Linux文件系统
目录 1、常见的linux文件系统 2、文件系统的组成inode的内容: 可以用stat命令,查看某个文件的inode信息inode的大小 inode号码使用 ls -i来查看文件的inode号码使用 df -i命令,查看每个硬盘分区的inode总数和已经使用的数量,可以使用df命令。系统打开一个文件的整个过程目录文件block块block调大 显示磁盘状态信息:CentOS6用: dumpe2f
目录
使用 df -i命令,查看每个硬盘分区的inode总数和已经使用的数量,可以使用df命令。
显示磁盘状态信息:CentOS6用: dumpe2fs 分区名 ,CentOS7用xfs_info 分区名
1、常见的linux文件系统
ext:linux中最早的文件系统,由于在性能和兼容性上具有很多缺陷,现在已经很少使用
ext2:是ext文件系统的升级版本,Red Hat Linux7.2版本以前的系统默认都是ext2文件系统,于1993年发布,支持最大16TB
的分区和最大2TB的文件(1TB=1024GB=1024*1024KB)
ext3:是ext2文件系统的升级版本,最大的区别就是带日志功能,以便系统突然停止时(比如断电)提高文件系统的可靠性,
支持最大16TB的分区和最大2TB的文件。
ext4 :是 ext3 文件系统的升级版。 ext4 在性能、 伸缩性和可靠性方面进行了大量改进。 ext4的变化可以说是翻天覆地的, 比如向下兼容 ext3、最大 1EB 文件系统和 16TB 文件、无限数量子目录、 Extents 连续数据块概念、 多块分配、 延 迟分配、 持久预分配、 快速 FSCK、日志校验、 无日志模式、 在线碎片整理、 inode 增强、 默认启用 barrier 等。 它是 CentOS 6.x 的默认文件系统
xfs :XFS 最早针对 IRIX 操作系统开发, 是一个高性能的日志型文件系统, 能够在断电以及操作系统崩溃的情况下保证文件系统数据的一致性。它是一个 64 位的文件系统,后来进行开源并且移植到了 Linux 操作系统中,目前 CentOS 7.x 将 XFS+LVM(逻辑卷管理)作为默认的文件系统。据官方所称,XFS 对于大文件的读写性能较好。单个文件系统最大可以支持8EB,单个文件可以支持16TB
swap :swap 是 Linux 中用于交换分区的文件系统(类似于 Windows 中的虚拟内存),当内存不够用时,使用交换分区暂时替代内存。一般大小为内存的 2 倍,但是不要超过 2GB。它是 Linux 的必需分区
NFS :NFS 是网络文件系统(Network File System)的缩写,是用来实现不同主机之间文件共享的一种网络服务,本地主机可以通过挂载的方式使用远程共享的资源
iso9660 :光盘的标准文件系统。Linux 要想使用光盘,必须支持 iso9660 文件系统
fat :就是 Windows 下的 fat16 文件系统,在 Linux 中识别为 fat
vfat :就是 Windows 下的 fat32 文件系统,在 Linux 中识别为 vfat。支持最大 32GB 的分区和最大 4GB 的文件
NTFS :就是 Windows 下的 NTFS 文件系统,不过 Linux 默认是不能识别 NTFS 文件系统的,如果需要识别, 则需要重新编译内核才能支持。 它比 fat32 文件系统更加安全, 速度更快,支持最大 2TB 的分区和最大 64GB 的文件
ufs :Sun 公司的操作系统 Solaris 和 SunOS 所采用的文件系统
proc :Linux 中基于内存的虚拟文件系统,用来管理内存存储目录/proc其实是linux内核对外提供的一个接口,
sysfs 和 proc 一样,也是基于内存的虚拟文件系统,用来管理内存存储目录/sys
tmpfs: 也是一种基于内存的虚拟文件系统,不过也可以使用 swap 交换分区
######################################################################
2、文件系统的组成
Linux文件系统具体由三部分组成:文件名,inode,block
inode的内容:
inode包含文件的元信息,相当于windows的文件的属性:
* 文件的字节数
* 文件拥有者的User ID
* 文件的Group ID
* 文件的读、写、执行权限
* 文件的时间戳,共有三个:
ctime指inode上一次变动的时间
mtime指文件内容上一次变动的时间
atime指文件上一次打开的时间
* 链接数,即有多少文件名指向这个inode
* 文件数据block的位置
可以用stat命令,查看某个文件的inode信息
[root@zabbix-server lianxi]# stat inode.txt
文件:"inode.txt"
大小:4 块:8 IO 块:4096 普通文件
设备:fd00h/64768d Inode:17399383 硬链接:1
权限:(0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid:( 0/ root) Gid:( 0/ root)
环境:unconfined_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0
最近访问:2023-03-02 15:49:20.384057399 +0800
最近更改:2023-03-02 15:50:54.088203475 +0800
最近改动:2023-03-02 15:50:54.088203475 +0800
创建时间:-
inode的大小
inode也会消耗硬盘空间,所以硬盘格式化的时候,操作系统自动将硬盘分成两个区域。一个是数据区,存放文件数据;另一个是inode区(inode table),存放inode所包含的信息。lixun的文件系统中把这部分区域又叫super block(超级块)。
每个inode节点的大小,一般是128字节或256字节。inode节点的总数,在格式化时就给定,假定在一块1GB的硬盘中,每个inode节点的大小为128字节,每1KB就设置一个inode,那么inode table的大小就会达到128MB,占整块硬盘的12.8%。
inode号码
每个inode都有一个号码,操作系统用inode号码来识别不同的文件。
Unix/Linux系统内部不使用文件名,而使用inode号码来识别文件。对于系统来说,文件名只是inode号码便于识别的别称或者绰号
使用 ls -i来查看文件的inode号码
[root@zabbix-server lianxi]# ls -i
17399383 inode.txt
使用 df -i命令,查看每个硬盘分区的inode总数和已经使用的数量,可以使用df命令。
[root@zabbix-server lianxi]# df -i
文件系统 Inode 已用(I) 可用(I) 已用(I)% 挂载点
devtmpfs 229876 401 229475 1% /dev
tmpfs 232878 1 232877 1% /dev/shm
tmpfs 232878 759 232119 1% /run
tmpfs 232878 16 232862 1% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos-root 8910848 43724 8867124 1% /
/dev/sda1 524288 327 523961 1% /boot
tmpfs 232878 1 232877 1% /run/user/0
每一个文件都必须由一个inode,所以有可能发生inode已经用完,但是硬盘还没有用完的情况,这样就无法在硬盘上面创建新文件
系统打开一个文件的整个过程
首先,系统找到这个文件名对应的inode号码;
其次,通过inode号码,获取inode信息;
最后,根据inode信息,找到文件数据所在的block,读出数据。
目录文件
在linux操作系统中,目录(directory)也是一种文件,打开一个目录,其实就是打开了一个目录文件
目录文件的结构很简单,就是一系列目录项的列表
每个目录项由两部分组成:所包含文件的文件名,以及该文件名所对应的inode号码
这也是为什么使用ls -h
[root@zabbix-server lianxi]# ll -id /etc
16777281 drwxr-xr-x. 81 root root 8192 3月 2 09:58 /etc
######################################################################
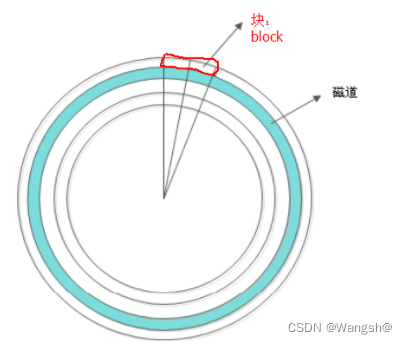
block块
操作系统读取硬盘的时候,不会一个个扇区(512字节)地读取,这样效率太低,而是一次性的连续读取多个扇区,即一次性读取一个块(block),这种由多个扇区组成的块,是文件存取的最小单位,块的大小,最常见是1kb,即连着2扇区组成一个block,或4kb,即八个扇区组成一个block。

block是真正存储数据的地方
block是文件系统中最小的存储单位
扇区是磁盘中最小的存储单位
######################################################################
block调大
优点:速度快,节约寻址时间,缺点:空间浪费
例如:2T硬盘,前1.5T,使用4k的block大小,后面500G格式化成64k块大小,用空间换时间
原因:
block大小(1KB,2KB,或4KB)和数量在格式化后就已经决定,不能改变,除非重新格式化,每个block只能保存一个文件的数据,要是文件数据小于一个block块,那么这个block的剩余空间不能被其他文件使用,要是文件数据大于一个block块,则占用多个block块
显示磁盘状态信息:CentOS6用: dumpe2fs 分区名 ,CentOS7用xfs_info 分区名
[root@monitor-vm ~]# xfs_info /dev/vda1
meta-data=/dev/vda1 isize=512 agcount=4, agsize=65536 blks
= sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1
= crc=1 finobt=0 spinodes=0
data = bsize=4096 blocks=262144, imaxpct=25
= sunit=0 swidth=0 blks
naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=1
log =internal bsize=4096 blocks=2560, version=2
= sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1
realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0
######################################################################
磁盘分区工具与挂载
1、磁盘常识
工厂生产的硬盘必须经过低级格式化,分区,高级格式化,三个处理步骤后,电脑才能利用他们存储数据,其中磁盘的低级格式化通常由生产厂家完成,目的是划定磁盘可供使用的扇区和磁道并标记有问题的扇区,而用户则需要使用操作系统提供的磁盘工具如fdisk,gdisk等重新进行硬盘分区和格式化。
2、磁盘两种分区表:MBR和GPT
MBR:将分区信息保存到磁盘的第一个扇区(MBR扇区)的64字节中,每个分区要占用16个字节,这意味着格式化的时候最多划分4个主分区,因为MBR分区表给定分区信息只有64个字节,这16个字节中存有活动状态标志、文件系统标识、起止柱面号、磁头号、扇区号、隐含扇区数目(4个字节)、分区总扇区数目(4个字节)等内容。
特点:
MBR分区主分区数目不能超过4个,很多时候,4个主分区并不能满足需要。
MBR分区方案无法支持超过2TB容量的磁盘。因为这一方案用4个字节存储分区的总扇区数,最大能表示2的32次方的扇区个数,按每扇区512字节计算,每个分区最大不能超过2TB。磁盘容量超过2TB以后,分区的起止位置也就无法表示了,BIOS将无法识别分区。(这种分区表逐渐将被淘汰,当然现在很多系统还在用)
GPT
GUID磁盘分割表(GUID Partition Table)的缩写,含义“全局唯一标识磁盘分区表”,是一个实体硬盘的分区表的结构布局的标准。
GPT的分区方案之所以比MBR更先进,是因为在GPT分区表头中可自定义分区数量的最大值,也就是说GPT分区表的大小不是固定的。在Windows中,微软设定GPT磁盘最大分区数量为128个。
特点
支持2TB以上的大硬盘。
每个磁盘的分区个数几乎没有限制。操作系统存在允许的最多分区数的限制,比如win限制128个
######################################################################
3、使用fdisk管理分区(MBR分区表)
1、fdisk -l 查看系统所有硬盘及分区
[root@zabbix-server ssh]# fdisk -l
磁盘 /dev/sda:21.5 GB, 21474836480 字节,41943040 个扇区
Units = 扇区 of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
扇区大小(逻辑/物理):512 字节 / 512 字节
I/O 大小(最小/最佳):512 字节 / 512 字节
磁盘标签类型:dos
磁盘标识符:0x0008f377
设备 Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 2048 2099199 1048576 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 2099200 41943039 19921920 8e Linux LVM
可以看到,已经存在的一个磁盘 /dev/sda 总共41943040个扇区,而这个磁盘已经分成了3个区,已经分配完成了,
要继续分配的话要新增加一块硬盘。
新增一块硬盘



新增硬盘成功,开启虚拟机,可以看到,新增加了一个硬盘,并且没有划分分区
[root@zabbix-server ~]# fdisk -l
磁盘 /dev/sda:21.5 GB, 21474836480 字节,41943040 个扇区
Units = 扇区 of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
扇区大小(逻辑/物理):512 字节 / 512 字节
I/O 大小(最小/最佳):512 字节 / 512 字节
磁盘标签类型:dos
磁盘标识符:0x0008f377
设备 Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 2048 2099199 1048576 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 2099200 41943039 19921920 8e Linux LVM
磁盘 /dev/sdb:21.5 GB, 21474836480 字节,41943040 个扇区
Units = 扇区 of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
扇区大小(逻辑/物理):512 字节 / 512 字节
I/O 大小(最小/最佳):512 字节 / 512 字节
######################################################################
2、进入fdisk工具进行分区操作
[root@zabbix-server ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
欢迎使用 fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2)。
更改将停留在内存中,直到您决定将更改写入磁盘。
使用写入命令前请三思。
Device does not contain a recognized partition table
使用磁盘标识符 0xa78730bb 创建新的 DOS 磁盘标签。
命令(输入 m 获取帮助):m
命令操作
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
g create a new empty GPT partition table
G create an IRIX (SGI) partition table
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
常用fdisk工具命令:
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition 删除分区
g create a new empty GPT partition table
G create an IRIX (SGI) partition table
l list known partition types 显示分区类型(linux系统内核,很多个分区的类型,id)
m print this menu 打印帮助菜单
n add a new partition 添加新的分区
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table 显示分区表
q quit without saving changes 不保存,退出
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id 改变分区类型
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit 写分区表信息到硬盘,保存操作并退出
x extra functionality (experts only)
分区操作:
[root@zabbix-server ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
欢迎使用 fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2)。
更改将停留在内存中,直到您决定将更改写入磁盘。
使用写入命令前请三思。
Device does not contain a recognized partition table
使用磁盘标识符 0xc57cdce7 创建新的 DOS 磁盘标签。
命令(输入 m 获取帮助):n --新增分区
Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p --新增主分区
分区号 (1-4,默认 1):1 --主分区只能有4个
起始 扇区 (2048-41943039,默认为 2048): --新增分区起始扇区,一般默认,直接回车
将使用默认值 2048
Last 扇区, +扇区 or +size{K,M,G} (2048-41943039,默认为 41943039):+1G --分区大小
分区 1 已设置为 Linux 类型,大小设为 1 GiB
命令(输入 m 获取帮助):n
Partition type:
p primary (1 primary, 0 extended, 3 free)
e extended
Select (default p): e --新增扩展分区
分区号 (2-4,默认 2):2 --扩展分区也要占用一个主分区
起始 扇区 (2099200-41943039,默认为 2099200): --默认起始扇区,从上一个主分区的终止扇区开始
将使用默认值 2099200
Last 扇区, +扇区 or +size{K,M,G} (2099200-41943039,默认为 41943039):+18G
分区 2 已设置为 Extended 类型,大小设为 18 GiB
命令(输入 m 获取帮助):p
磁盘 /dev/sdb:21.5 GB, 21474836480 字节,41943040 个扇区
Units = 扇区 of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
扇区大小(逻辑/物理):512 字节 / 512 字节
I/O 大小(最小/最佳):512 字节 / 512 字节
磁盘标签类型:dos
磁盘标识符:0xc57cdce7
设备 Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 2099199 1048576 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 2099200 39847935 18874368 5 Extended
命令(输入 m 获取帮助):n
Partition type:
p primary (1 primary, 1 extended, 2 free)
l logical (numbered from 5)
Select (default p): l --扩展分区只能有一个,现在只能新建主分区和逻辑分区
添加逻辑分区 5 --逻辑分区从5开始
起始 扇区 (2101248-39847935,默认为 2101248):
将使用默认值 2101248
Last 扇区, +扇区 or +size{K,M,G} (2101248-39847935,默认为 39847935):+2G
分区 5 已设置为 Linux 类型,大小设为 2 GiB
命令(输入 m 获取帮助):p
磁盘 /dev/sdb:21.5 GB, 21474836480 字节,41943040 个扇区
Units = 扇区 of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
扇区大小(逻辑/物理):512 字节 / 512 字节
I/O 大小(最小/最佳):512 字节 / 512 字节
磁盘标签类型:dos
磁盘标识符:0xc57cdce7
设备 Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 2099199 1048576 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 2099200 39847935 18874368 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 2101248 6295551 2097152 83 Linux
命令(输入 m 获取帮助):w --保存,将操作写入磁盘里
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
正在同步磁盘。
可以看到,刚才划分的分区就已经成功写入磁盘里了

分区格式化操作:
一般centos7使用xfs文件系统,centos6使用ext4文件系统,通常情况下使用官方建议的文件系统
[root@zabbix-server ~]# mkfs.xfs /dev/sdb1
meta-data=/dev/sdb1 isize=512 agcount=4, agsize=65536 blks
= sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1
= crc=1 finobt=0, sparse=0
data = bsize=4096 blocks=262144, imaxpct=25
= sunit=0 swidth=0 blks
naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=1
log =internal log bsize=4096 blocks=2560, version=2
= sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1
realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0
mkfs 命令非常简单易用,不过是不能调整分区的默认参数的(比如块大小是 4096),这些默认参数除非特殊情况,否则不需要调整,如果想要调整就需要使用 mke2fs 命令进行重新格式化,
建立挂载点
新建一个挂载目录/disk1,准备将主分区/dev/sda1 挂载到/disk1,挂载完了以后如果重启的话就会失效
[root@zabbix-server ~]# mkdir -p /disk1
[root@zabbix-server ~]# mount /dev/sdb1 /disk1
[root@zabbix-server ~]# df -h
文件系统 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
devtmpfs 898M 0 898M 0% /dev
tmpfs 910M 0 910M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 910M 9.6M 901M 2% /run
tmpfs 910M 0 910M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos-root 17G 2.2G 15G 13% /
/dev/sda1 1014M 151M 864M 15% /boot
tmpfs 182M 0 182M 0% /run/user/0
/dev/sdb1 1014M 33M 982M 4% /disk1
自动挂载
修改分区自动挂载文件 /etc/fstab 文件,添加自动挂载以后,当服务器重启的时候,磁盘会自动挂载到对应目录
[root@zabbix-server ~]# vim /etc/fstab
/dev/sdb1 /disk1 xfs defaults 0 0
######################################################################
4、使用gdisk管理分区(gpt分区表)
gpt分区表没有扩展分区和逻辑分区之分,只有主分区,一般windows对于gpt分区表的主分区数有一个128的数量限制
安装gdisk工具
yum install -y gdisk
进入gdisk进行分区
[root@zabbix-server ~]# gdisk /deb/sdb
GPT fdisk (gdisk) version 0.8.10
Problem opening /deb/sdb for reading! Error is 2.
The specified file does not exist!
[root@zabbix-server ~]# gdisk /dev/sdb
GPT fdisk (gdisk) version 0.8.10
Partition table scan:
MBR: not present
BSD: not present
APM: not present
GPT: not present
Creating new GPT entries.
Command (? for help): ?
b back up GPT data to a file
c change a partition's name
d delete a partition
i show detailed information on a partition
l list known partition types
n add a new partition
o create a new empty GUID partition table (GPT)
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
r recovery and transformation options (experts only)
s sort partitions
t change a partition's type code
v verify disk
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
? print this menu
gdisk常用命令
Command (? for help): ? # 查看帮助
b back up GPT data to a file
c change a partition's name
d delete a partition #删除分区
i show detailed information on a partition
l list known partition types
n add a new partition # 添加一个分区
o create a new empty GUID partition table (GPT)
p print the partition table # 打印分区表
q quit without saving changes # 退出不保存
r recovery and transformation options (experts only)
s sort partitions
t change a partition's type code #修改分区系统id
v verify disk
w write table to disk and exit # 写入分区表并退出
x extra functionality (experts only)
? print this menu分区操作:
[root@zabbix-server ~]# gdisk /dev/sdb
GPT fdisk (gdisk) version 0.8.10
Partition table scan:
MBR: not present
BSD: not present
APM: not present
GPT: not present
Creating new GPT entries.
Command (? for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 41943040 sectors, 20.0 GiB
Logical sector size: 512 bytes
Disk identifier (GUID): 8D21C732-A799-40B8-B25B-7F9DE91252D8
Partition table holds up to 128 entries
First usable sector is 34, last usable sector is 41943006
Partitions will be aligned on 2048-sector boundaries
Total free space is 41942973 sectors (20.0 GiB)
Number Start (sector) End (sector) Size Code Name
Command (? for help): n
Partition number (1-128, default 1): 1
First sector (34-41943006, default = 2048) or {+-}size{KMGTP}:
Last sector (2048-41943006, default = 41943006) or {+-}size{KMGTP}: +2G
Current type is 'Linux filesystem'
Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 8300): 8300
Changed type of partition to 'Linux filesystem'
Command (? for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 41943040 sectors, 20.0 GiB
Logical sector size: 512 bytes
Disk identifier (GUID): 8D21C732-A799-40B8-B25B-7F9DE91252D8
Partition table holds up to 128 entries
First usable sector is 34, last usable sector is 41943006
Partitions will be aligned on 2048-sector boundaries
Total free space is 37748669 sectors (18.0 GiB)
Number Start (sector) End (sector) Size Code Name
1 2048 4196351 2.0 GiB 8300 Linux filesystem
Command (? for help): w
Final checks complete. About to write GPT data. THIS WILL OVERWRITE EXISTING
PARTITIONS!!
Do you want to proceed? (Y/N): y
OK; writing new GUID partition table (GPT) to /dev/sdb.
The operation has completed successfully.查看分区
[root@zabbix-server ~]# fdisk -l
磁盘 /dev/sda:21.5 GB, 21474836480 字节,41943040 个扇区
Units = 扇区 of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
扇区大小(逻辑/物理):512 字节 / 512 字节
I/O 大小(最小/最佳):512 字节 / 512 字节
磁盘标签类型:dos
磁盘标识符:0x0008f377
设备 Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 2048 2099199 1048576 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 2099200 41943039 19921920 8e Linux LVM
WARNING: fdisk GPT support is currently new, and therefore in an experimental phase. Use at your own discretion.
磁盘 /dev/sdb:21.5 GB, 21474836480 字节,41943040 个扇区
Units = 扇区 of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
扇区大小(逻辑/物理):512 字节 / 512 字节
I/O 大小(最小/最佳):512 字节 / 512 字节
磁盘标签类型:gpt
Disk identifier: 8D21C732-A799-40B8-B25B-7F9DE91252D8
# Start End Size Type Name
1 2048 4196351 2G Linux filesyste Linux filesystem
5、swap交换分区
未扩大swap之前:
[root@zabbix-server ~]# free -h
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1.8G 432M 894M 10M 492M 1.2G
Swap: 2.0G 0B 2.0G
配置交换分区
[root@zabbix-server ~]# gdisk /dev/sdb
GPT fdisk (gdisk) version 0.8.10
Partition table scan:
MBR: protective
BSD: not present
APM: not present
GPT: present
Found valid GPT with protective MBR; using GPT.
Command (? for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 41943040 sectors, 20.0 GiB
Logical sector size: 512 bytes
Disk identifier (GUID): 8D21C732-A799-40B8-B25B-7F9DE91252D8
Partition table holds up to 128 entries
First usable sector is 34, last usable sector is 41943006
Partitions will be aligned on 2048-sector boundaries
Total free space is 37748669 sectors (18.0 GiB)
Number Start (sector) End (sector) Size Code Name
1 2048 4196351 2.0 GiB 8300 Linux filesystem
Command (? for help): n
Partition number (2-128, default 2): 2
First sector (34-41943006, default = 4196352) or {+-}size{KMGTP}:
Last sector (4196352-41943006, default = 41943006) or {+-}size{KMGTP}: +1G
Current type is 'Linux filesystem'
Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 8300): 8200
Changed type of partition to 'Linux swap'
Command (? for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 41943040 sectors, 20.0 GiB
Logical sector size: 512 bytes
Disk identifier (GUID): 8D21C732-A799-40B8-B25B-7F9DE91252D8
Partition table holds up to 128 entries
First usable sector is 34, last usable sector is 41943006
Partitions will be aligned on 2048-sector boundaries
Total free space is 35651517 sectors (17.0 GiB)
Number Start (sector) End (sector) Size Code Name
1 2048 4196351 2.0 GiB 8300 Linux filesystem
2 4196352 6293503 1024.0 MiB 8200 Linux swap
Command (? for help): w
Final checks complete. About to write GPT data. THIS WILL OVERWRITE EXISTING
PARTITIONS!!
Do you want to proceed? (Y/N): y
OK; writing new GUID partition table (GPT) to /dev/sdb.
The operation has completed successfully.
######################################################################
格式化交换分区
[root@zabbix-server ~]# mkswap /dev/sdb2
正在设置交换空间版本 1,大小 = 1048572 KiB
无标签,UUID=efd3c262-1b70-435f-9b54-b79f305585bc
临时生效swap
[root@zabbix-server ~]# swapon /dev/sdb2
[root@zabbix-server ~]# free -h
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1.8G 439M 884M 10M 495M 1.2G
Swap: 3.0G 0B 3.0G
swap由2G变成3G
永久生效:要写入/etc/fstab文件里面
/dev/sdb2 swap swap defaults 0 0
######################################################################
5、将一个已经生效的分区改成swap分区
[root@zabbix-server ~]# gdisk /dev/sdb
GPT fdisk (gdisk) version 0.8.10
Partition table scan:
MBR: protective
BSD: not present
APM: not present
GPT: present
Found valid GPT with protective MBR; using GPT.
Command (? for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 41943040 sectors, 20.0 GiB
Logical sector size: 512 bytes
Disk identifier (GUID): 8D21C732-A799-40B8-B25B-7F9DE91252D8
Partition table holds up to 128 entries
First usable sector is 34, last usable sector is 41943006
Partitions will be aligned on 2048-sector boundaries
Total free space is 35651517 sectors (17.0 GiB)
Number Start (sector) End (sector) Size Code Name
1 2048 4196351 2.0 GiB 8300 Linux filesystem
2 4196352 6293503 1024.0 MiB 8200 Linux swap
Command (? for help): t
Partition number (1-2): 1
Current type is 'Linux filesystem'
Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 8300): 8200
Changed type of partition to 'Linux swap'
Command (? for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 41943040 sectors, 20.0 GiB
Logical sector size: 512 bytes
Disk identifier (GUID): 8D21C732-A799-40B8-B25B-7F9DE91252D8
Partition table holds up to 128 entries
First usable sector is 34, last usable sector is 41943006
Partitions will be aligned on 2048-sector boundaries
Total free space is 35651517 sectors (17.0 GiB)
Number Start (sector) End (sector) Size Code Name
1 2048 4196351 2.0 GiB 8200 Linux swap
2 4196352 6293503 1024.0 MiB 8200 Linux swap
######################################################################
/etc/fstab 文件修复:
如果/etc/fstab文件挂载目录信息出错,服务器会启动不了,需要修复fstab文件
报错的情况下继续登录,修改/etc/fstab 报错,可能改不了,是挂载的问题,
mount -o remount,rw /然后修改,最后重启!

开放原子开发者工作坊旨在鼓励更多人参与开源活动,与志同道合的开发者们相互交流开发经验、分享开发心得、获取前沿技术趋势。工作坊有多种形式的开发者活动,如meetup、训练营等,主打技术交流,干货满满,真诚地邀请各位开发者共同参与!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容





所有评论(0)