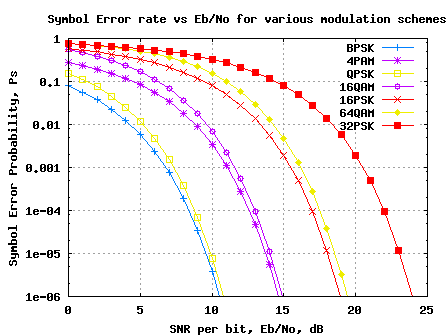
未编码下QAM,PAM,PSK系统的误码率理论公式
未编码下QAM,PAM,PSK系统 误码率的理论公式
误符号率
最佳基带传输系统(匹配滤波),信道误符号率(symbol error rate) 的最终表达式。
符号能量
E
s
E_s
Es 与 比特能量
E
b
E_b
Eb 之间的关系是
E
s
=
E
b
log
2
M
E_s=E_b\log_2 M
Es=Eblog2M
PAM,ASK
对于PAM 或ASK星座映射,星座大小为
M
M
M,两个星座的最小距离为
d
min
=
12
log
2
M
M
2
−
1
E
b
d_{\min} = \sqrt{\frac{12\log_2 M}{M^2-1}E_b}
dmin=M2−112log2MEb
P
e
=
2
(
1
−
1
M
)
Q
(
d
min
2
N
0
)
=
(
1
−
1
M
)
e
r
f
c
(
d
2
σ
)
=
(
1
−
1
M
)
e
r
f
c
[
3
M
2
−
1
⋅
E
b
log
2
M
N
0
]
P_e=2\left(1-\frac{1}{M}\right)Q\left(\frac{d_{\min}}{\sqrt{2N_0}}\right)= \left(1-\frac{1}{M}\right)\mathrm{erfc}\left(\frac{d}{\sqrt{2}\sigma}\right)=\left(1-\frac{1}{M}\right)\mathrm{erfc}\left[\sqrt{\frac{3}{M^2-1}\cdot\frac{E_b\log_2M}{N_0}}\right]
Pe=2(1−M1)Q(2N0dmin)=(1−M1)erfc(2σd)=(1−M1)erfc[M2−13⋅N0Eblog2M]
特别的,当
M
=
2
M=2
M=2, bpsk
P b = 1 2 e r f c ( E / N 0 ) P_b = \frac{1}{2}\mathrm{erfc}(\sqrt{E/N_0}) Pb=21erfc(E/N0)
QAM
对于QAM,可以相当于两路PAM信号,因此有
P
e
,
M
−
QAM
=
1
−
(
1
−
P
e
,
M
−
PAM
)
2
=
2
P
e
,
M
−
PAM
(
1
−
1
2
P
e
,
M
−
PAM
)
≈
2
P
e
,
M
−
PAM
=
2
(
1
−
1
M
)
e
r
f
c
[
3
M
−
1
⋅
0.5
E
b
log
2
M
N
0
]
\begin{equation} \begin{aligned} P_{e,M-\text{QAM}} &= 1-(1-P_{e,\sqrt{M}-\text{PAM}})^2\\ &=2P_{e,\sqrt{M}-\text{PAM}}\left(1-\frac{1}{2}P_{e,\sqrt{M}-\text{PAM}}\right)\\ &\approx 2P_{e,\sqrt{M}-\text{PAM}}\\ &=2\left(1-\frac{1}{\sqrt{M}}\right)\mathrm{erfc}\left[\sqrt{\frac{3}{M-1}\cdot\frac{0.5E_b\log_2M}{N_0}}\right] \end{aligned} \end{equation}
Pe,M−QAM=1−(1−Pe,M−PAM)2=2Pe,M−PAM(1−21Pe,M−PAM)≈2Pe,M−PAM=2(1−M1)erfc[M−13⋅N00.5Eblog2M]
For QPSK system,BER
P
e
,
QPSK
=
e
r
f
c
(
E
b
/
N
0
)
P_{e,\textrm{QPSK}}=\mathrm{erfc}(\sqrt{E_b/N_0})
Pe,QPSK=erfc(Eb/N0)
PSK
P e = 2 Q ( ( 2 log 2 M ) sin 2 ( π M ) E b N 0 ) = e r f c ( sin ( π M ) E b log 2 M N 0 ) P_e=2Q\left(\sqrt{(2\log_2M)\sin^2\left(\frac{\pi}{M}\right)\frac{E_b}{N_0}}\right)=\mathrm{erfc}\left(\sin\left(\frac{\pi}{M}\right)\sqrt{\frac{E_b \log_2 M }{N_0}}\right) Pe=2Q((2log2M)sin2(Mπ)N0Eb)=erfc(sin(Mπ)N0Eblog2M)

误比特率 Pb
典型的通信系统使用格雷编码调制映射,即相邻符号中对应的信息比特只相差一个比特。当一个符号被错误判决时,它通常会落入相邻的符号内,因此每个符号错误都会导致
log
2
M
\log_2 M
log2M 比特种的一个比特出错,因此符号错误和比特错误(bit errior rate)之间的关系是
P
b
≈
P
s
/
log
2
M
P_b\approx P_s/\log_2M
Pb≈Ps/log2M
PAM
P b , PAM = 1 log 2 M ( 1 − 1 M ) e r f c [ 3 M 2 − 1 ⋅ E b log 2 M N 0 ] P_{b,\text{PAM}}=\frac{1}{\log_2M}\left(1-\frac{1}{M}\right)\mathrm{erfc}\left[\sqrt{\frac{3}{M^2-1}\cdot\frac{E_b\log_2M}{N_0}}\right] Pb,PAM=log2M1(1−M1)erfc[M2−13⋅N0Eblog2M]
QAM
P b , QAM = 2 log 2 M ( 1 − 1 M ) e r f c [ 3 M − 1 ⋅ 0.5 E b log 2 M N 0 ] P_{b,\text{QAM}}=\frac{2}{\log_2M}\left(1-\frac{1}{\sqrt{M}}\right)\mathrm{erfc}\left[\sqrt{\frac{3}{M-1}\cdot\frac{0.5E_b\log_2M}{N_0}}\right] Pb,QAM=log2M2(1−M1)erfc[M−13⋅N00.5Eblog2M]
PSK
P b , PSK = 1 log 2 M e r f c ( sin ( π M ) E b log 2 M N 0 ) P_{b,\text{PSK}}=\frac{1}{\log_2M}\mathrm{erfc}\left(\sin\left(\frac{\pi}{M}\right)\sqrt{\frac{E_b \log_2 M }{N_0}}\right) Pb,PSK=log2M1erfc(sin(Mπ)N0Eblog2M)
注意 P b , bpsk = P b , QPSK = 0.5 e r f c E b / N 0 P_{b,\text{bpsk}}=P_{b,\text{QPSK}}=0.5\mathrm{erfc}{\sqrt{E_b/N_0}} Pb,bpsk=Pb,QPSK=0.5erfcEb/N0

Q(x) and erfc
Q
(
x
)
=
1
2
π
∫
x
∞
exp
(
−
t
2
/
2
)
d
t
Q(x)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}}\int_{x}^{\infty}\exp(-t^{2}/2)dt
Q(x)=2π1∫x∞exp(−t2/2)dt
The Q function is related to the complementary error function, erfc, according to
Q
(
x
)
=
1
2
e
r
f
c
(
x
2
)
,
e
r
f
c
(
x
)
=
2
Q
(
2
x
)
Q(x) = \frac{1}{2}\mathrm{erfc}\left(\frac{x}{\sqrt{2}}\right),\mathrm{erfc}(x)=2Q(\sqrt{2}x)
Q(x)=21erfc(2x),erfc(x)=2Q(2x)
[1] Modulation roundup: error rates, noise, and capacity
[2] J. Proakis and M. Salehi, Digital Communications, 5th Edition, 5th edition. Boston: McGraw-Hill Education, 2007.

开放原子开发者工作坊旨在鼓励更多人参与开源活动,与志同道合的开发者们相互交流开发经验、分享开发心得、获取前沿技术趋势。工作坊有多种形式的开发者活动,如meetup、训练营等,主打技术交流,干货满满,真诚地邀请各位开发者共同参与!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容





所有评论(0)