
鸿蒙开发ArkUI -常用布局
在设置Grid的行列数量与占比时,如果仅设置行、列数量与占比中的一个,即仅设置rowsTemplate或仅设置columnsTemplate属性,网格单元按照设置的方向排列,超出Grid显示区域后,Grid拥有可滚动能力。当使用懒加载方式渲染网格时,为了更好的滚动体验,减少滑动时出现白块,Grid组件中也可通过cachedCount属性设置GridItem的预加载数量,只在懒加载LazyForEa
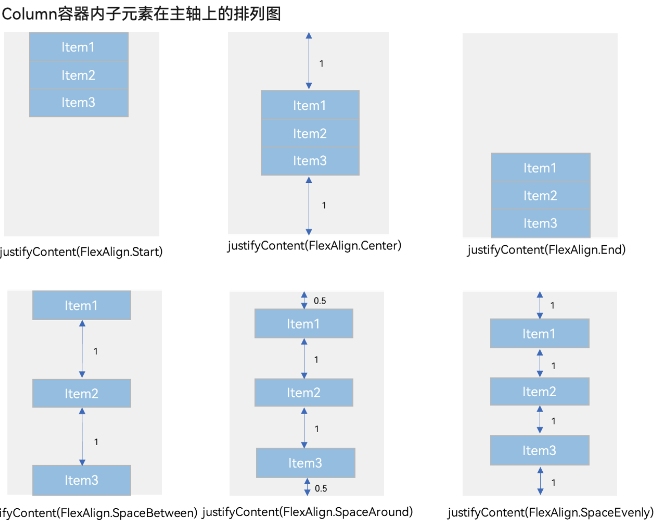
线性布局(Row/Column)
间距/主轴排列方式/交叉轴对齐方式
Column({}) {
Column() {}.width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
Column() {}.width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xD2B48C)
Column() {}.width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
}
.width('100%')
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.End)
.backgroundColor('rgb(242,242,242)')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Start)

自适应拉伸
Blank,在容器主轴方向自动填充空白空间,达到自适应拉伸效果。
Row() {
Text('Bluetooth').fontSize(18)
Blank()
Toggle({ type: ToggleType.Switch, isOn: true })
}.backgroundColor(0xFFFFFF).borderRadius(15).padding({ left: 12 }).width('100%')
自适应缩放
父容器尺寸确定时,可使用layoutWeight属性设置子组件和兄弟元素在主轴上的权重;或者使用百分比设置子组件和兄弟元素的宽度。
layoutWeight属性:
Column() {
Text('1:2:3').width('100%')
Row() {
Column() {
Text('layoutWeight(1)')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
}.layoutWeight(1).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3).height('100%')
Column() {
Text('layoutWeight(2)')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
}.layoutWeight(2).backgroundColor(0xD2B48C).height('100%')
Column() {
Text('layoutWeight(3)')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
}.layoutWeight(3).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3).height('100%')
}.backgroundColor(0xffd306).height('30%')
}
百分比属性:
Column() {
Row() {
Column() {
Text('left width 20%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
}.width('20%').backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3).height('100%')
Column() {
Text('center width 50%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
}.width('50%').backgroundColor(0xD2B48C).height('100%')
Column() {
Text('right width 30%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
}.width('30%').backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3).height('100%')
}.backgroundColor(0xffd306).height('30%')
}
自适应延伸
在线性布局中,开发者可以进行竖向或者横向的布局。当一屏无法完全显示时,可以在Column或Row组件的外层包裹一个可滚动的容器组件Scroll来实现可滑动的线性布局。
@Entry
@Component
struct ScrollExample {
scroller: Scroller = new Scroller();
private arr: number[] = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
build() {
Scroll(this.scroller) {
Column() {
ForEach(this.arr, (item) => {
Text(item.toString())
.width('90%')
.height(150)
.backgroundColor(0xFFFFFF)
.borderRadius(15)
.fontSize(16)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.margin({ top: 10 })
}, item => item)
}.width('100%')
}
.backgroundColor(0xDCDCDC)
.scrollable(ScrollDirection.Vertical) // 滚动方向纵向
.scrollBar(BarState.On) // 滚动条常驻显示
.scrollBarColor(Color.Gray) // 滚动条颜色
.scrollBarWidth(10) // 滚动条宽度
.edgeEffect(EdgeEffect.Spring) // 滚动到边沿后回弹
}
}
层叠布局(Stack)
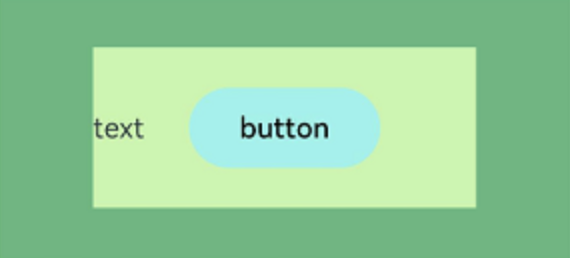
Stack组件为容器组件,其中子组件默认进行居中堆叠。
Column(){
Stack({ }) {
Column(){}.width('90%').height('100%').backgroundColor('#ff58b87c')
Text('text').width('60%').height('60%').backgroundColor('#ffc3f6aa')
Button('button').width('30%').height('30%').backgroundColor('#ff8ff3eb').fontColor('#000')
}.width('100%').height(150).margin({ top: 50 })
}
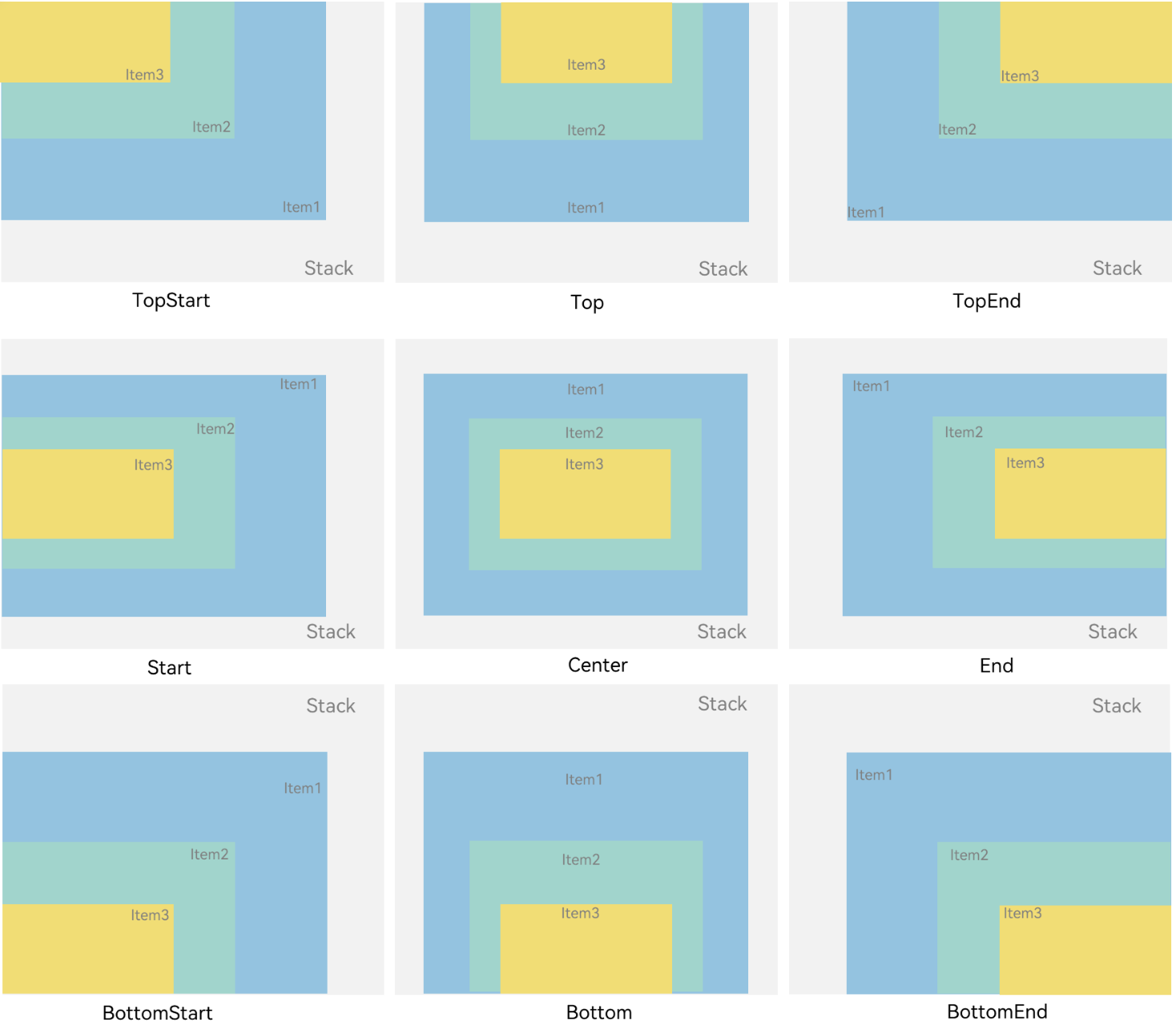
对齐方式
Stack组件通过alignContent参数实现位置的相对移动。如图2所示,支持九种对齐方式。
Z序控制
Stack容器中兄弟组件显示层级关系可以通过Z序控制的zIndex属性改变。zIndex值越大,显示层级越高,即zIndex值大的组件会覆盖在zIndex值小的组件上方。
Stack({ alignContent: Alignment.BottomStart }) {
Column() {
Text('Stack子元素1').fontSize(20)
}.width(100).height(100).backgroundColor(0xffd306).zIndex(2)
Column() {
Text('Stack子元素2').fontSize(20)
}.width(150).height(150).backgroundColor(Color.Pink).zIndex(1)
Column() {
Text('Stack子元素3').fontSize(20)
}.width(200).height(200).backgroundColor(Color.Grey)
}.margin({ top: 100 }).width(350).height(350).backgroundColor(0xe0e0e0)

弹性布局(Flex)
布局方向
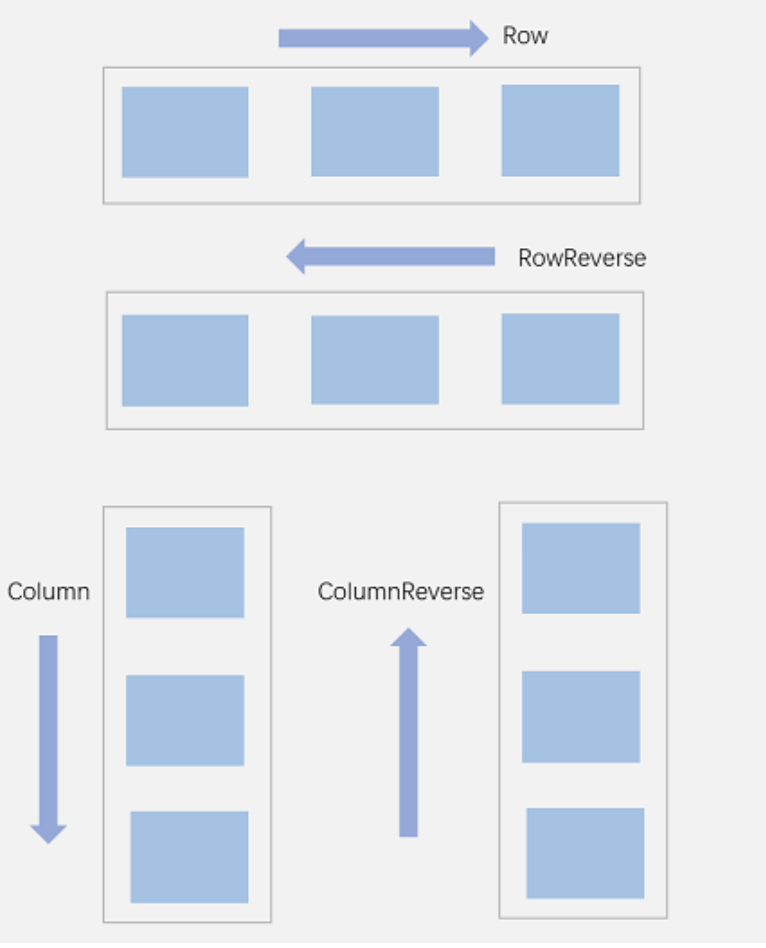
Flex({ direction: FlexDirection.Row }) {
Text('1').width('33%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
Text('2').width('33%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xD2B48C)
Text('3').width('33%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
}
.height(70)
.width('90%')
.padding(10)
.backgroundColor(0xAFEEEE)

布局换行
FlexWrap. Wrap:换行,每一行子组件按照主轴方向排列。
FlexWrap. NoWrap(默认值):不换行。如果子组件的宽度总和大于父元素的宽度,则子组件会被压缩宽度。
FlexWrap. WrapReverse:换行,每一行子组件按照主轴反方向排列。
Flex({ wrap: FlexWrap.Wrap }) {
Text('1').width('50%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
Text('2').width('50%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xD2B48C)
Text('3').width('50%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xD2B48C)
}
.width('90%')
.padding(10)
.backgroundColor(0xAFEEEE)
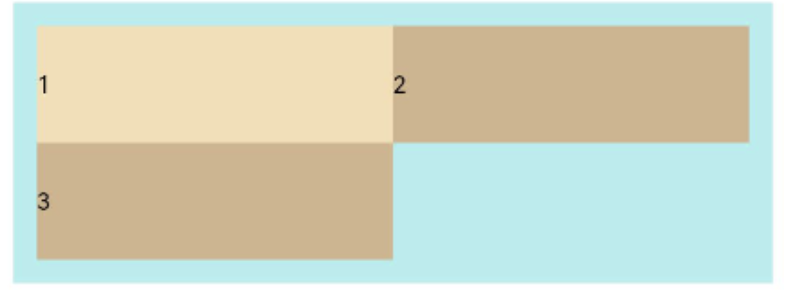
主轴对齐方式
通过justifyContent参数设置在主轴方向的对齐方式。
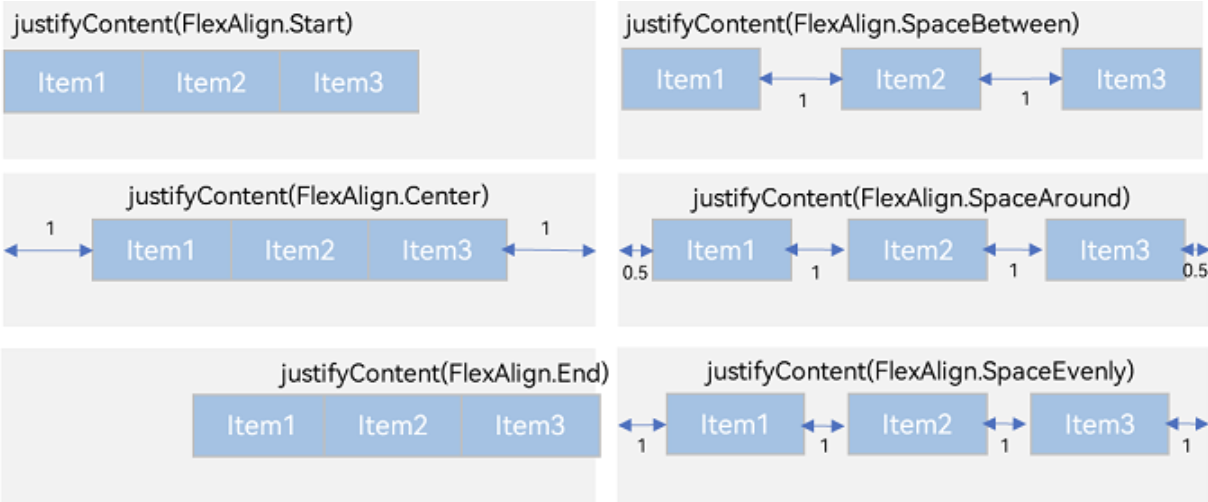
Flex({ justifyContent: FlexAlign.Start }) {
Text('1').width('20%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
Text('2').width('20%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xD2B48C)
Text('3').width('20%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
}
.width('90%')
.padding({ top: 10, bottom: 10 })
.backgroundColor(0xAFEEEE)
交叉轴对齐方式
容器组件设置交叉轴对齐
ItemAlign.Auto:使用Flex容器中默认配置。
ItemAlign.Start:交叉轴方向首部对齐。
ItemAlign.Center:交叉轴方向居中对齐。
ItemAlign.End:交叉轴方向底部对齐。
ItemAlign.Stretch:交叉轴方向拉伸填充,在未设置尺寸时,拉伸到容器尺寸。
ItemAlign. Baseline:交叉轴方向文本基线对齐。
Flex({ alignItems: ItemAlign.Auto }) {
Text('1').width('33%').height(30).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
Text('2').width('33%').height(40).backgroundColor(0xD2B48C)
Text('3').width('33%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
}
.size({ width: '90%', height: 80 })
.padding(10)
.backgroundColor(0xAFEEEE)
子组件设置交叉轴对齐
子组件的alignSelf属性也可以设置子组件在父容器交叉轴的对齐格式,且会覆盖Flex布局容器中alignItems配置。如下例所示:
Flex({ direction: FlexDirection.Row, alignItems: ItemAlign.Center }) { // 容器组件设置子组件居中
Text('alignSelf Start').width('25%').height(80)
.alignSelf(ItemAlign.Start)
.backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
Text('alignSelf Baseline')
.alignSelf(ItemAlign.Baseline)
.width('25%')
.height(80)
.backgroundColor(0xD2B48C)
Text('alignSelf Baseline').width('25%').height(100)
.backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
.alignSelf(ItemAlign.Baseline)
Text('no alignSelf').width('25%').height(100)
.backgroundColor(0xD2B48C)
Text('no alignSelf').width('25%').height(100)
.backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
}.width('90%').height(220).backgroundColor(0xAFEEEE)

内容对齐
可以通过alignContent参数设置子组件各行在交叉轴剩余空间内的对齐方式,只在多行的flex布局中生效,可选值有:
FlexAlign.Start:子组件各行与交叉轴起点对齐。
FlexAlign.Center:子组件各行在交叉轴方向居中对齐。
FlexAlign.End:子组件各行与交叉轴终点对齐。
FlexAlign.SpaceBetween:子组件各行与交叉轴两端对齐,各行间垂直间距平均分布。
FlexAlign.SpaceAround:子组件各行间距相等,是元素首尾行与交叉轴两端距离的两倍。
FlexAlign.SpaceEvenly: 子组件各行间距,子组件首尾行与交叉轴两端距离都相等。
Flex({ justifyContent: FlexAlign.SpaceBetween, wrap: FlexWrap.Wrap, alignContent: FlexAlign.Start }) {
Text('1').width('30%').height(20).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
Text('2').width('60%').height(20).backgroundColor(0xD2B48C)
Text('3').width('40%').height(20).backgroundColor(0xD2B48C)
Text('4').width('30%').height(20).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
Text('5').width('20%').height(20).backgroundColor(0xD2B48C)
}
.width('90%')
.height(100)
.backgroundColor(0xAFEEEE)

自适应拉伸
flexBasis:设置子组件在父容器主轴方向上的基准尺寸。如果设置了该值,则子项占用的空间为设置的值;如果没设置该属性,那子项的空间为width/height的值。
flexGrow:设置父容器的剩余空间分配给此属性所在组件的比例。用于“瓜分”父组件的剩余空间。
flexShrink: 当父容器空间不足时,子组件的压缩比例。
Flex() {
Text('flexGrow(2)')
.flexGrow(2)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
Text('flexGrow(3)')
.flexGrow(3)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor(0xD2B48C)
Text('no flexGrow')
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
}.width(400).height(120).padding(10).backgroundColor(0xAFEEEE)
场景实例
使用弹性布局,可以实现子组件沿水平方向排列,两端对齐,子组件间距平分,竖直方向上子组件居中的效果。
@Entry
@Component
struct FlexExample {
build() {
Column() {
Column({ space: 5 }) {
Flex({ direction: FlexDirection.Row, wrap: FlexWrap.NoWrap, justifyContent: FlexAlign.SpaceBetween, alignItems: ItemAlign.Center }) {
Text('1').width('30%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
Text('2').width('30%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xD2B48C)
Text('3').width('30%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
}
.height(70)
.width('90%')
.backgroundColor(0xAFEEEE)
}.width('100%').margin({ top: 5 })
}.width('100%')
}
}

相对布局(RelativeContainer)
基本概念
- 锚点:通过锚点设置当前元素基于哪个元素确定位置。
- 对齐方式:通过对齐方式,设置当前元素是基于锚点的上中下对齐,还是基于锚点的左中右对齐。
设置依赖关系
锚点设置
RelativeContainer父组件为锚点,__container__代表父容器的id,ID默认为“container”,其余子元素的ID通过id属性设置。未设置ID的子元素在RelativeContainer中不会显示。
设置相对于锚点的对齐位置
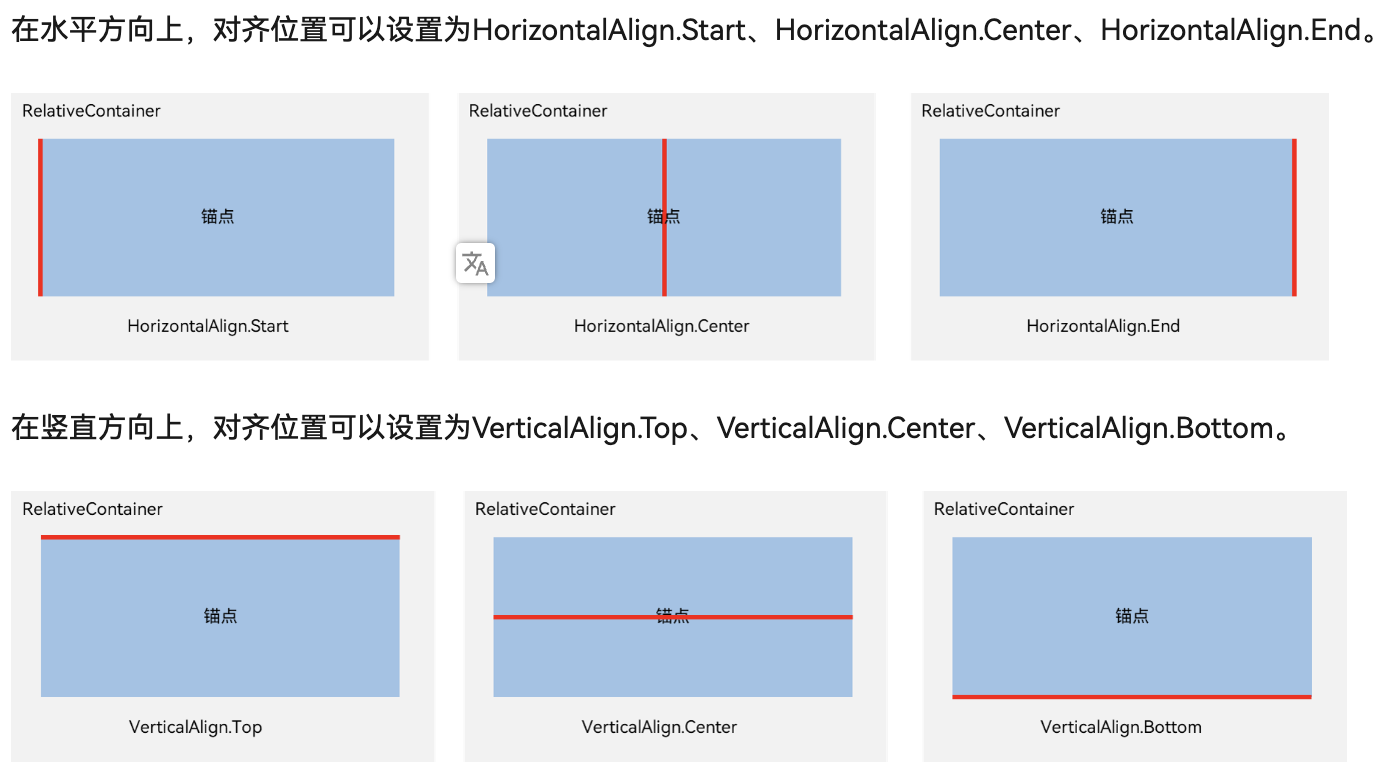
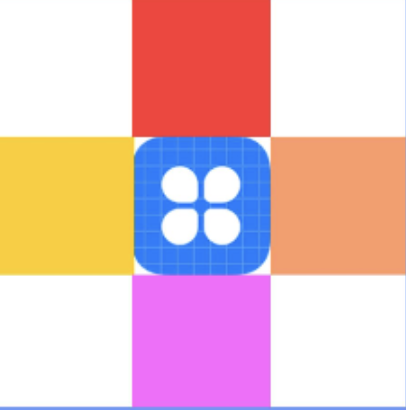
场景实例
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Row() {
RelativeContainer() {
Row()
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#FF3333')
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: '__container__', align: VerticalAlign.Top }, //以父容器为锚点,竖直方向顶头对齐
middle: { anchor: '__container__', align: HorizontalAlign.Center } //以父容器为锚点,水平方向居中对齐
})
.id('row1') //设置锚点为row1
Row() {
Image($r('app.media.icon'))
}
.height(100).width(100)
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: 'row1', align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }, //以row1组件为锚点,竖直方向低端对齐
left: { anchor: 'row1', align: HorizontalAlign.Start } //以row1组件为锚点,水平方向开头对齐
})
.id('row2') //设置锚点为row2
Row()
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#FFCC00')
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: 'row2', align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.id('row3') //设置锚点为row3
Row()
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#FF9966')
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: 'row2', align: VerticalAlign.Top },
left: { anchor: 'row2', align: HorizontalAlign.End },
})
.id('row4') //设置锚点为row4
Row()
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#FF66FF')
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: 'row2', align: VerticalAlign.Bottom },
middle: { anchor: 'row2', align: HorizontalAlign.Center }
})
.id('row5') //设置锚点为row5
}
.width(300).height(300)
.border({ width: 2, color: '#6699FF' })
}
.height('100%').margin({ left: 30 })
}
}

轮播(Swiper)
布局与约束
Swiper作为一个容器组件,在自身尺寸属性未被设置时,会自动根据子组件的大小设置自身的尺寸。如果开发者对Swiper组件设置了固定的尺寸,则在轮播显示过程中均以该尺寸生效;否则,在轮播过程中,会根据子组件的大小自动调整自身的尺寸。
private swiperController: SwiperController = new SwiperController();
Swiper(this.swiperController) {
Text("0")
.width('90%')
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor(Color.Gray)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.fontSize(30)
Text("1")
.width('90%')
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor(Color.Green)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.fontSize(30)
Text("2")
.width('90%')
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.fontSize(30)
}
.loop(true)
.autoPlay(true) // 轮播
.interval(1000) // 间隔
.vertical(false) //false:设置水平方向上轮播: true:设置垂直方向轮播:
.displayCount(2) //一个页面内同时显示多个子组件:设置一个页面内显示两个子组件
.indicatorStyle({
size: 30,
left: 0,
color: Color.Red
}) // 自定义导航点样式(示例:导航点直径设为30VP,左边距为0,导航点颜色设为红色)
...
this.swiperController.showNext(); // 通过controller切换到后一页
this.swiperController.showPrevious(); // 通过controller切换到前一页
创建网格(Grid/GridItem)
ArkUI提供了Grid容器组件和子组件GridItem,用于构建网格布局。Grid用于设置网格布局相关参数,GridItem定义子组件相关特征。Grid组件支持使用条件渲染、循环渲染、懒加载等渲染控制方式生成子组件。Grid的子组件必须是GridItem组件。
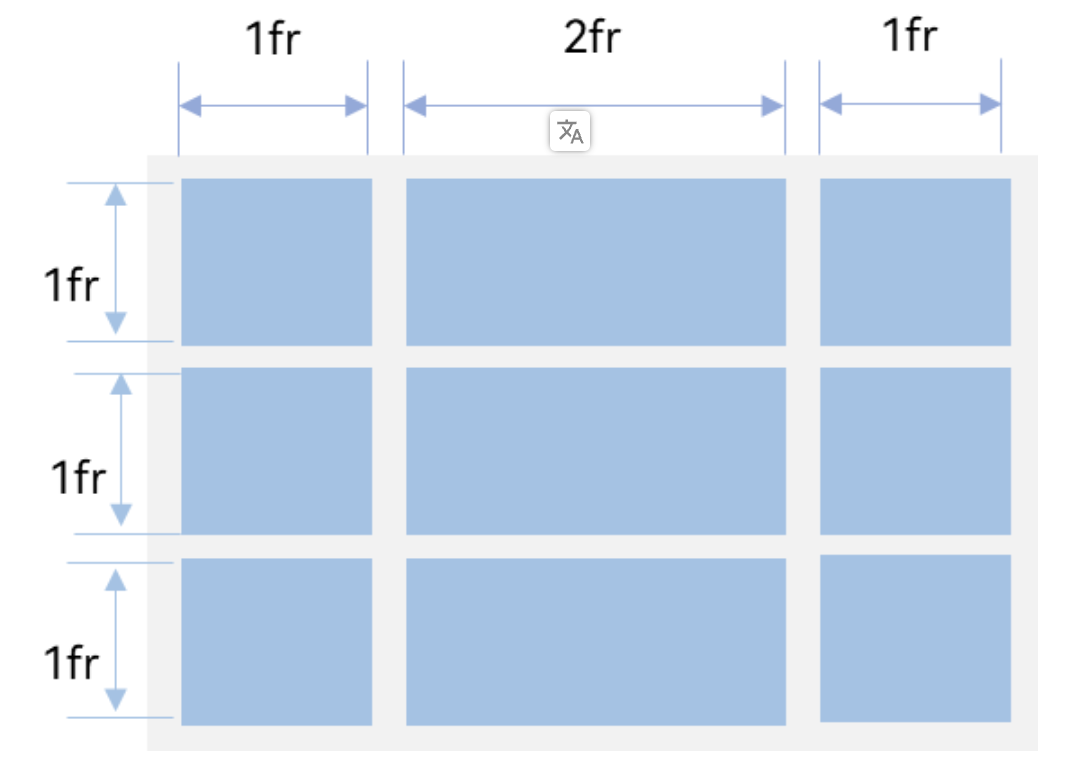
设置Grid行列数量与占比
Grid() {
...
}
.rowsTemplate('1fr 1fr 1fr')
.columnsTemplate('1fr 2fr 1fr')
设置子组件所占行列数
GridItem() {
Text(key)
...
}
.columnStart(1)
.columnEnd(2)
.rowStart(5)
.rowEnd(6)
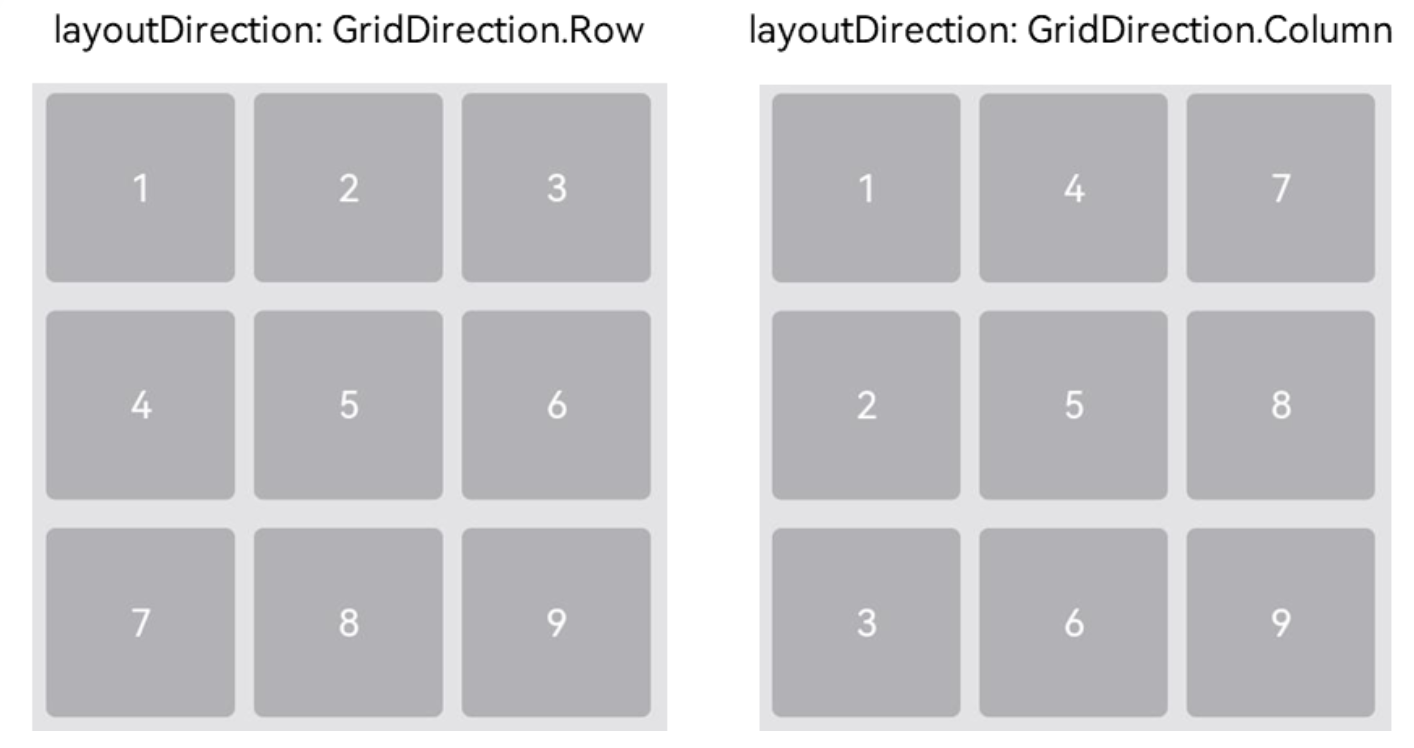
设置主轴方向
若没有设置行列数量与占比,可以通过layoutDirection可以设置网格布局的主轴方向,决定子组件的排列方式。此时可以结合minCount和maxCount属性来约束主轴方向上的网格数量。
-
layoutDirection属性仅在不设置rowsTemplate和columnsTemplate时生效,此时元素在layoutDirection方向上排列。
-
仅设置rowsTemplate时,Grid主轴为水平方向,交叉轴为垂直方向。
-
仅设置columnsTemplate时,Grid主轴为垂直方向,交叉轴为水平方向。
Grid() {
...
}
.maxCount(3)
.layoutDirection(GridDirection.Row)
设置行列间距
Grid() {
...
}
.columnsGap(10)
.rowsGap(15)
构建可滚动的网格布局
在设置Grid的行列数量与占比时,如果仅设置行、列数量与占比中的一个,即仅设置rowsTemplate或仅设置columnsTemplate属性,网格单元按照设置的方向排列,超出Grid显示区域后,Grid拥有可滚动能力。
@Component
struct Shopping {
@State services: Array<string> = ['直播', '进口', ...]
...
build() {
Column({ space: 5 }) {
Grid() {
ForEach(this.services, (service: string, index) => {
GridItem() {
...
}
.width('25%')
}, service => service)
}
.rowsTemplate('1fr 1fr') // 只设置rowsTemplate属性,当内容超出Grid区域时,可水平滚动。
.rowsGap(15)
...
}
...
}
}
控制滚动位置
Column({ space: 5 }) {
Grid(this.scroller) {
...
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr')
...
Row({space: 20}) {
Button('上一页')
.onClick(() => {
this.scroller.scrollPage({
next: false
})
})
Button('下一页')
.onClick(() => {
this.scroller.scrollPage({
next: true
})
})
}
}
...
性能优化
适用于数据量较小的布局场景,当构建具有大量网格项的可滚动网格布局时,推荐使用数据懒加载方式实现按需迭代加载数据,从而提升列表性能。
当使用懒加载方式渲染网格时,为了更好的滚动体验,减少滑动时出现白块,Grid组件中也可通过cachedCount属性设置GridItem的预加载数量,只在懒加载LazyForEach中生效。
设置预加载数量后,会在Grid显示区域前后各缓存cachedCount*列数个GridItem,超出显示和缓存范围的GridItem会被释放。
Grid() {
LazyForEach(this.dataSource, item => {
GridItem() {
...
}
})
}
.cachedCount(3)

开放原子开发者工作坊旨在鼓励更多人参与开源活动,与志同道合的开发者们相互交流开发经验、分享开发心得、获取前沿技术趋势。工作坊有多种形式的开发者活动,如meetup、训练营等,主打技术交流,干货满满,真诚地邀请各位开发者共同参与!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容





所有评论(0)