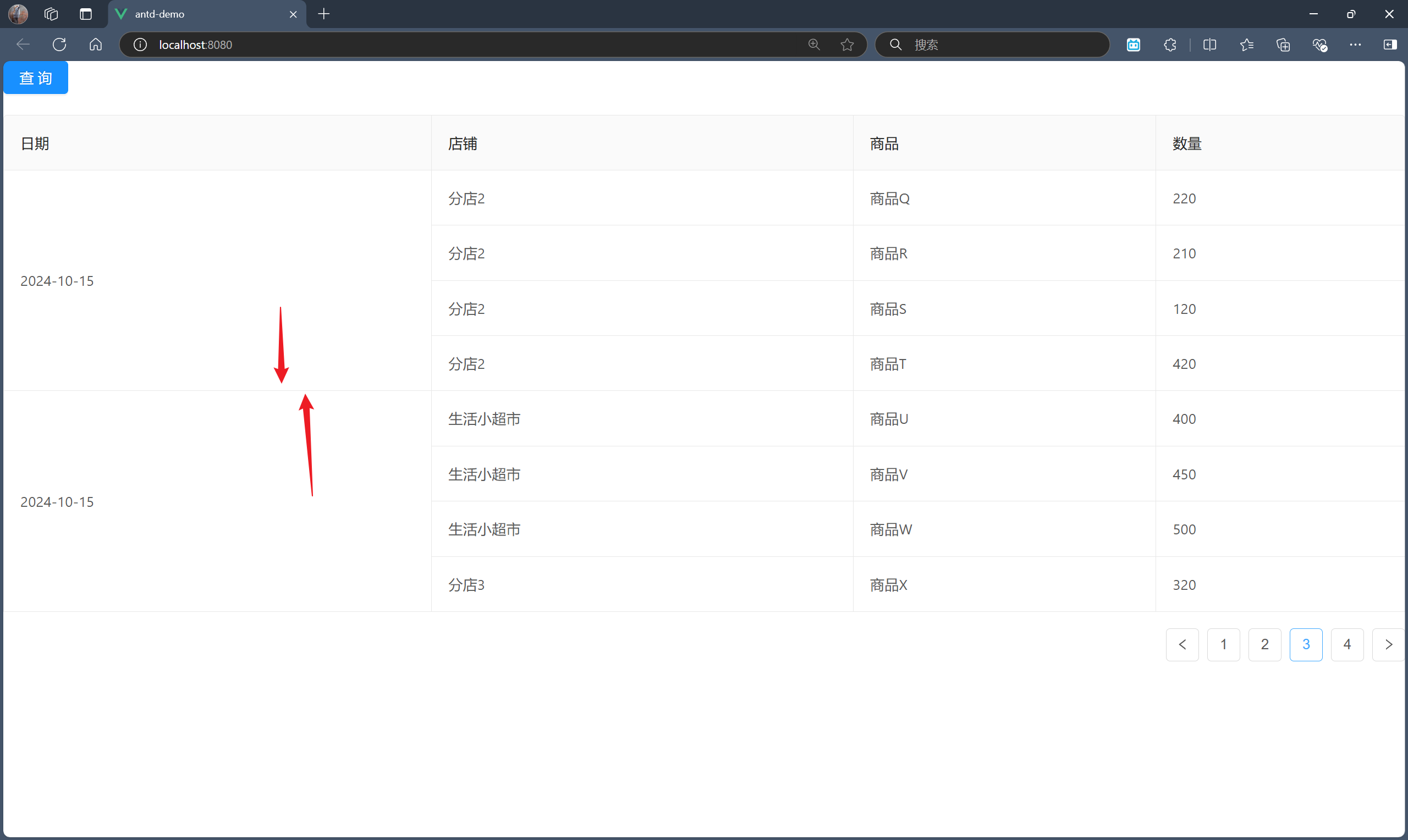
步骤三:合并店铺列的同一记录下的同一店铺的行单元格
其实这一步与步骤二并无多大差别,且不需要修改原来的代码,仅需扩展即可,因为合并的是不同列。
这里就不啰嗦了,直接贴完成步骤三后的完整代码:
<template>
<div>
<a-button type="primary" style="margin-bottom: 20px;" @click="getDataInfo">
查询
</a-button>
<!-- 4.将 dataInfo 作为数据源提供给 `a-table` 组件,即设置 `:data-source="dataInfo"`。 -->
<a-table :columns="columns" :data-source="dataInfo" @change="handleTableChange" :pagination="pagination" bordered>
</a-table>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from 'axios';
export default {
data() {
const columns = [
{
title: '日期',
dataIndex: 'dateStr',
customRender: (text, row, index) => {
return {
children: text,
attrs: {
rowSpan: row.dateRowSpan,
},
};
},
},
{
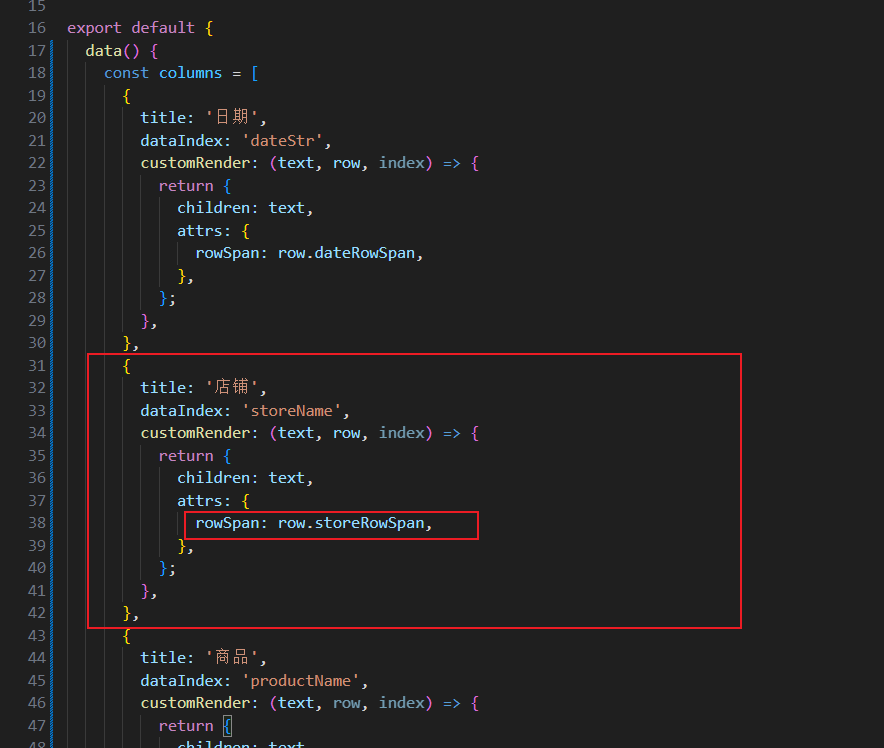
title: '店铺',
dataIndex: 'storeName',
customRender: (text, row, index) => {
return {
children: text,
attrs: {
rowSpan: row.storeRowSpan,
},
};
},
},
{
title: '商品',
dataIndex: 'productName',
customRender: (text, row, index) => {
return {
children: text,
attrs: {
rowSpan: 1,
},
};
},
},
{
title: '数量',
dataIndex: 'productCount',
customRender: (text, row, index) => {
return {
children: text,
attrs: {
rowSpan: 1,
},
};
},
},
];
return {
columns,
dataInfo: [],
pagination: {}
};
},
methods: {
// 1.获取采购商品信息
getDataInfo() {
// 模拟向后端发送请求,实际是从本地 public/data.json 下拿数据
axios.get('/data.json')
.then(response => {
let info = response.data;
// 2.清空上一次查询保存在本地数据 dataInfo 的数据。
this.dataInfo = [];
// 3.将这一次查询到的数据「平面化/铺平/展开」后,加入到 dataInfo 中。并记录好每一层的索引 Id,作为合并标识。
info.forEach((record, recordId) => {
record.storeList.forEach((store, storeId) => {
store.productList.forEach((product, productId) => {
let row = {
recordId,
dateStr: record.date,
storeId,
storeName: store.storeName,
productId,
productName: product.productName,
productCount: product.count
}
this.dataInfo.push(row);
})
})
})
// console.log("dataInfo", this.dataInfo)
// 并为第 1 页设置相同日期的行合并即调用事件方法 `handleTableChange`。
this.handleTableChange({
current: 1,
pageSize: 8
})
})
.catch(error => {
console.error("Error loading the data.json file:", error);
});
},
// 添加用户点击页号时的事件方法
handleTableChange(pagination, filters, sorter) {
// 参数 pagination 与 data 中的 pagination 并不是同一个对象,前者是在传参时创建的新对象
// 因此我们必须更新当前的分页器
this.pagination = pagination;
// 用户点击的页号,最小为 1
let currentPage = pagination.current;
// 每页大小,即每页最多的记录数
let pageSize = pagination.pageSize;
// 获取当前页的数据列表
let currentPageList = this.dataInfo.slice((currentPage - 1) * pageSize, currentPage * 10);
// 步骤二:合并日期列的同一记录下的行单元格
// 1.对于每个合并的分组的第一条记录,日期单元格合并行数 rowSpan 应当设置为该分组中的记录数
// 2.对于每个合并的分组的其它记录,日期单元格合并行数 rowSpan 应当设置为 0,表示该单元格不进行渲染
let i = 0;
// 注意,为什么不是 i < pageSize 呢?这是由于最后一页的记录数可能不足 pageSize
while (i < currentPageList.length) {
// 合并分组的第一条记录
let firstRow = currentPageList[i]
i++;
// 统计该分组的记录数
let groupRecordCount = 1;
while (i < currentPageList.length
&& firstRow.recordId === currentPageList[i].recordId) {
groupRecordCount++;
// 对应上述注释的第 2 点
currentPageList[i].dateRowSpan = 0;
i++;
}
// 对应上述注释的第 1 点
firstRow.dateRowSpan = groupRecordCount;
}
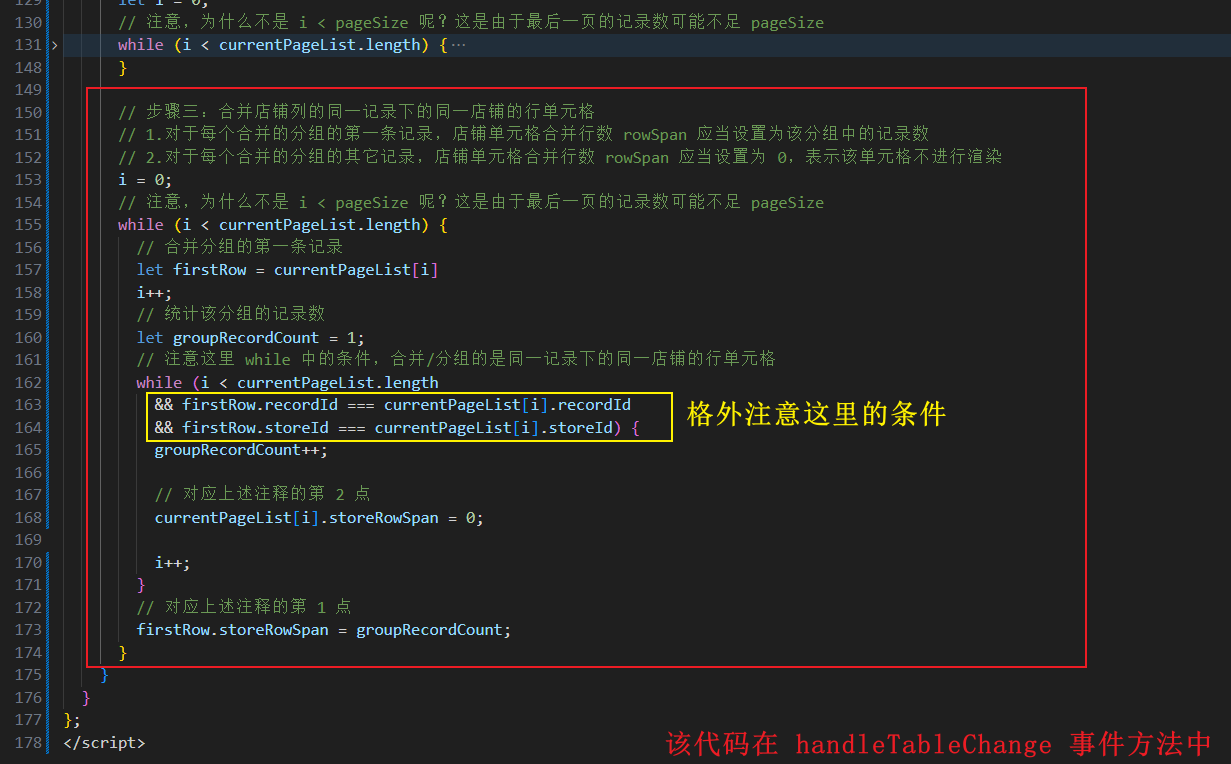
// 步骤三:合并店铺列的同一记录下的同一店铺的行单元格
// 1.对于每个合并的分组的第一条记录,店铺单元格合并行数 rowSpan 应当设置为该分组中的记录数
// 2.对于每个合并的分组的其它记录,店铺单元格合并行数 rowSpan 应当设置为 0,表示该单元格不进行渲染
i = 0;
// 注意,为什么不是 i < pageSize 呢?这是由于最后一页的记录数可能不足 pageSize
while (i < currentPageList.length) {
// 合并分组的第一条记录
let firstRow = currentPageList[i]
i++;
// 统计该分组的记录数
let groupRecordCount = 1;
// 注意这里 while 中的条件,合并/分组的是同一记录下的同一店铺的行单元格
while (i < currentPageList.length
&& firstRow.recordId === currentPageList[i].recordId
&& firstRow.storeId === currentPageList[i].storeId) {
groupRecordCount++;
// 对应上述注释的第 2 点
currentPageList[i].storeRowSpan = 0;
i++;
}
// 对应上述注释的第 1 点
firstRow.storeRowSpan = groupRecordCount;
}
}
}
};
</script>
npm run serve 启动服务,点击“查询”按钮,查看效果。
6.总结
至此,我们的需求已经基本实现了。但还有几个可以完善的思考🧐:
- 同一记录或同一记录下的同一店铺的所有行是否应该在同一页显示,如果需要该怎么根据数据对 pageSize 进行调整?
- 同一记录或同一记录下的同一店铺的所有行如果溢出到了下一页的数据,那么溢出部分合并显示为空白是否会更加合适呢?
这些问题,可能在未来某一天会有这样的业务需求,那到时候我们再分析吧,哈哈哈。

开放原子开发者工作坊旨在鼓励更多人参与开源活动,与志同道合的开发者们相互交流开发经验、分享开发心得、获取前沿技术趋势。工作坊有多种形式的开发者活动,如meetup、训练营等,主打技术交流,干货满满,真诚地邀请各位开发者共同参与!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献9条内容
已为社区贡献9条内容





所有评论(0)