【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER&&SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER
在Apollo星火计划学习笔记——Apollo路径规划算法原理与实践与【Apollo学习笔记】——Planning模块讲到……Stage::Process的函数会依次调用task_list中的TASK,本文将会继续以LaneFollow为例依次介绍其中的TASK部分究竟做了哪些工作。由于个人能力所限,文章可能有纰漏的地方,还请批评斧正。在配置文件中,我们可以看到LaneFollow所需要执行的所有
文章目录
TASK系列解析文章
1.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之LANE_CHANGE_DECIDER
2.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_REUSE_DECIDER
3.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_BORROW_DECIDER
4.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDER
5.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_PATH_OPTIMIZER
6.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_ASSESSMENT_DECIDER
7.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_DECIDER
8.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之RULE_BASED_STOP_DECIDER
9.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER&&SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER
10.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之SPEED_HEURISTIC_OPTIMIZER
11.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之SPEED_DECIDER
12.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
13.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_NONLINEAR_SPEED_OPTIMIZER(一)
14.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_NONLINEAR_SPEED_OPTIMIZER(二)
前言
在Apollo星火计划学习笔记——Apollo路径规划算法原理与实践与【Apollo学习笔记】——Planning模块讲到……Stage::Process的PlanOnReferenceLine函数会依次调用task_list中的TASK,本文将会继续以LaneFollow为例依次介绍其中的TASK部分究竟做了哪些工作。由于个人能力所限,文章可能有纰漏的地方,还请批评斧正。
在modules/planning/conf/scenario/lane_follow_config.pb.txt配置文件中,我们可以看到LaneFollow所需要执行的所有task。
stage_config: {
stage_type: LANE_FOLLOW_DEFAULT_STAGE
enabled: true
task_type: LANE_CHANGE_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_REUSE_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_LANE_BORROW_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDER
task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_PATH_OPTIMIZER
task_type: PATH_ASSESSMENT_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_DECIDER
task_type: RULE_BASED_STOP_DECIDER
task_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER
task_type: SPEED_HEURISTIC_OPTIMIZER
task_type: SPEED_DECIDER
task_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER
task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
# task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_NONLINEAR_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
task_type: RSS_DECIDER
本文将继续介绍LaneFollow的第9个TASK——SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER以及第12个TASK——SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER
SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER功能简介
产生速度可行驶边界

所形成的区域是非凸的,不能用之前凸优化的方法去做,需要用动态规划的方法去做。
SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER功能简介
产生速度规划边界

 在障碍物的上方或下方确定可行使区域。
在障碍物的上方或下方确定可行使区域。
SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER相关配置
modules/planning/proto/task_config.proto
// SpeedBoundsDeciderConfig
message SpeedBoundsDeciderConfig {
optional double total_time = 1 [default = 7.0];
optional double boundary_buffer = 2 [default = 0.1];
optional double max_centric_acceleration_limit = 3 [default = 2.0];
optional double minimal_kappa = 4 [default = 0.00001];
optional double point_extension = 5 [default = 1.0];
optional double lowest_speed = 6 [default = 2.5];
optional double collision_safety_range = 7 [default = 1.0];
optional double static_obs_nudge_speed_ratio = 8;
optional double dynamic_obs_nudge_speed_ratio = 9;
}
modules/planning/conf/planning_config.pb.txt
default_task_config: {
task_type: ST_BOUNDS_DECIDER
st_bounds_decider_config {
total_time: 7.0
}
}
SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER相关配置
modules/planning/conf/planning_config.pb.txt
default_task_config: {
task_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER
speed_bounds_decider_config {
total_time: 7.0
boundary_buffer: 0.1
max_centric_acceleration_limit: 2.0
point_extension: 0.0
lowest_speed: 2.5
static_obs_nudge_speed_ratio: 0.6
dynamic_obs_nudge_speed_ratio: 0.8
}
}
SpeedBoundsFinalDecider对应的Decider同样是SpeedBoundsDecider,和SpeedBoundsPrioriDecider不同的是配置参数,从Apollo中的默认配置参数来看,SpeedBoundsFinalDecider会根据DP过程生成的决策结果和更小的boundary_buffer生成更加精确的STBoundary。
SPEED_BOUNDS_DECIDER流程
通过modules/planning/tasks/task_factory.cc,我们可以看到SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER和SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER按以下方式进行注册:
task_factory_.Register(
TaskConfig::SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER,
[](const TaskConfig& config,
const std::shared_ptr<DependencyInjector>& injector) -> Task* {
return new SpeedBoundsDecider(config, injector);
});
task_factory_.Register(
TaskConfig::SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER,
[](const TaskConfig& config,
const std::shared_ptr<DependencyInjector>& injector) -> Task* {
return new SpeedBoundsDecider(config, injector);
});
也据此可知,SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER、SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER代码实现的部分在modules/planning/tasks/deciders/speed_bounds_decider/speed_bounds_decider.cc中。
Speed bounds decider 主要完成以下任务:
- 将障碍物映射到ST图中
- 创建速度限制
- 获取路径长度以及时间长度作为ST边界
SpeedBoundsDecider是一个继承自Decider的派生类。当task_list中运行task::Execute()时,SpeedBoundsDecider中的Process部分开始运行。
-
输入:frame 和reference_line_info。通过计算PathData/ReferenceLine/PathDecision/PlanningStartPoint等等信息,来得到ST_Graph。
-
Process:
- 将障碍物映射到ST图中。
(boundary_mapper.ComputeSTBoundary(path_decision).code() == ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR) {}此处将会遍历所有的障碍物去生成ST graph。当有纵向决策产生时,会对边界进行细微调整。再此之后,所有的障碍物的st_boundary会送入一个boundaries vector之中进行保存。 - 创建速度限制。
if (!speed_limit_decider.GetSpeedLimits(path_decision->obstacles(), &speed_limit).ok())此处会遍历每一个离散的路径点并且找到其速度限制。在每一个循环中,基本速度会取决于map/path_curvature/nudge obstacles等因素。对于nudge obstacles,需要找到最近的障碍物。 - 获取路径长度以及时间长度作为搜索边界。时间长度来自于配置文件
total_time: 7.0(配置部分已有介绍)
- 将障碍物映射到ST图中。
-
输出:boundaries/speed_limit 会存储在reference_line_info的st_graph_data中。

Status SpeedBoundsDecider::Process(
Frame *const frame, ReferenceLineInfo *const reference_line_info) {
// retrieve data from frame and reference_line_info
const PathData &path_data = reference_line_info->path_data();
const TrajectoryPoint &init_point = frame->PlanningStartPoint();
const ReferenceLine &reference_line = reference_line_info->reference_line();
PathDecision *const path_decision = reference_line_info->path_decision();
// 1. Map obstacles into st graph
auto time1 = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
// 构造一个STBoundary映射对象
STBoundaryMapper boundary_mapper(
speed_bounds_config_, reference_line, path_data,
path_data.discretized_path().Length(), speed_bounds_config_.total_time(),
injector_);
// FLAGS_use_st_drivable_boundary: True to use st_drivable boundary in speed planning
// default: false
// 清除STBoundary
if (!FLAGS_use_st_drivable_boundary) {
path_decision->EraseStBoundaries();
}
// 将障碍物投影到ST Gragh上
if (boundary_mapper.ComputeSTBoundary(path_decision).code() ==
ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR) {
const std::string msg = "Mapping obstacle failed.";
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
auto time2 = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
std::chrono::duration<double> diff = time2 - time1;
ADEBUG << "Time for ST Boundary Mapping = " << diff.count() * 1000
<< " msec.";
// 所有的障碍物的st_boundary送入到一个boundaries vector之中进行保存
std::vector<const STBoundary *> boundaries;
for (auto *obstacle : path_decision->obstacles().Items()) {
const auto &id = obstacle->Id();
const auto &st_boundary = obstacle->path_st_boundary();
if (!st_boundary.IsEmpty()) {
if (st_boundary.boundary_type() == STBoundary::BoundaryType::KEEP_CLEAR) {
path_decision->Find(id)->SetBlockingObstacle(false);
} else {
path_decision->Find(id)->SetBlockingObstacle(true);
}
boundaries.push_back(&st_boundary);
}
}
const double min_s_on_st_boundaries = SetSpeedFallbackDistance(path_decision);
// 2. Create speed limit along path
SpeedLimitDecider speed_limit_decider(speed_bounds_config_, reference_line,
path_data);
SpeedLimit speed_limit;
if (!speed_limit_decider
.GetSpeedLimits(path_decision->obstacles(), &speed_limit)
.ok()) {
const std::string msg = "Getting speed limits failed!";
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
// 3. Get path_length as s axis search bound in st graph
const double path_data_length = path_data.discretized_path().Length();
// 4. Get time duration as t axis search bound in st graph
const double total_time_by_conf = speed_bounds_config_.total_time();
// Load generated st graph data back to frame
StGraphData *st_graph_data = reference_line_info_->mutable_st_graph_data();
// Add a st_graph debug info and save the pointer to st_graph_data for
// optimizer logging
auto *debug = reference_line_info_->mutable_debug();
STGraphDebug *st_graph_debug = debug->mutable_planning_data()->add_st_graph();
st_graph_data->LoadData(boundaries, min_s_on_st_boundaries, init_point,
speed_limit, reference_line_info->GetCruiseSpeed(),
path_data_length, total_time_by_conf, st_graph_debug);
// Create and record st_graph debug info
RecordSTGraphDebug(*st_graph_data, st_graph_debug);
return Status::OK();
}
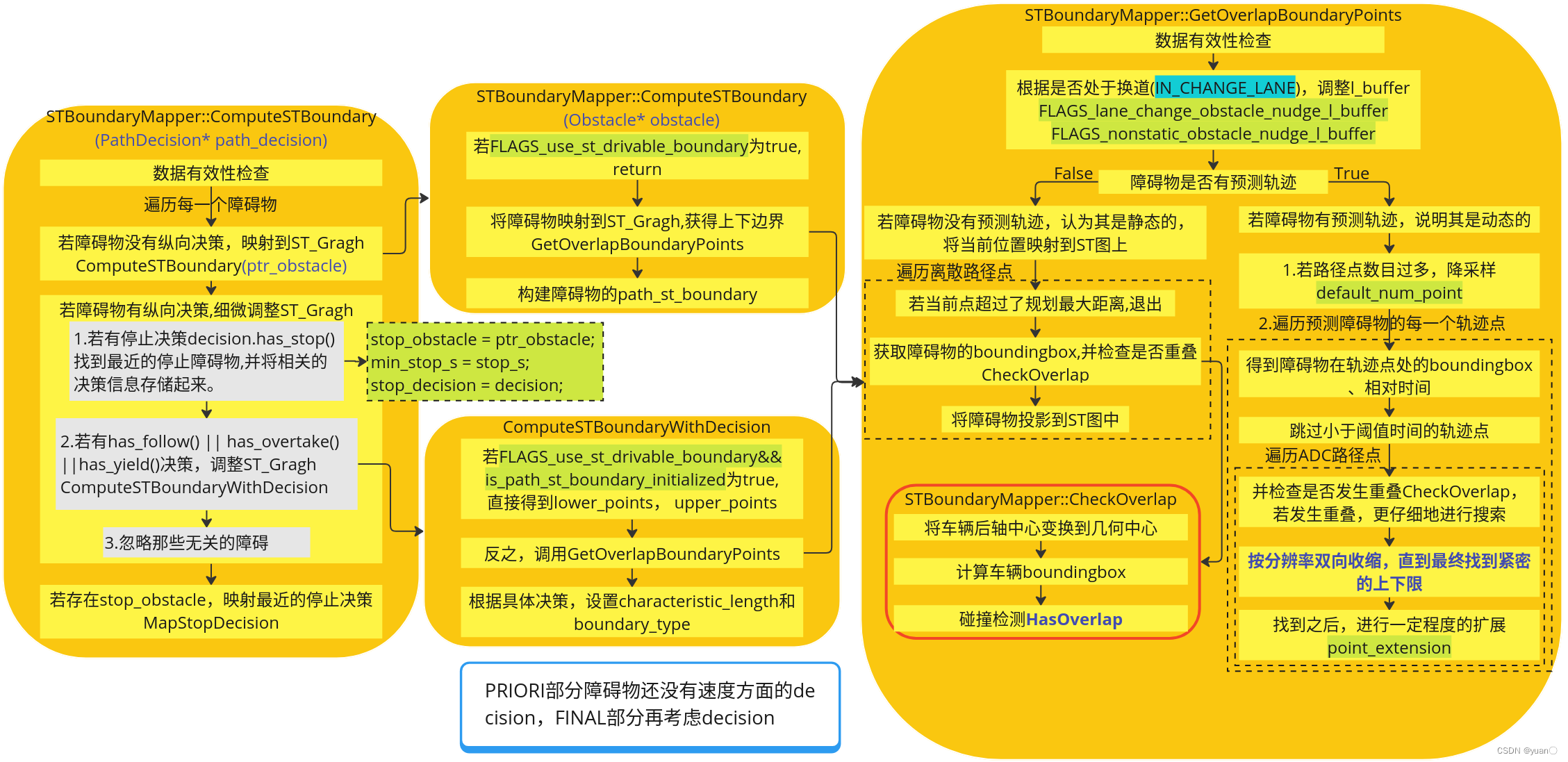
将障碍物映射到ST图中
由Process部分代码可知,(boundary_mapper.ComputeSTBoundary(path_decision).code() == ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR) {}此处是函数的入口。
该部分的流程示意图如下图所示:

ComputeSTBoundary(PathDecision* path_decision)
ComputeSTBoundary将会遍历所有的障碍物去生成ST graph。当有纵向决策产生时,会对边界进行细微调整。再此之后,所有的障碍物的st_boundary会送入一个boundaries vector之中进行保存。
Status STBoundaryMapper::ComputeSTBoundary(PathDecision* path_decision) const {
// Sanity checks.
CHECK_GT(planning_max_time_, 0.0);
if (path_data_.discretized_path().size() < 2) {
AERROR << "Fail to get params because of too few path points. path points "
"size: "
<< path_data_.discretized_path().size() << ".";
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR,
"Fail to get params because of too few path points");
}
// Go through every obstacle.
Obstacle* stop_obstacle = nullptr;
ObjectDecisionType stop_decision;
double min_stop_s = std::numeric_limits<double>::max();
for (const auto* ptr_obstacle_item : path_decision->obstacles().Items()) {
Obstacle* ptr_obstacle = path_decision->Find(ptr_obstacle_item->Id());
ACHECK(ptr_obstacle != nullptr);
// If no longitudinal decision has been made, then plot it onto ST-graph.
if (!ptr_obstacle->HasLongitudinalDecision()) {
ComputeSTBoundary(ptr_obstacle);
continue;
}
// If there is a longitudinal decision, then fine-tune boundary.
const auto& decision = ptr_obstacle->LongitudinalDecision();
if (decision.has_stop()) {
// 1. Store the closest stop fence info.
// TODO(all): store ref. s value in stop decision; refine the code then.
common::SLPoint stop_sl_point;
reference_line_.XYToSL(decision.stop().stop_point(), &stop_sl_point);
const double stop_s = stop_sl_point.s();
if (stop_s < min_stop_s) {
stop_obstacle = ptr_obstacle;
min_stop_s = stop_s;
stop_decision = decision;
}
} else if (decision.has_follow() || decision.has_overtake() ||
decision.has_yield()) {
// 2. Depending on the longitudinal overtake/yield decision,
// fine-tune the upper/lower st-boundary of related obstacles.
ComputeSTBoundaryWithDecision(ptr_obstacle, decision);
} else if (!decision.has_ignore()) {
// 3. Ignore those unrelated obstacles.
AWARN << "No mapping for decision: " << decision.DebugString();
}
}
if (stop_obstacle) {
bool success = MapStopDecision(stop_obstacle, stop_decision);
if (!success) {
const std::string msg = "Fail to MapStopDecision.";
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
}
return Status::OK();
}
ComputeSTBoundary(Obstacle* obstacle)
调用GetOverlapBoundaryPoints来获取给定障碍物的上下点,然后在此基础上制定STBoundary。它还根据以前记录的决策标记边界类型。
void STBoundaryMapper::ComputeSTBoundary(Obstacle* obstacle) const {
if (FLAGS_use_st_drivable_boundary) {
return;
}
std::vector<STPoint> lower_points;
std::vector<STPoint> upper_points;
// Map the given obstacle onto the ST-Graph.
if (!GetOverlapBoundaryPoints(path_data_.discretized_path(), *obstacle,
&upper_points, &lower_points)) {
return;
}
// 构建障碍物的boundary
auto boundary = STBoundary::CreateInstance(lower_points, upper_points);
boundary.set_id(obstacle->Id());
// TODO(all): potential bug here.
const auto& prev_st_boundary = obstacle->path_st_boundary();
const auto& ref_line_st_boundary = obstacle->reference_line_st_boundary();
if (!prev_st_boundary.IsEmpty()) {
boundary.SetBoundaryType(prev_st_boundary.boundary_type());
} else if (!ref_line_st_boundary.IsEmpty()) {
boundary.SetBoundaryType(ref_line_st_boundary.boundary_type());
}
obstacle->set_path_st_boundary(boundary);
}
GetOverlapBoundaryPoints
将给定的障碍物映射到ST图中。
// Map the given obstacle onto the ST-Graph.
// The boundary is represented as upper and lower points for every s of interests.
// Note that upper_points.size() = lower_points.size()
bool STBoundaryMapper::GetOverlapBoundaryPoints(
const std::vector<PathPoint>& path_points, const Obstacle& obstacle,
std::vector<STPoint>* upper_points,
std::vector<STPoint>* lower_points) const {
// Sanity checks.
DCHECK(upper_points->empty());
DCHECK(lower_points->empty());
if (path_points.empty()) {
AERROR << "No points in path_data_.discretized_path().";
return false;
}
const auto* planning_status = injector_->planning_context()
->mutable_planning_status()
->mutable_change_lane();
// lane_change_obstacle_nudge_l_buffer: minimum l-distance to nudge when changing lane (meters);0.3
// nonstatic_obstacle_nudge_l_buffer: minimum l-distance to nudge a non-static obstacle (meters);0.4
double l_buffer =
planning_status->status() == ChangeLaneStatus::IN_CHANGE_LANE
? FLAGS_lane_change_obstacle_nudge_l_buffer
: FLAGS_nonstatic_obstacle_nudge_l_buffer;
// Draw the given obstacle on the ST-graph.
const auto& trajectory = obstacle.Trajectory();
if (trajectory.trajectory_point().empty()) {
// For those with no predicted trajectories, just map the obstacle's
// current position to ST-graph and always assume it's static.
if (!obstacle.IsStatic()) {
AWARN << "Non-static obstacle[" << obstacle.Id()
<< "] has NO prediction trajectory."
<< obstacle.Perception().ShortDebugString();
}
// 遍历离散路径点
for (const auto& curr_point_on_path : path_points) {
// planning_max_distance_ = path_data.discretized_path().Length()
// 若当前点超过了规划最大距离,退出
if (curr_point_on_path.s() > planning_max_distance_) {
break;
}
// 获取障碍物的boundingbox
const Box2d& obs_box = obstacle.PerceptionBoundingBox();
if (CheckOverlap(curr_point_on_path, obs_box, l_buffer)) {
// If there is overlapping, then plot it on ST-graph.
const double backward_distance = -vehicle_param_.front_edge_to_center();
const double forward_distance = obs_box.length();
double low_s =
std::fmax(0.0, curr_point_on_path.s() + backward_distance);
double high_s = std::fmin(planning_max_distance_,
curr_point_on_path.s() + forward_distance);
// It is an unrotated rectangle appearing on the ST-graph.
// 静止的障碍物在ST图中就是一个矩形
// TODO(jiacheng): reconsider the backward_distance, it might be
// unnecessary, but forward_distance is indeed meaningful though.
lower_points->emplace_back(low_s, 0.0);
lower_points->emplace_back(low_s, planning_max_time_);
upper_points->emplace_back(high_s, 0.0);
upper_points->emplace_back(high_s, planning_max_time_);
break;
}
}
} else {
// For those with predicted trajectories (moving obstacles):
// 1. Subsample to reduce computation time.
const int default_num_point = 50;
DiscretizedPath discretized_path;
if (path_points.size() > 2 * default_num_point) {
const auto ratio = path_points.size() / default_num_point;
std::vector<PathPoint> sampled_path_points;
for (size_t i = 0; i < path_points.size(); ++i) {
if (i % ratio == 0) {
sampled_path_points.push_back(path_points[i]);
}
}
discretized_path = DiscretizedPath(std::move(sampled_path_points));
} else {
discretized_path = DiscretizedPath(path_points);
}
// 2. Go through every point of the predicted obstacle trajectory.
for (int i = 0; i < trajectory.trajectory_point_size(); ++i) {
const auto& trajectory_point = trajectory.trajectory_point(i);
// 得到障碍物在轨迹点处的boundingbox
const Box2d obs_box = obstacle.GetBoundingBox(trajectory_point);
// 得到障碍物在轨迹点处的相对时间
double trajectory_point_time = trajectory_point.relative_time();
static constexpr double kNegtiveTimeThreshold = -1.0;
// 跳过小于阈值时间的轨迹点
if (trajectory_point_time < kNegtiveTimeThreshold) {
continue;
}
// 步长
const double step_length = vehicle_param_.front_edge_to_center();
// FLAGS_max_trajectory_len: (unit: meter) max possible trajectory length. 1000.0
auto path_len =
std::min(FLAGS_max_trajectory_len, discretized_path.Length());
// Go through every point of the ADC's path.
for (double path_s = 0.0; path_s < path_len; path_s += step_length) {
// 估计当前车辆的位置
const auto curr_adc_path_point =
discretized_path.Evaluate(path_s + discretized_path.front().s());
if (CheckOverlap(curr_adc_path_point, obs_box, l_buffer)) {
// Found overlap, start searching with higher resolution
const double backward_distance = -step_length;
const double forward_distance = vehicle_param_.length() +
vehicle_param_.width() +
obs_box.length() + obs_box.width();
const double default_min_step = 0.1; // in meters
const double fine_tuning_step_length = std::fmin(
default_min_step, discretized_path.Length() / default_num_point);
bool find_low = false;
bool find_high = false;
double low_s = std::fmax(0.0, path_s + backward_distance);
double high_s =
std::fmin(discretized_path.Length(), path_s + forward_distance);
// Keep shrinking by the resolution bidirectionally until finally
// locating the tight upper and lower bounds.
while (low_s < high_s) {
if (find_low && find_high) {
break;
}
if (!find_low) {
const auto& point_low = discretized_path.Evaluate(
low_s + discretized_path.front().s());
if (!CheckOverlap(point_low, obs_box, l_buffer)) {
low_s += fine_tuning_step_length;
} else {
find_low = true;
}
}
if (!find_high) {
const auto& point_high = discretized_path.Evaluate(
high_s + discretized_path.front().s());
if (!CheckOverlap(point_high, obs_box, l_buffer)) {
high_s -= fine_tuning_step_length;
} else {
find_high = true;
}
}
}
if (find_high && find_low) {
lower_points->emplace_back(
low_s - speed_bounds_config_.point_extension(),
trajectory_point_time);
upper_points->emplace_back(
high_s + speed_bounds_config_.point_extension(),
trajectory_point_time);
}
break;
}
}
}
}
// Sanity checks and return.
DCHECK_EQ(lower_points->size(), upper_points->size());
return (lower_points->size() > 1 && upper_points->size() > 1);
}
ComputeSTBoundaryWithDecision
对于产生纵向决策的障碍物产生的ST boundary进行调整。
// Fine-tune the boundary for yielding or overtaking obstacles.
// Increase boundary on the s-dimension or set the boundary type, etc., when necessary.
void STBoundaryMapper::ComputeSTBoundaryWithDecision(
Obstacle* obstacle, const ObjectDecisionType& decision) const {
DCHECK(decision.has_follow() || decision.has_yield() ||
decision.has_overtake())
<< "decision is " << decision.DebugString()
<< ", but it must be follow or yield or overtake.";
std::vector<STPoint> lower_points;
std::vector<STPoint> upper_points;
if (FLAGS_use_st_drivable_boundary &&
obstacle->is_path_st_boundary_initialized()) {
const auto& path_st_boundary = obstacle->path_st_boundary();
lower_points = path_st_boundary.lower_points();
upper_points = path_st_boundary.upper_points();
} else {
if (!GetOverlapBoundaryPoints(path_data_.discretized_path(), *obstacle,
&upper_points, &lower_points)) {
return;
}
}
auto boundary = STBoundary::CreateInstance(lower_points, upper_points);
// get characteristic_length and boundary_type.
STBoundary::BoundaryType b_type = STBoundary::BoundaryType::UNKNOWN;
double characteristic_length = 0.0;
if (decision.has_follow()) {
characteristic_length = std::fabs(decision.follow().distance_s());
b_type = STBoundary::BoundaryType::FOLLOW;
} else if (decision.has_yield()) {
characteristic_length = std::fabs(decision.yield().distance_s());
boundary = STBoundary::CreateInstance(lower_points, upper_points)
.ExpandByS(characteristic_length);
b_type = STBoundary::BoundaryType::YIELD;
} else if (decision.has_overtake()) {
characteristic_length = std::fabs(decision.overtake().distance_s());
b_type = STBoundary::BoundaryType::OVERTAKE;
} else {
DCHECK(false) << "Obj decision should be either yield or overtake: "
<< decision.DebugString();
}
boundary.SetBoundaryType(b_type);
boundary.set_id(obstacle->Id());
boundary.SetCharacteristicLength(characteristic_length);
obstacle->set_path_st_boundary(boundary);
}
SetSpeedFallbackDistance
找到障碍物路径上最低的 s 值,该 s 值将用作速度回退的距离。
double SpeedBoundsDecider::SetSpeedFallbackDistance(
PathDecision *const path_decision) {
// Set min_s_on_st_boundaries to guide speed fallback.
static constexpr double kEpsilon = 1.0e-6;
double min_s_non_reverse = std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity();
double min_s_reverse = std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity();
// 遍历障碍物
for (auto *obstacle : path_decision->obstacles().Items()) {
const auto &st_boundary = obstacle->path_st_boundary();
// 障碍物ST边界为空,跳过
if (st_boundary.IsEmpty()) {
continue;
}
// 获取st边界底部左侧点和右侧点的s值,并选择较小的值作为最低的s值
const auto left_bottom_point_s = st_boundary.bottom_left_point().s();
const auto right_bottom_point_s = st_boundary.bottom_right_point().s();
const auto lowest_s = std::min(left_bottom_point_s, right_bottom_point_s);
// 如果左侧点的 s 值减去右侧点的 s 值大于 kEpsilon(即左侧点在右侧点之后),则说明这是一个反向行驶的边界
if (left_bottom_point_s - right_bottom_point_s > kEpsilon) {
// 更新 min_s_reverse,将其设置为最低的 s 值
if (min_s_reverse > lowest_s) {
min_s_reverse = lowest_s;
}
} else if (min_s_non_reverse > lowest_s) {
// 更新 min_s_non_reverse,将其设置为最低的 s 值。
min_s_non_reverse = lowest_s;
}
}
min_s_reverse = std::max(min_s_reverse, 0.0);
min_s_non_reverse = std::max(min_s_non_reverse, 0.0);
return min_s_non_reverse > min_s_reverse ? 0.0 : min_s_non_reverse;
}
创建速度限制
SpeedLimits来源于三个部分:
- 来自于地图的速度限制
- 来自于道路曲率的速度限制
- 来自于Nudge障碍物的速度限制
该部分流程图如下所示:

GetSpeedLimits
Status SpeedLimitDecider::GetSpeedLimits(
const IndexedList<std::string, Obstacle>& obstacles,
SpeedLimit* const speed_limit_data) const {
CHECK_NOTNULL(speed_limit_data);
const auto& discretized_path = path_data_.discretized_path();
const auto& frenet_path = path_data_.frenet_frame_path();
// 遍历离散路径点
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < discretized_path.size(); ++i) {
const double path_s = discretized_path.at(i).s();
const double reference_line_s = frenet_path.at(i).s();
if (reference_line_s > reference_line_.Length()) {
AWARN << "path w.r.t. reference line at [" << reference_line_s
<< "] is LARGER than reference_line_ length ["
<< reference_line_.Length() << "]. Please debug before proceeding.";
break;
}
// (1) speed limit from map
double speed_limit_from_reference_line =
reference_line_.GetSpeedLimitFromS(reference_line_s);
// (2) speed limit from path curvature
// -- 2.1: limit by centripetal force (acceleration)
const double speed_limit_from_centripetal_acc =
// max_centric_acceleration_limit default = 2.0
std::sqrt(speed_bounds_config_.max_centric_acceleration_limit() /
std::fmax(std::fabs(discretized_path.at(i).kappa()),
speed_bounds_config_.minimal_kappa()));
// (3) speed limit from nudge obstacles
// TODO(all): in future, expand the speed limit not only to obstacles with
// nudge decisions.
double speed_limit_from_nearby_obstacles =
std::numeric_limits<double>::max();
const double collision_safety_range =
speed_bounds_config_.collision_safety_range();// default = 1.0
// 遍历障碍物
for (const auto* ptr_obstacle : obstacles.Items()) {
// 跳过虚拟的障碍物
if (ptr_obstacle->IsVirtual()) {
continue;
}
// 障碍物没有横向Nudge决策,跳过
if (!ptr_obstacle->LateralDecision().has_nudge()) {
continue;
}
/* ref line:
* -------------------------------
* start_s end_s
* ------| adc |---------------
* ------------| obstacle |------
*/
// TODO(all): potential problem here;
// frenet and cartesian coordinates are mixed.
const double vehicle_front_s =
reference_line_s + vehicle_param_.front_edge_to_center();
const double vehicle_back_s =
reference_line_s - vehicle_param_.back_edge_to_center();
const double obstacle_front_s =
ptr_obstacle->PerceptionSLBoundary().end_s();
const double obstacle_back_s =
ptr_obstacle->PerceptionSLBoundary().start_s();
// 若车辆与障碍物在s方向上没有发生重合,跳过
if (vehicle_front_s < obstacle_back_s ||
vehicle_back_s > obstacle_front_s) {
continue;
}
const auto& nudge_decision = ptr_obstacle->LateralDecision().nudge();
// Please notice the differences between adc_l and frenet_point_l
const double frenet_point_l = frenet_path.at(i).l();
// obstacle is on the right of ego vehicle (at path point i)
bool is_close_on_left =
(nudge_decision.type() == ObjectNudge::LEFT_NUDGE) &&
(frenet_point_l - vehicle_param_.right_edge_to_center() -
collision_safety_range <
ptr_obstacle->PerceptionSLBoundary().end_l());
// obstacle is on the left of ego vehicle (at path point i)
bool is_close_on_right =
(nudge_decision.type() == ObjectNudge::RIGHT_NUDGE) &&
(ptr_obstacle->PerceptionSLBoundary().start_l() -
collision_safety_range <
frenet_point_l + vehicle_param_.left_edge_to_center());
// TODO(all): dynamic obstacles do not have nudge decision
if (is_close_on_left || is_close_on_right) {
double nudge_speed_ratio = 1.0;
// 静态障碍物 x 0.6
if (ptr_obstacle->IsStatic()) {
nudge_speed_ratio =
speed_bounds_config_.static_obs_nudge_speed_ratio(); // static_obs_nudge_speed_ratio: 0.6
} else {
// 动态障碍物 x 0.8
nudge_speed_ratio =
speed_bounds_config_.dynamic_obs_nudge_speed_ratio(); // dynamic_obs_nudge_speed_ratio: 0.8
}
speed_limit_from_nearby_obstacles =
nudge_speed_ratio * speed_limit_from_reference_line;
break;
}
}
double curr_speed_limit = 0.0;
// FLAGS_enable_nudge_slowdown: True to slow down when nudge obstacles
if (FLAGS_enable_nudge_slowdown) {
curr_speed_limit =
std::fmax(speed_bounds_config_.lowest_speed(), // lowest_speed:2.5
std::min({speed_limit_from_reference_line,
speed_limit_from_centripetal_acc,
speed_limit_from_nearby_obstacles}));
} else {
curr_speed_limit =
std::fmax(speed_bounds_config_.lowest_speed(),
std::min({speed_limit_from_reference_line,
speed_limit_from_centripetal_acc}));
}
speed_limit_data->AppendSpeedLimit(path_s, curr_speed_limit);
}
return Status::OK();
}
设置标志位(is_close_on_left、is_close_on_right)部分的示意图如下:

GetSpeedLimitFromS
double ReferenceLine::GetSpeedLimitFromS(const double s) const {
// 对于速度限制列表speed_limit_中已经有的部分,直接返回相应的值。
for (const auto& speed_limit : speed_limit_) {
if (s >= speed_limit.start_s && s <= speed_limit.end_s) {
return speed_limit.speed_limit;
}
}
const auto& map_path_point = GetReferencePoint(s);
// FLAGS_planning_upper_speed_limit: Maximum speed (m/s) in planning;31.3
double speed_limit = FLAGS_planning_upper_speed_limit;
bool speed_limit_found = false;
// 根据lane_waypoint道路的情况进行速度限制
for (const auto& lane_waypoint : map_path_point.lane_waypoints()) {
if (lane_waypoint.lane == nullptr) {
AWARN << "lane_waypoint.lane is nullptr.";
continue;
}
speed_limit_found = true;
speed_limit =
std::fmin(lane_waypoint.lane->lane().speed_limit(), speed_limit);
}
// 若未找到lane_waypoint.lane,根据道路类型进行限制
if (!speed_limit_found) {
// use default speed limit based on road_type
// FLAGS_default_city_road_speed_limit: default speed limit (m/s) for city road. 35 mph
speed_limit = FLAGS_default_city_road_speed_limit;
hdmap::Road::Type road_type = GetRoadType(s);
if (road_type == hdmap::Road::HIGHWAY) {
// FLAGS_default_highway_speed_limit: default speed limit (m/s) for highway. 65 mph
speed_limit = FLAGS_default_highway_speed_limit;
}
}
return speed_limit;
}
参考
[1] Planning Piecewise Jerk Nonlinear Speed Optimizer Introduction
[2] Apollo规划控制学习笔记
[3] 1.10 Speed Bounds Prior Decider

开放原子开发者工作坊旨在鼓励更多人参与开源活动,与志同道合的开发者们相互交流开发经验、分享开发心得、获取前沿技术趋势。工作坊有多种形式的开发者活动,如meetup、训练营等,主打技术交流,干货满满,真诚地邀请各位开发者共同参与!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献29条内容
已为社区贡献29条内容





所有评论(0)