【CSS】1827- 一次搞懂数据大屏适配方案 (vw vh、rem、scale)
作者:懒惰的智慧https://juejin.cn/post/7163932925955112996前言当接到可视化大屏需求时,你是否会有以下疑问????如何做一款定制化的数据大屏?发可视化数据大屏如何做自适应?vmvh、rem、scale到底哪种比较好?时间不够,有没有偷懒的方法?最近在公司开发了一个可视化大屏,开发定制化大屏,大家可能都一个感受,开发大屏主要是两方面的工作:大屏之关键-前期的自
作者:懒惰的智慧
https://juejin.cn/post/7163932925955112996
前言
当接到可视化大屏需求时,你是否会有以下疑问👇
如何做一款定制化的数据大屏?
发可视化数据大屏如何做自适应?
vmvh、rem、scale到底哪种比较好?
时间不够,有没有偷懒的方法?
最近在公司开发了一个可视化大屏,开发定制化大屏,大家可能都一个感受,开发大屏主要是两方面的工作:
大屏之关键-前期的自适应适配根据 ui 稿绘制图表,调细节
而解决了适配问题后,后面就只是一个慢工出细活,耗时间的事情了。
适配方案分析
看了网上的各种方案,目前大家采用的大概有 3 种👇
| 方案 | 实现方式 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| vm vh | 1.按照设计稿的尺寸,将px按比例计算转为vw和vh | 1.可以动态计算图表的宽高,字体等,灵活性较高 2.当屏幕比例跟 ui 稿不一致时,不会出现两边留白情况 | 1.每个图表都需要单独做字体、间距、位移的适配,比较麻烦 |
| scale | 1.通过 scale 属性,根据屏幕大小,对图表进行整体的等比缩放 | 1.代码量少,适配简单 2.一次处理后不需要在各个图表中再去单独适配 | 1.因为是根据 ui 稿等比缩放,当大屏跟 ui 稿的比例不一样时,会出现周边留白情况 2.当缩放比例过大时候,字体会有一点点模糊,就一点点 3.当缩放比例过大时候,事件热区会偏移。 |
| rem + vm vh | 1.获得 rem 的基准值 2.动态的计算html根元素的font-size 3.图表中通过 vm vh 动态计算字体、间距、位移等 | 1.布局的自适应代码量少,适配简单 | 1.因为是根据 ui 稿等比缩放,当大屏跟 ui 稿的比例不一样时,会出现周边留白情况 2.图表需要单个做字体、间距、位移的适配 |
以上 3 种方案在实际应用中该怎么选择视具体情况而定,也有看到大家说自适应在地图的适配中会有一些兼容问题,我这边还没有实践过。
如果想简单,客户能同意留白,选用
scale即可如果需要兼容不同比例的大屏,并且想在不同比例中都有比较好的效果,图表占满屏幕,类似于移动端的响应式,可以采用 vm vh 的方案
至于 rem,个人觉得就是 scale 和 vm vh 的综合,最终的效果跟
scale差不多
接下来介绍下三种方案的具体实现,方案中的代码都以 vue2.0 和 vue-cli3 搭建的 vue 项目为例,因为是 demo,图表的一些细节就没有过多细致的调整了
方案一:vw vh
上效果
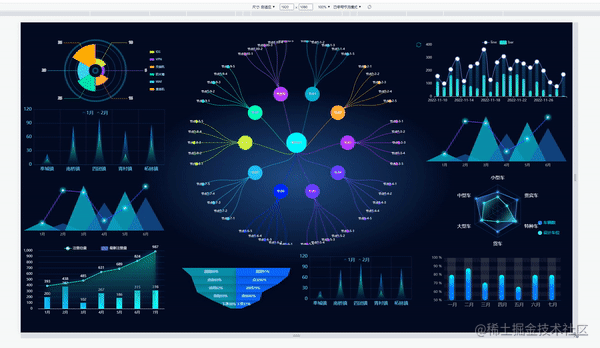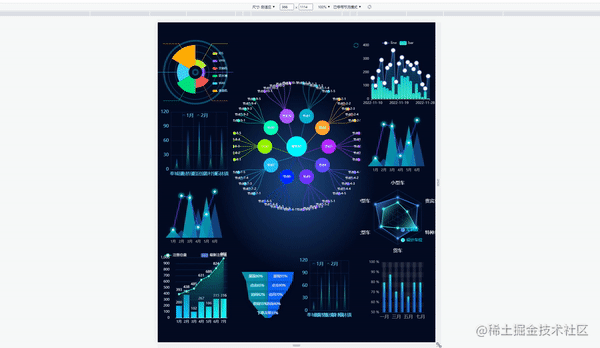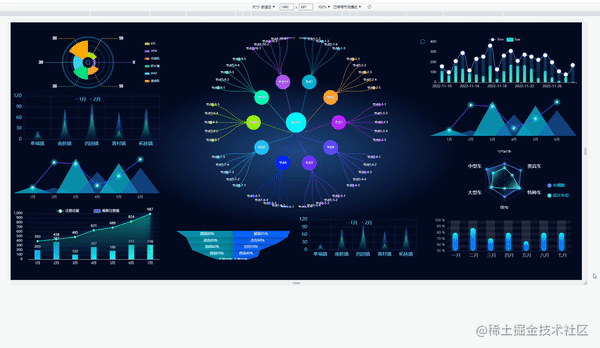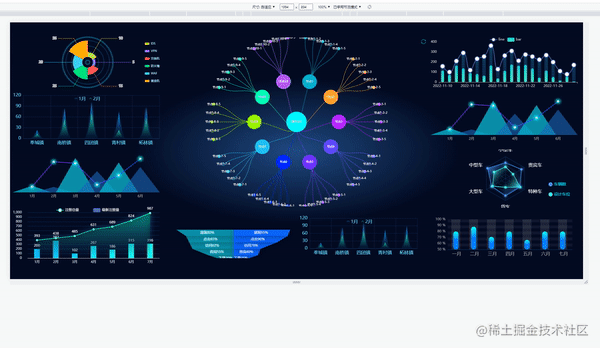
当屏幕的尺寸比例刚好是 16:9 时
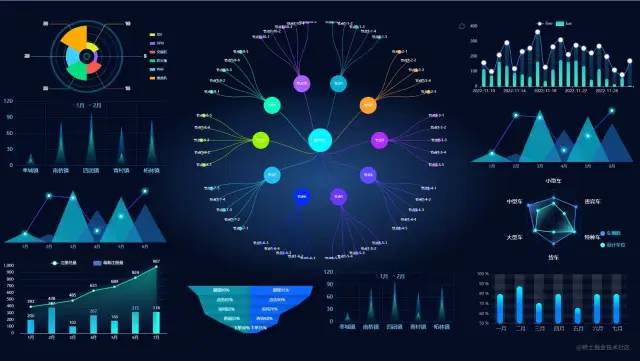
当屏幕的尺寸比例大于 16:9 时
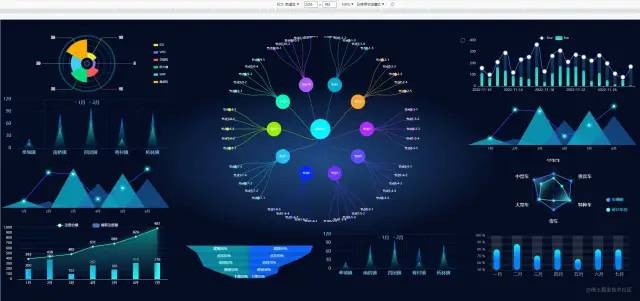
当屏幕的尺寸比例小于 16:9 时
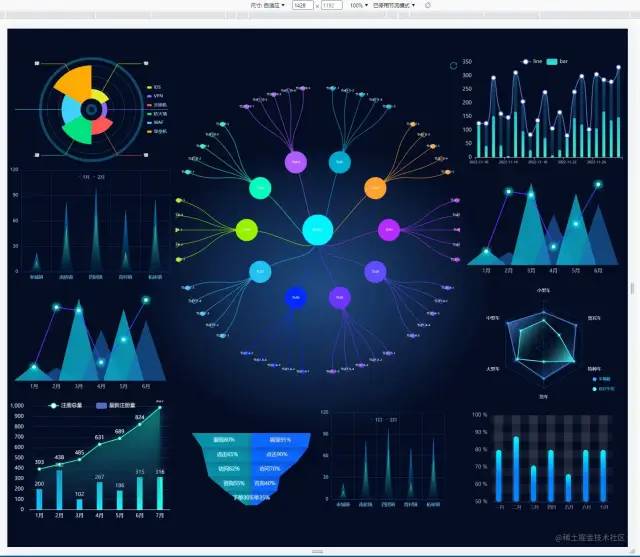
实现思路
按照设计稿的尺寸,将px按比例计算转为vw和vh,转换公式如下
假设设计稿尺寸为 1920*1080(做之前一定问清楚 ui 设计稿的尺寸)
即:
网页宽度=1920px
网页高度=1080px
我们都知道
网页宽度=100vw
网页宽度=100vh
所以,在 1920px*1080px 的屏幕分辨率下
1920px = 100vw
1080px = 100vh
这样一来,以一个宽 300px 和 200px 的 div 来说,其所占的宽高,以 vw 和 vh 为单位,计算方式如下:
vwDiv = (300px / 1920px ) * 100vw
vhDiv = (200px / 1080px ) * 100vh
所以,就在 1920*1080 的屏幕分辨率下,计算出了单个 div 的宽高
当屏幕放大或者缩小时,div 还是以 vw 和 vh 作为宽高的,就会自动适应不同分辨率的屏幕话不多说,上代码
css 方案 - sass
util.scss
// 使用 scss 的 math 函数,https://sass-lang.com/documentation/breaking-changes/slash-div
@use "sass:math";
// 默认设计稿的宽度
$designWidth: 1920;
// 默认设计稿的高度
$designHeight: 1080;
// px 转为 vw 的函数
@function vw($px) {
@return math.div($px, $designWidth) * 100vw;
}
// px 转为 vh 的函数
@function vh($px) {
@return math.div($px, $designHeight) * 100vh;
}路径配置
只需在vue.config.js里配置一下utils.scss的路径,就可以全局使用了
vue.config.js
const path = require("path");
function resolve(dir) {
return path.join(__dirname, dir);
}
module.exports = {
publicPath: "",
configureWebpack: {
name: "app name",
resolve: {
alias: {
"@": resolve("src"),
},
},
},
css: {
// 全局配置 utils.scs,详细配置参考 vue-cli 官网
loaderOptions: {
sass: {
prependData: `@import "@/styles/utils.scss";`,
},
},
},
};在 .vue 中使用
<template>
<div class="box">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
name: "Box",
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped="scoped">
/*
直接使用 vw 和 vh 函数,将像素值传进去,得到的就是具体的 vw vh 单位
*/
.box{
width: vw(300);
height: vh(100);
font-size: vh(16);
background-color: black;
margin-left: vw(10);
margin-top: vh(10);
border: vh(2) solid red;
}
</style>css 方案 - less
utils.less
@charset "utf-8";
// 默认设计稿的宽度
@designWidth: 1920;
// 默认设计稿的高度
@designHeight: 1080;
.px2vw(@name, @px) {
@{name}: (@px / @designWidth) * 100vw;
}
.px2vh(@name, @px) {
@{name}: (@px / @designHeight) * 100vh;
}
.px2font(@px) {
font-size: (@px / @designWidth) * 100vw;
}路径配置
在vue.config.js里配置一下utils.less
const path = require("path");
function resolve(dir) {
return path.join(__dirname, dir);
}
module.exports = {
publicPath: "",
configureWebpack: {
name: "app name",
resolve: {
alias: {
"@": resolve("src"),
},
},
},
css: {
// 全局配置utils.scss
loaderOptions: {
less: {
additionalData: `@import "@/styles/utils.less";`,
},
},
},
};在 .vue 文件中使用
<template>
<div class="box">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
name: "Box",
}
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped="scoped">
/*
直接使用 vw 和 vh 函数,将像素值传进去,得到的就是具体的 vw vh单位
*/
.box{
.px2vw(width, 300);
.px2vh(height, 100);
.px2font(16);
.px2vw(margin-left, 300);
.px2vh(margin-top, 100);
background-color: black;
}
</style>定义 js 样式处理函数
// 定义设计稿的宽高
const designWidth = 1920;
const designHeight = 1080;
// px转vw
export const px2vw = (_px) => {
return (_px * 100.0) / designWidth + 'vw';
};
export const px2vh = (_px) => {
return (_px * 100.0) / designHeight + 'vh';
};
export const px2font = (_px) => {
return (_px * 100.0) / designWidth + 'vw';
};屏幕变化后,图表自动调整
这种使用方式有个弊端,就是屏幕尺寸发生变化后,需要手动刷新一下才能完成自适应调整
为了解决这个问题,你需要在各个图表中监听页面尺寸变化,重新调整图表,在 vue 项目中,也可以借助element-resize-detector,最好封装个 resize 的指令,在各图表中就只要使用该指令就可以了,毕竟作为程序员,能偷懒就偷懒
安装 element-resize-detector
npm install element-resize-detector --save
引入工具包在组件中使用或者在单独的 js 中使用
import resizeDetector from 'element-resize-detector'
封装 directive
// directive.js
import * as ECharts from "echarts";
import elementResizeDetectorMaker from "element-resize-detector";
import Vue from "vue";
const HANDLER = "_vue_resize_handler";
function bind(el, binding) {
el[HANDLER] = binding.value
? binding.value
: () => {
let chart = ECharts.getInstanceByDom(el);
if (!chart) {
return;
}
chart.resize();
};
// 监听绑定的div大小变化,更新 echarts 大小
elementResizeDetectorMaker().listenTo(el, el[HANDLER]);
}
function unbind(el) {
// window.removeEventListener("resize", el[HANDLER]);
elementResizeDetectorMaker().removeListener(el, el[HANDLER]);
delete el[HANDLER];
}
// 自定义指令:v-chart-resize 示例:v-chart-resize="fn"
Vue.directive("chart-resize", { bind, unbind });main.js 中引入
import '@/directive/directive';html 代码
<template>
<div class="linechart">
<div ref="chart" v-chart-resize class="chart"></div>
</div>
</template>这里要注意的是,图表中如果需要 tab 切换动态更新图表数据,在更新数据时一定不要用 echarts 的 dispose 方法先将图表移除,再重新绘制,因为 resize 指令中挂载到的图表实例还是旧的,就监听不到新的 chart 元素的 resize 了,更新数据只需要用 chart 的 setOption 方法重新设置配置项即可。
图表字体、间距、位移等尺寸自适应
echarts 的字体大小只支持具体数值(像素),不能用百分比或者 vw 等尺寸,一般字体不会去做自适应,当宽高比跟 ui 稿比例出入太大时,会出现文字跟图表重叠的情况
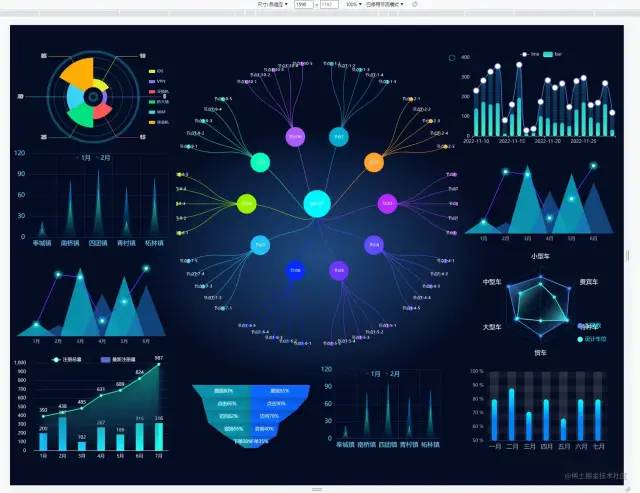
这里我们就需要封装一个工具函数,来处理图表中文字自适应了👇
默认情况下,这里以你的设计稿是 1920*1080 为例,即网页宽度是 1920px (做之前一定问清楚 ui 设计稿的尺寸)
把这个函数写在一个单独的工具文件
dataUtil.js里面,在需要的时候调用其原理是计算出当前屏幕宽度和默认设计宽度的比值,将原始的尺寸乘以该值
另外,其它 echarts 的配置项,比如间距、定位、边距也可以用该函数
编写 dataUtil.js 工具函数
// Echarts图表字体、间距自适应
export const fitChartSize = (size,defalteWidth = 1920) => {
let clientWidth = window.innerWidth||document.documentElement.clientWidth||document.body.clientWidth;
if (!clientWidth) return size;
let scale = (clientWidth / defalteWidth);
return Number((size*scale).toFixed(3));
}将函数挂载到原型上
import {fitChartSize} from '@src/utils/dataUtil.js'
Vue.prototype.fitChartFont = fitChartSize;这样你可以在
.vue文件中直接使用this.fitChartSize()调用
<template>
<div class="chartsdom" ref="chart" v-chart-resize></div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "dashboardChart",
data() {
return {
option: null,
};
},
mounted() {
this.getEchart();
},
methods: {
getEchart() {
let myChart = this.$echarts.init(this.$refs.chart);
const option = {
backgroundColor: "transparent",
tooltip: {
trigger: "item",
formatter: "{a} <br/>{b} : {c}%",
},
grid: {
left: this.fitChartSize(10),
right: this.fitChartSize(20),
top: this.fitChartSize(20),
bottom: this.fitChartSize(10),
containLabel: true,
},
calculable: true,
series: [
{
color: ["#0db1cdcc"],
name: "计划投入",
type: "funnel",
width: "45%",
height: "70%",
x: "5%",
minSize: "10%",
funnelAlign: "right",
center: ["50%", "50%"], // for pie
data: [
{
value: 30,
name: "下单30%",
},
{
value: 55,
name: "咨询55%",
},
{
value: 65,
name: "点击65%",
},
{
value: 60,
name: "访问62%",
},
{
value: 80,
name: "展现80%",
},
].sort(function (a, b) {
return a.value - b.value;
}),
roseType: true,
label: {
normal: {
formatter: function () {},
position: "inside",
},
},
itemStyle: {
normal: {
borderWidth: 0,
shadowBlur: this.fitChartSize(20),
shadowOffsetX: 0,
shadowOffsetY: this.fitChartSize(5),
shadowColor: "rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3)",
},
},
},
{
color: ["#0C66FF"],
name: "实际投入",
type: "funnel",
width: "45%",
height: "70%",
x: "50%",
minSize: "10%",
funnelAlign: "left",
center: ["50%", "50%"], // for pie
data: [
{
value: 35,
name: "下单35%",
},
{
value: 40,
name: "咨询40%",
},
{
value: 70,
name: "访问70%",
},
{
value: 90,
name: "点击90%",
},
{
value: 95,
name: "展现95%",
},
].sort(function (a, b) {
return a.value - b.value;
}),
roseType: true,
label: {
normal: {
position: "inside",
},
},
itemStyle: {
normal: {
borderWidth: 0,
shadowBlur: this.fitChartSize(20),
shadowOffsetX: 0,
shadowOffsetY: this.fitChartSize(5),
shadowColor: "rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3)",
},
},
},
],
};
myChart.setOption(option, true);
},
},
beforeDestroy() {},
};
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.chartsdom {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>方案二:scale
通过 css 的 scale 属性,根据屏幕大小,对图表进行整体的等比缩放,从而达到自适应效果
上效果
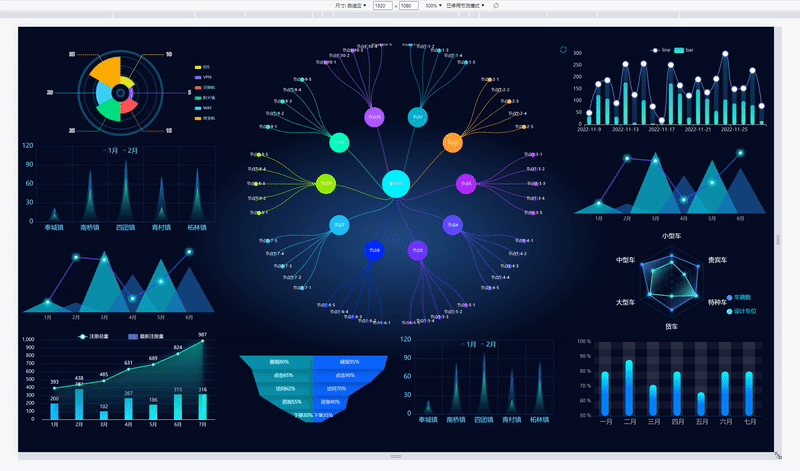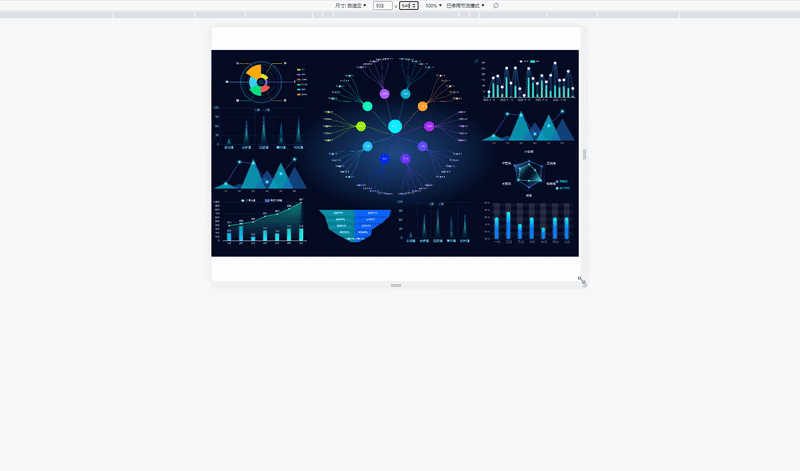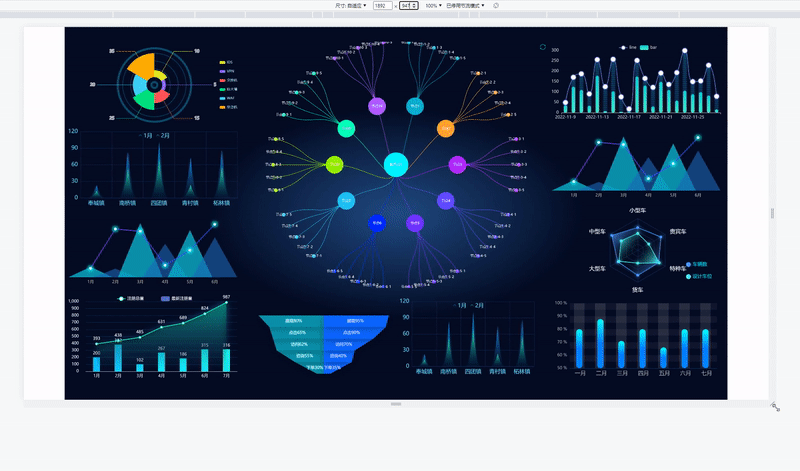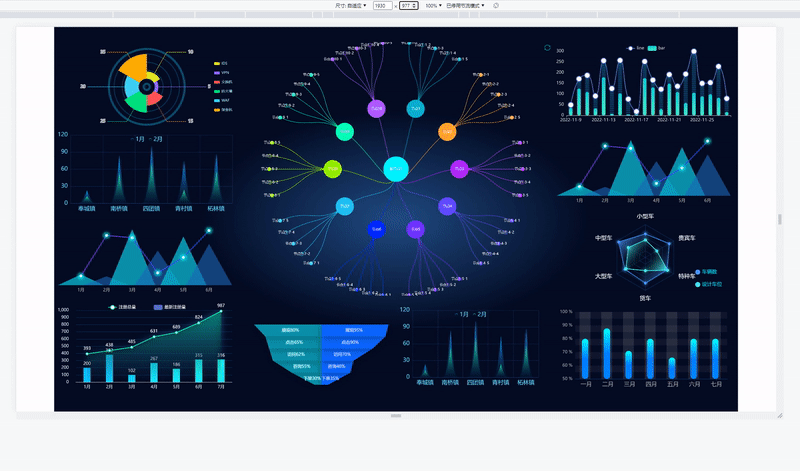
当屏幕的尺寸比例刚好是 16:9 时,页面能刚好全屏展示,内容占满显示器
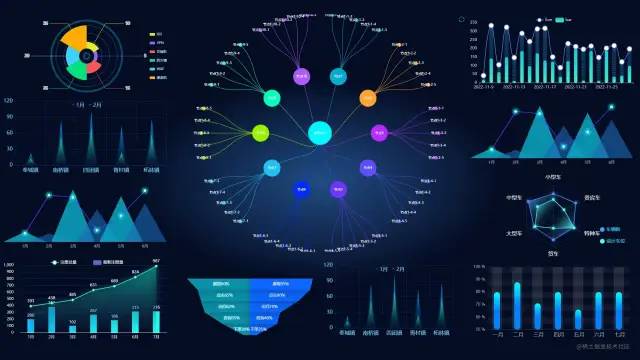
当屏幕的尺寸比例小于 16:9 时,页面上下留白,左右占满并上下居中,显示比例保持 16:9
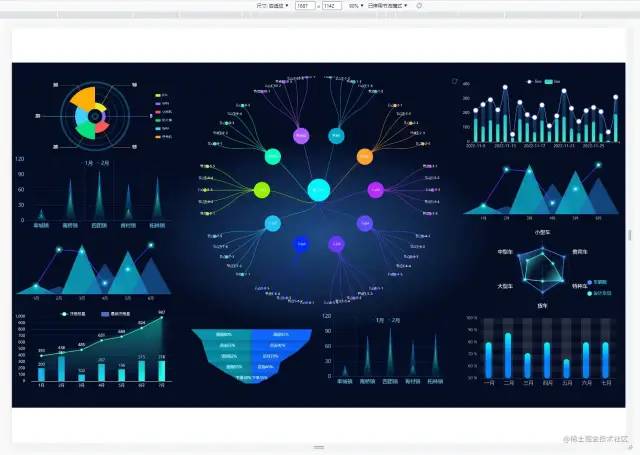
当屏幕尺寸比例大于 16:9 时,页面左右留白,上下占满并居中,显示比例保持 16:9
话不多说,上代码
html 部分
<div className="screen-wrapper">
<div className="screen" id="screen">
</div>
</div>js 部分
<script>
export default {
mounted() {
// 初始化自适应 ----在刚显示的时候就开始适配一次
handleScreenAuto();
// 绑定自适应函数 ---防止浏览器栏变化后不再适配
window.onresize = () => handleScreenAuto();
},
deleted() {
window.onresize = null;
},
methods: {
// 数据大屏自适应函数
handleScreenAuto() {
const designDraftWidth = 1920; //设计稿的宽度
const designDraftHeight = 960; //设计稿的高度
// 根据屏幕的变化适配的比例
const scale =
document.documentElement.clientWidth /
document.documentElement.clientHeight <
designDraftWidth / designDraftHeight
? document.documentElement.clientWidth / designDraftWidth
: document.documentElement.clientHeight / designDraftHeight;
// 缩放比例
document.querySelector(
'#screen',
).style.transform = `scale(${scale}) translate(-50%, -50%)`;
},
},
};
</script>css部分
/*
除了设计稿的宽高是根据您自己的设计稿决定以外,其他复制粘贴就完事
*/
.screen-root {
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
.screen {
display: inline-block;
width: 1920px; //设计稿的宽度
height: 960px; //设计稿的高度
transform-origin: 0 0;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: -50%;
}
}实现思路
如何缩放
当屏幕宽高比 < 设计稿宽高比,我们需要缩放的比例是屏幕宽度 / 设计稿宽度当屏幕宽高比 > 设计稿宽高比,我们需要缩放的比例是屏幕高度 / 设计稿高度
const scale = document.documentElement.clientWidth / document.documentElement.clientHeight < designDraftWidth / designDraftHeight ?
(document.documentElement.clientWidth / designDraftWidth) :
(document.documentElement.clientHeight / designDraftHeight);如果我们拿到的设计稿宽高为: 1920 * 960 px ,而我们的屏幕大小是 1440 * 900 px,那么 1440/900 = 1.6,920/960 = 2
因为 1.6 < 2 (当前屏幕宽高比小于设计稿宽高比)
所以我们需要缩放的比例是:屏幕宽度除以设计稿宽度 = 1440/1920 = 0.75
如何居中
首先我们利用 transform:translate(-50%,-50%) ,将动画的基点设为左上角
transform-origin:设置动画的基点(中心点),默认点是元素的中心点
语法
transform-origin: x-axis y-axis z-axis;
然后利用transform:translate(-50%,-50%),将图表沿 x,y 轴移动 50%
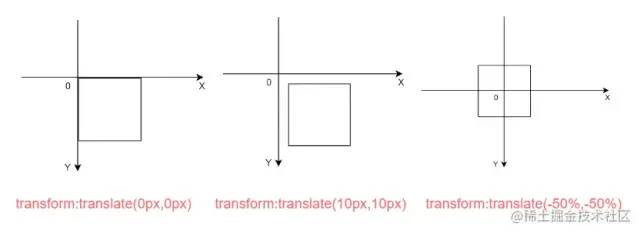
接下来利用绝对定位将图表定位到中间位置
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;偷懒方法-插件
v-scale-screen是使用 css 属性 transform 实现缩放效果的一个大屏自适应组件,通过 scale 进行等比例计算,达到等比例缩放的效果,同时也支持铺满全屏,宽度等比,高度等比,等自适应方案,具体可查大屏自适应终极解决方案[1]
方案三:rem + vw wh
上效果
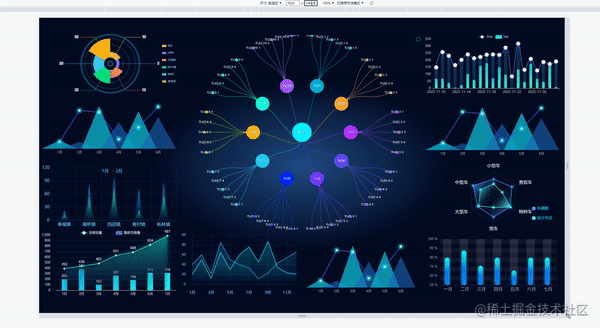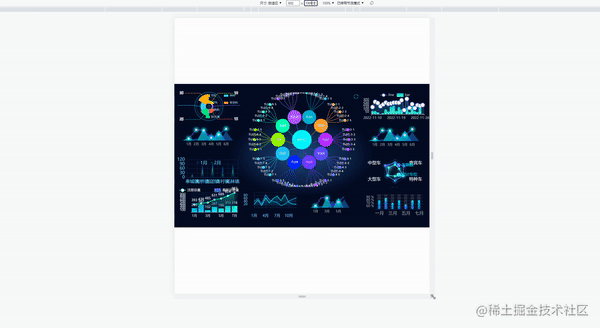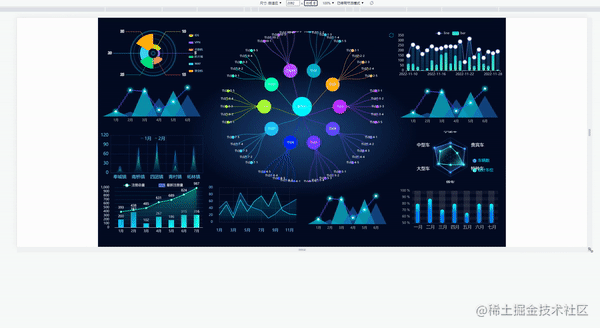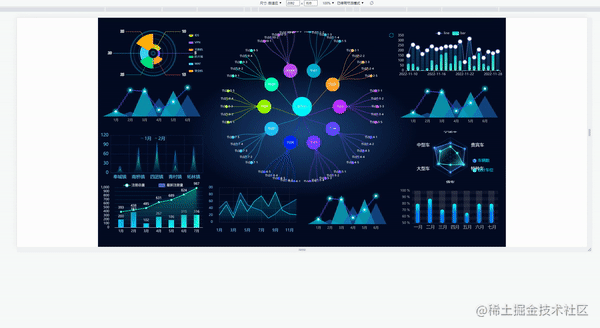
当屏幕的尺寸比例刚好是 16:9 时,页面能刚好全屏展示,内容占满显示器
当屏幕的尺寸比例小于 16:9 时,页面上下留白,左右占满并上下居中,显示比例保持 16:9
当屏幕尺寸比例大于 16:9 时,页面左右留白,上下占满并居中,显示比例保持 16:9
实现思路
关于 rem
rem(font size of the root element),是 css3 中新增的一个大小单位,即相对于根元素 font-size 值的大小。
自适应思路
动态的计算出页面的 fontsize 从而改变 rem 的大小。
拿 1920 * 1080 的标准屏幕大小为例,将屏幕分为
10份,先计算rem 的基准值:1920 / 10 = 192;把所有元素的长、宽、位置、字体大小等原来的 px 单位全部转换成 rem;
网页加载后,用 js 去计算当前浏览器的宽度,并设置 html 的 font-size 为 (
当前浏览器窗口宽度 / 10) 。
这样的话 10rem 就刚好等于浏览器窗口的宽度,也就可以保证 100% 宽度,等比例缩放设计稿的页面了。
因此 rem + vm vh 方案要解决三件事
获得 rem 的基准值;
页面内写一段 js 代码,动态的计算
html根元素的font-size;屏幕变化后,图表自动调整和图表字体、间距、位移等的自适应。
实现方案
第一点:获得 rem 的基准值
首先安装
@njleonzhang/postcss-px-to-rem这个包
npm i @njleonzhang/postcss-px-to-rem -D在项目根目录新建
.postcssrc.js配置文件
module.exports = {
plugins: {
autoprefixer: {},
"@njleonzhang/postcss-px-to-rem": {
unitToConvert: 'px', // (String) 要转换的单位,默认是 px。
widthOfDesignLayout: 1920, // (Number) 设计布局的宽度。对于pc仪表盘,一般是 1920.
unitPrecision: 3, // (Number) 允许 rem 单位增长到的十进制数字.
selectorBlackList: ['.ignore', '.hairlines'], // (Array) 要忽略并保留为 px 的选择器.
minPixelValue: 1, // (Number) 设置要替换的最小像素值.
mediaQuery: false // (Boolean) 允许在媒体查询中转换 px.
}
}
}配置完成后,页面内的 px 就会被转换成 rem 了
第二点:动态的计算html根元素的font-size
在工具函数文件中新建一个 rem.js 文件,用于动态计算 font-size
(function init(screenRatioByDesign = 16 / 9) {
let docEle = document.documentElement
function setHtmlFontSize() {
var screenRatio = docEle.clientWidth / docEle.clientHeight;
var fontSize = (
screenRatio > screenRatioByDesign
? (screenRatioByDesign / screenRatio)
: 1
) * docEle.clientWidth / 10;
docEle.style.fontSize = fontSize.toFixed(3) + "px";
console.log(docEle.style.fontSize);
}
setHtmlFontSize()
window.addEventListener('resize', setHtmlFontSize)
})()2. 在入口文件 main.js 中引入 rem.js 文件
import './utils/rem.js';至此,页面就已经可以实现 16:9 自适应了。
第三点:屏幕变化,图表自适应
屏幕变化后,图表自动调整字体、间距、位移等,此处参考上面 vm vh 的实现方式即可,在此就不重复赘述了
参考资料
推荐一个echarts 的案列网站,需要什么直接图表直接在上面去找,可以省去很多查 echarts 配置的时间全网echarts案例资源大总结和echarts的高效使用技巧(细节版)[2]
scale 方案参考: 数据大屏最简单自适应方案,无需适配rem单位[3]
vm vh 方案参考: Vue+Echarts企业级大屏项目适配方案[4]
rem 方案参考:数据大屏rem适配方案[5]
参考资料
[1]
大屏自适应终极解决方案: https://juejin.cn/post/7075253747567296548
[2]全网echarts案例资源大总结和echarts的高效使用技巧(细节版): https://juejin.cn/post/7078834647005822983
[3]数据大屏最简单自适应方案,无需适配rem单位: https://juejin.cn/post/7148733509744459790
[4]Vue+Echarts企业级大屏项目适配方案: https://juejin.cn/post/7009081081760579591#heading-31
[5]数据大屏rem适配方案: https://juejin.cn/post/7035930041498206216#heading-0
往期回顾
#
如何使用 TypeScript 开发 React 函数式组件?
#
#
#
#
6 个你必须明白 Vue3 的 ref 和 reactive 问题
#
#

回复“加群”,一起学习进步

开放原子开发者工作坊旨在鼓励更多人参与开源活动,与志同道合的开发者们相互交流开发经验、分享开发心得、获取前沿技术趋势。工作坊有多种形式的开发者活动,如meetup、训练营等,主打技术交流,干货满满,真诚地邀请各位开发者共同参与!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献23条内容
已为社区贡献23条内容





所有评论(0)