Java自定义线程池
一、Java语言本身也是多线程,回顾Java创建线程方式如下:1、继承Thread类,(Thread类实现Runnable接口),来个类图加深印象。2、实现Runnable接口实现无返回值、实现run()方法,啥时候run,黑话了。3、实现Callable接口重写call()+FutureTask获取.public class CustomThread {public static void ma
一、Java语言本身也是多线程,回顾Java创建线程方式如下:
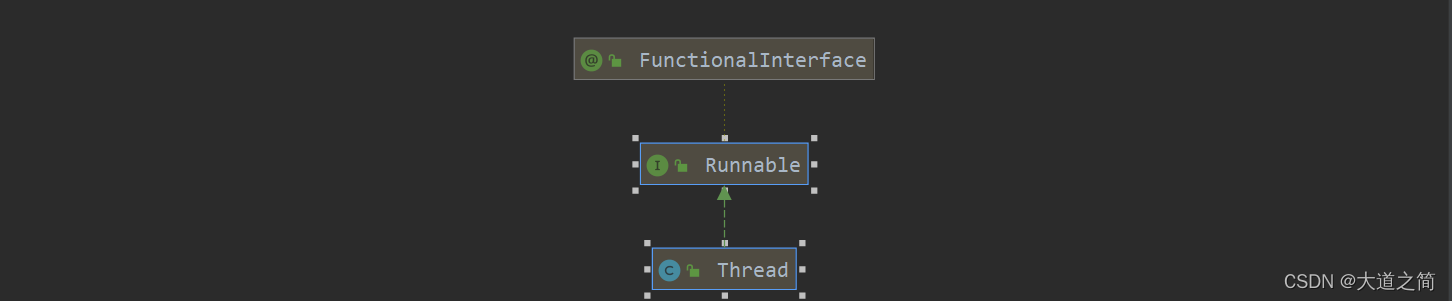
1、继承Thread类,(Thread类实现Runnable接口),来个类图加深印象。

2、实现Runnable接口实现无返回值、实现run()方法,啥时候run,黑话了。
3、实现Callable接口重写call()+FutureTask获取.
public class CustomThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 自定义线程
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Custom Run");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
},"custom-thread-1").start();
}
}
实战案例:自定义线程HttpClient旧版本的清理过期连接
public static class IdleConnectionMonitorThread extends Thread {
private final HttpClientConnectionManager connMgr;
private volatile boolean shutdown;
public IdleConnectionMonitorThread(HttpClientConnectionManager connMgr) {
super();
this.connMgr = connMgr;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (!shutdown) {
synchronized (this) {
wait(5000);
// Close expired connections
connMgr.closeExpiredConnections();
// Optionally, close connections
// that have been idle longer than 30 sec
connMgr.closeIdleConnections(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
// terminate
}
}
public void shutdown() {
shutdown = true;
synchronized (this) {
notifyAll();
}
}
}根据volatile+标志实现线程的暂停和停止
xxl-job清理日志的线程
public class JobLogFileCleanThread {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JobLogFileCleanThread.class);
private static JobLogFileCleanThread instance = new JobLogFileCleanThread();
public static JobLogFileCleanThread getInstance(){
return instance;
}
private Thread localThread;
private volatile boolean toStop = false;
public void start(final long logRetentionDays){
// limit min value
if (logRetentionDays < 3 ) {
return;
}
localThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (!toStop) {
try {
// clean log dir, over logRetentionDays
File[] childDirs = new File(XxlJobFileAppender.getLogPath()).listFiles();
if (childDirs!=null && childDirs.length>0) {
// today
Calendar todayCal = Calendar.getInstance();
todayCal.set(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY,0);
todayCal.set(Calendar.MINUTE,0);
todayCal.set(Calendar.SECOND,0);
todayCal.set(Calendar.MILLISECOND,0);
Date todayDate = todayCal.getTime();
for (File childFile: childDirs) {
// valid
if (!childFile.isDirectory()) {
continue;
}
if (childFile.getName().indexOf("-") == -1) {
continue;
}
// file create date
Date logFileCreateDate = null;
try {
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
logFileCreateDate = simpleDateFormat.parse(childFile.getName());
} catch (ParseException e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
if (logFileCreateDate == null) {
continue;
}
if ((todayDate.getTime()-logFileCreateDate.getTime()) >= logRetentionDays * (24 * 60 * 60 * 1000) ) {
FileUtil.deleteRecursively(childFile);
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!toStop) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
try {
TimeUnit.DAYS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
if (!toStop) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
logger.info(">>>>>>>>>>> xxl-job, executor JobLogFileCleanThread thread destroy.");
}
});
localThread.setDaemon(true);
localThread.setName("xxl-job, executor JobLogFileCleanThread");
localThread.start();
}
public void toStop() {
toStop = true;
if (localThread == null) {
return;
}
// interrupt and wait
localThread.interrupt();
try {
localThread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}4、基于线程池集中管理创建线程系列周期.【本篇文章重点介绍】
5、多个自定义线程顺序执行
// 方式1:线程内join()方法,等待线程完成
public static void test1(){
// Thread1
final Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ThreadUtil.pauseThreadSeconds(1);
System.out.println("Thread1 Run");
}
});
final Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
thread1.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ThreadUtil.pauseThreadSeconds(1);
System.out.println("Thread2 Run");
}
});
final Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
thread2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ThreadUtil.pauseThreadSeconds(1);
System.out.println("Thread3 Run");
}
});
final Thread thread4 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
thread3.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ThreadUtil.pauseThreadSeconds(1);
System.out.println("Thread4 Run");
}
});
// 线程执行
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
thread4.start();
} // 方式2:多个子线程交替start()+join()
public static void test2() throws InterruptedException {
// Thread1
final Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ThreadUtil.pauseThreadSeconds(1);
System.out.println("Thread1 Run");
}
});
// Thread2
final Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ThreadUtil.pauseThreadSeconds(1);
System.out.println("Thread2 Run");
}
});
// Thread3
final Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ThreadUtil.pauseThreadSeconds(1);
System.out.println("Thread3 Run");
}
});
// Thread4
final Thread thread4 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ThreadUtil.pauseThreadSeconds(1);
System.out.println("Thread4 Run");
}
});
thread1.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.start();
thread2.join();
thread3.start();
thread3.join();
thread4.start();
thread4.join();
} // 方法3:单个线程线程池依次提交
public static void test3(){
// Thread1
final Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ThreadUtil.pauseThreadSeconds(1);
System.out.println("Thread1 Run");
}
});
// Thread2
final Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ThreadUtil.pauseThreadSeconds(1);
System.out.println("Thread2 Run");
}
});
// Thread3
final Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ThreadUtil.pauseThreadSeconds(1);
System.out.println("Thread3 Run");
}
});
// Thread4
final Thread thread4 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ThreadUtil.pauseThreadSeconds(1);
System.out.println("Thread4 Run");
}
});
singleThreadEventExecutor.execute(thread1);
singleThreadEventExecutor.execute(thread2);
singleThreadEventExecutor.execute(thread3);
singleThreadEventExecutor.execute(thread4);
singleThreadEventExecutor.shutdown();
} // 方法4:CountDownLatch数目为1,,线程栏珊定时器倒计时
public static void test4(){
// Thread1
final Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ThreadUtil.pauseThreadSeconds(1);
System.out.println("Thread1 Run");
countDownLatch1.countDown();
}
});
// Thread2
final Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
countDownLatch1.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ThreadUtil.pauseThreadSeconds(1);
System.out.println("Thread2 Run");
countDownLatch2.countDown();
}
});
// Thread3
final Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
countDownLatch2.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ThreadUtil.pauseThreadSeconds(1);
System.out.println("Thread3 Run");
countDownLatch3.countDown();
}
});
// Thread4
final Thread thread4 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
countDownLatch3.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ThreadUtil.pauseThreadSeconds(1);
System.out.println("Thread4 Run");
}
});
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
thread4.start();
}二、JDK线程池工具类.
1、Executors工具类,是JDK中Doug Lea大佬实现供开发者使用。

随着JDK版本迭代逐渐加入了基于工作窃取算法的线程池了,阿里编码规范也推荐开发者自定义线程池,禁止生产直接使用Executos线程池工具类,因此很有可能造成OOM异常。同时在某些类型的线程池里面,使用无界队列还会导致maxinumPoolSize、keepAliveTime、handler等参数失效。因此目前在大厂的开发规范中会强调禁止使用Executors来创建线程池。这里说道阻塞队列。LinkedBlockingQueue。

定时任务线程池案例:并发执行格式化时间计数.
package com.boot.skywalk.thread;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class ShcheduledJob {
private static SimpleDateFormat formate=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
private static AtomicInteger atomicInteger=new AtomicInteger(0);
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add("Tom");
list.add("Jack");
list.add("Mock");
list.add("Boot");
list.add("Tool");
System.out.println("主线程执行结束时间:"+formate.format(new Date()));
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
// list
list.parallelStream().forEach(name->{
scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(name+"子线程-"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行:"+atomicInteger.incrementAndGet()+"执行时间"+formate.format(new Date()));
}
}, 5L, 5L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
});
System.out.println("主线程执行结束时间:"+formate.format(new Date()));
}
}并发执行如下:

 2、自定义线程池工具类基于ThreadPoolExecutor实现,那个JDK封装的线程池工具类也是基于这个ThreadPoolExecutor实现的。
2、自定义线程池工具类基于ThreadPoolExecutor实现,那个JDK封装的线程池工具类也是基于这个ThreadPoolExecutor实现的。
public class ConstomThreadPool extends ThreadPoolExecutor{
/**
*
* @param corePoolSize 核心线程池
* @param maximumPoolSize 线程池最大数量
* @param keepAliveTime 线程存活时间
* @param unit TimeUnit
* @param workQueue 工作队列,自定义大小
* @param poolName 线程工厂自定义线程名称
*/
public ConstomThreadPool(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, String poolName) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue);
setThreadFactory(new CustomThreadFactory(poolName, false));
}
}自定义线程工厂类,这样线程命名有开发者控制实现了,这样参数可以做到可配置化,生产环境可以供不同业务模块使用,如果系统配置值不生效,就给一个默认值,更加满足业务需要.
/**
* 自定义线程工厂
*/
public class CustomThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
/**
* 线程前缀,采用AtomicInteger实现线程编号线程安全自增
*/
private final AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(1);
/**
* 线程命名前缀
*/
private final String namePrefix;
/**
* 线程工厂创建的线程是否是守护线程
*/
private final boolean isDaemon;
public CustomThreadFactory(String prefix, boolean daemin) {
if (StringUtils.isNoneBlank(prefix)) {
this.namePrefix = prefix;
} else {
this.namePrefix = "thread_pool";
}
// 是否是守护线程
isDaemon = daemin;
}
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread thread = new Thread(r, namePrefix + "-" + atomicInteger.getAndIncrement());
thread.setDaemon(isDaemon);
// 设置线程优先级
if (thread.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY) {
thread.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
}
return thread;
}
}这里Spring框架提供的自定义线程池工厂类,当然了一些开源包也会提供这样的轮子,这个比较简单了.
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class CustomizableThreadFactory extends CustomizableThreadCreator implements ThreadFactory {
/**
* Create a new CustomizableThreadFactory with default thread name prefix.
*/
public CustomizableThreadFactory() {
super();
}
/**
* Create a new CustomizableThreadFactory with the given thread name prefix.
* @param threadNamePrefix the prefix to use for the names of newly created threads
*/
public CustomizableThreadFactory(String threadNamePrefix) {
super(threadNamePrefix);
}
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable runnable) {
return createThread(runnable);
}
}Dubbo提供的线程池工厂,可设置是否为守护线程.
package org.apache.dubbo.common.utils;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class NamedThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
protected static final AtomicInteger POOL_SEQ = new AtomicInteger(1);
protected final AtomicInteger mThreadNum;
protected final String mPrefix;
protected final boolean mDaemon;
protected final ThreadGroup mGroup;
public NamedThreadFactory() {
this("pool-" + POOL_SEQ.getAndIncrement(), false);
}
public NamedThreadFactory(String prefix) {
this(prefix, false);
}
public NamedThreadFactory(String prefix, boolean daemon) {
this.mThreadNum = new AtomicInteger(1);
this.mPrefix = prefix + "-thread-";
this.mDaemon = daemon;
SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
this.mGroup = s == null ? Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup() : s.getThreadGroup();
}
public Thread newThread(Runnable runnable) {
String name = this.mPrefix + this.mThreadNum.getAndIncrement();
Thread ret = new Thread(this.mGroup, runnable, name, 0L);
ret.setDaemon(this.mDaemon);
return ret;
}
public ThreadGroup getThreadGroup() {
return this.mGroup;
}
}Dubbo提供的线程池拒绝策略扩展实现.
package com.alibaba.dubbo.common.threadpool.support;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.Constants;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.logger.Logger;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.logger.LoggerFactory;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.utils.JVMUtil;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
/**
* Abort Policy.
* Log warn info when abort.
*/
public class AbortPolicyWithReport extends ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy {
protected static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AbortPolicyWithReport.class);
private final String threadName;
private final URL url;
private static volatile long lastPrintTime = 0;
private static Semaphore guard = new Semaphore(1);
public AbortPolicyWithReport(String threadName, URL url) {
this.threadName = threadName;
this.url = url;
}
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
String msg = String.format("Thread pool is EXHAUSTED!" +
" Thread Name: %s, Pool Size: %d (active: %d, core: %d, max: %d, largest: %d), Task: %d (completed: %d)," +
" Executor status:(isShutdown:%s, isTerminated:%s, isTerminating:%s), in %s://%s:%d!",
threadName, e.getPoolSize(), e.getActiveCount(), e.getCorePoolSize(), e.getMaximumPoolSize(), e.getLargestPoolSize(),
e.getTaskCount(), e.getCompletedTaskCount(), e.isShutdown(), e.isTerminated(), e.isTerminating(),
url.getProtocol(), url.getIp(), url.getPort());
logger.warn(msg);
dumpJStack();
throw new RejectedExecutionException(msg);
}
private void dumpJStack() {
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
//dump every 10 minutes
if (now - lastPrintTime < 10 * 60 * 1000) {
return;
}
if (!guard.tryAcquire()) {
return;
}
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
String dumpPath = url.getParameter(Constants.DUMP_DIRECTORY, System.getProperty("user.home"));
SimpleDateFormat sdf;
String OS = System.getProperty("os.name").toLowerCase();
// window system don't support ":" in file name
if(OS.contains("win")){
sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd_HH-mm-ss");
}else {
sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd_HH:mm:ss");
}
String dateStr = sdf.format(new Date());
FileOutputStream jstackStream = null;
try {
jstackStream = new FileOutputStream(new File(dumpPath, "Dubbo_JStack.log" + "." + dateStr));
JVMUtil.jstack(jstackStream);
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("dump jstack error", t);
} finally {
guard.release();
if (jstackStream != null) {
try {
jstackStream.flush();
jstackStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
lastPrintTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
});
}
}应用场景如下:
public class CachedThreadPool implements ThreadPool {
@Override
public Executor getExecutor(URL url) {
String name = url.getParameter(Constants.THREAD_NAME_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_THREAD_NAME);
int cores = url.getParameter(Constants.CORE_THREADS_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_CORE_THREADS);
int threads = url.getParameter(Constants.THREADS_KEY, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
int queues = url.getParameter(Constants.QUEUES_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_QUEUES);
int alive = url.getParameter(Constants.ALIVE_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_ALIVE);
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(cores, threads, alive, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
queues == 0 ? new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>() :
(queues < 0 ? new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()
: new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(queues)),
new NamedInternalThreadFactory(name, true), new AbortPolicyWithReport(name, url));
}3、SpringBoot框架提供的自定义线程池,基于异步注解@Async名称和一些业务自定义配置项,很好的实现了业务间线程池的隔离。
@Configuration
public class ThreadPoolConfig {
/**
*
* @return ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
*/
@Bean("serviceTaskA")
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor serviceTaskA() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(2);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(2);
executor.setQueueCapacity(10);
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("service-a");
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
return executor;
}
/**
*
* @return ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
*/
@Bean("serviceTaskB")
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor serviceTaskB() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(2);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(2);
executor.setQueueCapacity(10);
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("service-b");
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
return executor;
}
}整体来看是Spring框架对JDK的线程池做了封装,公开发者使用,毕竟框架嘛,肯定是把方便留给开发者。

4、并发流线程池。
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(4);
list.add("A");
list.add("B");
list.add("C");
list.add("D");
list.parallelStream().forEach(string -> {
string = string + "paralleStream";
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":-> "+string);
});运行实例:

说明:并发流默认使用系统公共的线程池ForkJoinWorkerThread,供整个程序使用。

类图如下,基于分治法,双端窃取算法实现的一种线程池。
ForkJoin实现的了自己的线程工厂命名。
 也可以自定义并发流线程,然后提交任务,一般并发流适用于短暂耗时业务,避免拖垮整个线程池业务.
也可以自定义并发流线程,然后提交任务,一般并发流适用于短暂耗时业务,避免拖垮整个线程池业务.
public ForkJoinPool(int parallelism,
ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory factory,
UncaughtExceptionHandler handler,
boolean asyncMode) {
this(checkParallelism(parallelism),
checkFactory(factory),
handler,
asyncMode ? FIFO_QUEUE : LIFO_QUEUE,
"ForkJoinPool-" + nextPoolId() + "-worker-");
checkPermission();
}ForkJoin计算案例代码:
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask;
public class SimpleTaskExample {
private static class SimpleTask extends RecursiveTask<Long> {
private long arr[];
private int start,end;
private static final int THRESHOLD=10;
// 计算拆分次数
private static int index=1;
public SimpleTask(long[] arr,int start,int end){
this.arr=arr;
this.start=start;
this.end=end;
}
@Override
protected Long compute() {
// 如果阈值小于指定值
if(end-start<THRESHOLD){
long sum=0;
for(int i=start;i<end;i++){
sum+=arr[i];
System.out.println("thread name:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+",index"+index++);
}
return sum;
}else{
int mid=start+(end-start)/2;
SimpleTask leftTask = new SimpleTask(arr, start, mid);
SimpleTask rightTask = new SimpleTask(arr, mid, end);
// fork计算
leftTask.fork();
rightTask.fork();
// join聚合
Long leftResult = leftTask.join();
Long rightResult = rightTask.join();
return leftResult+rightResult;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
long[] num = new long[1000];
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
num[i]=30+i;
}
ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool();
SimpleTask simpleTask = new SimpleTask(num, 0, num.length);
Long result = forkJoinPool.invoke(simpleTask);
System.out.println("result:"+result);
}
}运行示例如下:

synchionized实现的获取id.
/**
* Sequence number for creating workerNamePrefix.
*/
private static int poolNumberSequence; private static final synchronized int nextPoolId() {
return ++poolNumberSequence;
}cpu核数减一.
private static ForkJoinPool makeCommonPool() {
int parallelism = -1;
ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory factory = null;
UncaughtExceptionHandler handler = null;
try { // ignore exceptions in accessing/parsing properties
String pp = System.getProperty
("java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.parallelism");
String fp = System.getProperty
("java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.threadFactory");
String hp = System.getProperty
("java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.exceptionHandler");
if (pp != null)
parallelism = Integer.parseInt(pp);
if (fp != null)
factory = ((ForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory)ClassLoader.
getSystemClassLoader().loadClass(fp).newInstance());
if (hp != null)
handler = ((UncaughtExceptionHandler)ClassLoader.
getSystemClassLoader().loadClass(hp).newInstance());
} catch (Exception ignore) {
}
if (factory == null) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() == null)
factory = defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory;
else // use security-managed default
factory = new InnocuousForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory();
}
if (parallelism < 0 && // default 1 less than #cores
(parallelism = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() - 1) <= 0)
parallelism = 1;
if (parallelism > MAX_CAP)
parallelism = MAX_CAP;
return new ForkJoinPool(parallelism, factory, handler, LIFO_QUEUE,
"ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-");
}5、实现一个基于系统公用线程池工具类,运行这个系统中的异步业务.
public final class CustomExecutors {
/**
* 核心线程数大小
*/
private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE=5;
/**
* 核心线程池大小
*/
private static final int MAX_POOL_SIZE=10;
/**
* 线程存活时间
*/
private static final int KEEP_ALIVE_TIME=60;
/**
* 工作队列大小
*/
private static final LinkedBlockingQueue queue=new LinkedBlockingQueue(100);
/**
* 自定义线程池名前缀
*/
private static final String POOL_PREFIX_NAME="Custom-Common-Pool";
private CustomExecutors(){
//throw new XXXXException("un support create pool!");
}
private static ConstomThreadPool constomThreadPool;
/**
* 静态块初始化只执行一次,不关闭,整个系统公用一个线程池
*/
static {
constomThreadPool=new ConstomThreadPool(CORE_POOL_SIZE,MAX_POOL_SIZE,KEEP_ALIVE_TIME,TimeUnit.SECONDS,queue,POOL_PREFIX_NAME);
}
/**
* 单例模式获取线程池
* @return ExecutorService
*/
private static ExecutorService getInstance(){
return constomThreadPool;
}
private static Future<?> submit(Runnable task){
return constomThreadPool.submit(task);
}
private static <T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result){
return constomThreadPool.submit(task,result);
}
private static <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task){
return constomThreadPool.submit(task);
}
private static void execute(Runnable task){
constomThreadPool.execute(task);
}
}三、业界知名自定义线程池扩展使用.
1、org.apache.tomcat.util.threads;【Tomcat线程池】

2、XXL-JOB分布式任务调度框架的快慢线程池,线程池任务隔离.
public class JobTriggerPoolHelper {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JobTriggerPoolHelper.class);
// ---------------------- trigger pool ----------------------
// fast/slow thread pool
private ThreadPoolExecutor fastTriggerPool = null;
private ThreadPoolExecutor slowTriggerPool = null;
public void start(){
fastTriggerPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
10,
XxlJobAdminConfig.getAdminConfig().getTriggerPoolFastMax(),
60L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(1000),
new ThreadFactory() {
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "xxl-job, admin JobTriggerPoolHelper-fastTriggerPool-" + r.hashCode());
}
});
slowTriggerPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
10,
XxlJobAdminConfig.getAdminConfig().getTriggerPoolSlowMax(),
60L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(2000),
new ThreadFactory() {
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "xxl-job, admin JobTriggerPoolHelper-slowTriggerPool-" + r.hashCode());
}
});
}
public void stop() {
//triggerPool.shutdown();
fastTriggerPool.shutdownNow();
slowTriggerPool.shutdownNow();
logger.info(">>>>>>>>> xxl-job trigger thread pool shutdown success.");
}
// job timeout count
private volatile long minTim = System.currentTimeMillis()/60000; // ms > min
private volatile ConcurrentMap<Integer, AtomicInteger> jobTimeoutCountMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* add trigger
*/
public void addTrigger(final int jobId,
final TriggerTypeEnum triggerType,
final int failRetryCount,
final String executorShardingParam,
final String executorParam,
final String addressList) {
// choose thread pool
ThreadPoolExecutor triggerPool_ = fastTriggerPool;
AtomicInteger jobTimeoutCount = jobTimeoutCountMap.get(jobId);
if (jobTimeoutCount!=null && jobTimeoutCount.get() > 10) { // job-timeout 10 times in 1 min
triggerPool_ = slowTriggerPool;
}
// trigger
triggerPool_.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// do trigger
XxlJobTrigger.trigger(jobId, triggerType, failRetryCount, executorShardingParam, executorParam, addressList);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
// check timeout-count-map
long minTim_now = System.currentTimeMillis()/60000;
if (minTim != minTim_now) {
minTim = minTim_now;
jobTimeoutCountMap.clear();
}
// incr timeout-count-map
long cost = System.currentTimeMillis()-start;
if (cost > 500) { // ob-timeout threshold 500ms
AtomicInteger timeoutCount = jobTimeoutCountMap.putIfAbsent(jobId, new AtomicInteger(1));
if (timeoutCount != null) {
timeoutCount.incrementAndGet();
}
}
}
}
});
}
// ---------------------- helper ----------------------
private static JobTriggerPoolHelper helper = new JobTriggerPoolHelper();
public static void toStart() {
helper.start();
}
public static void toStop() {
helper.stop();
}
/**
* @param jobId
* @param triggerType
* @param failRetryCount
* >=0: use this param
* <0: use param from job info config
* @param executorShardingParam
* @param executorParam
* null: use job param
* not null: cover job param
*/
public static void trigger(int jobId, TriggerTypeEnum triggerType, int failRetryCount, String executorShardingParam, String executorParam, String addressList) {
helper.addTrigger(jobId, triggerType, failRetryCount, executorShardingParam, executorParam, addressList);
}
}①、定义两个线程池,一个是fastTriggerPool,另一个是slowTriggerPool。
②、定义一个容器ConcurrentMap,存放每个任务的执行慢次数,60秒后自动清空该容器。
③、在线程的run()方法中计算每个任务的耗时,如果大于500ms,则任务的慢执行次数+1。

3、基于线程池动态监控动态线程池

引用图片,线程池常见问题

4、ES线程池.
ES的并发工具包,org.elasticsearch.common.util.concurrent,es的线程池配置在elasticsearch.yml中配置.


ES中的线程池类型,ThreadPoolType:

ES自定义线程池拒绝策略:

ES自定义线程池命名:

如创建索引、查询、bulk写入等都有指定的默认线程池大小的,如果使用云服务可以在租户concole配置,生产可以配置search队列和write对列值告警,方便监控ES。
5、Prometheus的监控线程池,单个线程池定时上报数据,
PushMeterRegistry类的ScheduledExecutorService

public void start(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
if (scheduledExecutorService != null)
stop();
if (config.enabled()) {
logger.info("publishing metrics for " + this.getClass().getSimpleName() + " every "
+ TimeUtils.format(config.step()));
scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(threadFactory);
// time publication to happen just after StepValue finishes the step
long stepMillis = config.step().toMillis();
long initialDelayMillis = stepMillis - (clock.wallTime() % stepMillis) + 1;
scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(this::publishSafely, initialDelayMillis, stepMillis,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
public void stop() {
if (scheduledExecutorService != null) {
scheduledExecutorService.shutdown();
scheduledExecutorService = null;
}
}定义了一套完整的线程池进行上报数据.

SpringBoot自动注入
@AutoConfiguration(after = { MetricsAutoConfiguration.class, SimpleMetricsExportAutoConfiguration.class,
TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class, TaskSchedulingAutoConfiguration.class })
@ConditionalOnClass(ExecutorServiceMetrics.class)
@ConditionalOnBean({ Executor.class, MeterRegistry.class })
public class TaskExecutorMetricsAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired
public void bindTaskExecutorsToRegistry(Map<String, Executor> executors, MeterRegistry registry) {
executors.forEach((beanName, executor) -> {
if (executor instanceof ThreadPoolTaskExecutor) {
monitor(registry, safeGetThreadPoolExecutor((ThreadPoolTaskExecutor) executor), beanName);
}
else if (executor instanceof ThreadPoolTaskScheduler) {
monitor(registry, safeGetThreadPoolExecutor((ThreadPoolTaskScheduler) executor), beanName);
}
});
}
private void monitor(MeterRegistry registry, ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor, String name) {
if (threadPoolExecutor != null) {
new ExecutorServiceMetrics(threadPoolExecutor, name, Collections.emptyList()).bindTo(registry);
}
}
private ThreadPoolExecutor safeGetThreadPoolExecutor(ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor) {
try {
return taskExecutor.getThreadPoolExecutor();
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
return null;
}
}
private ThreadPoolExecutor safeGetThreadPoolExecutor(ThreadPoolTaskScheduler taskScheduler) {
try {
return taskScheduler.getScheduledThreadPoolExecutor();
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
return null;
}
}
}监控线程池的方法核心逻辑
public void bindTo(MeterRegistry registry) {
if (executorService == null) {
return;
}
String className = executorService.getClass().getName();
if (executorService instanceof ThreadPoolExecutor) {
monitor(registry, (ThreadPoolExecutor) executorService);
}
else if (executorService instanceof ForkJoinPool) {
monitor(registry, (ForkJoinPool) executorService);
}
else if (allowIllegalReflectiveAccess) {
if (className.equals("java.util.concurrent.Executors$DelegatedScheduledExecutorService")) {
monitor(registry, unwrapThreadPoolExecutor(executorService, executorService.getClass()));
}
else if (className.equals("java.util.concurrent.Executors$FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService")) {
monitor(registry,
unwrapThreadPoolExecutor(executorService, executorService.getClass().getSuperclass()));
}
else {
log.warn("Failed to bind as {} is unsupported.", className);
}
}
else {
log.warn("Failed to bind as {} is unsupported or reflective access is not allowed.", className);
}
}
/**
* Every ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor created by {@link Executors} is wrapped. Also,
* {@link Executors#newSingleThreadExecutor()} wrap a regular
* {@link ThreadPoolExecutor}.
*/
@Nullable
private ThreadPoolExecutor unwrapThreadPoolExecutor(ExecutorService executor, Class<?> wrapper) {
try {
Field e = wrapper.getDeclaredField("e");
e.setAccessible(true);
return (ThreadPoolExecutor) e.get(executor);
}
catch (NoSuchFieldException | IllegalAccessException | RuntimeException e) {
// Cannot use InaccessibleObjectException since it was introduced in Java 9,
// so catch all RuntimeExceptions instead
// Do nothing. We simply can't get to the underlying ThreadPoolExecutor.
log.info("Cannot unwrap ThreadPoolExecutor for monitoring from {} due to {}: {}", wrapper.getName(),
e.getClass().getName(), e.getMessage());
}
return null;
}
private void monitor(MeterRegistry registry, @Nullable ThreadPoolExecutor tp) {
if (tp == null) {
return;
}
FunctionCounter.builder(metricPrefix + "executor.completed", tp, ThreadPoolExecutor::getCompletedTaskCount)
.tags(tags).description("The approximate total number of tasks that have completed execution")
.baseUnit(BaseUnits.TASKS).register(registry);
Gauge.builder(metricPrefix + "executor.active", tp, ThreadPoolExecutor::getActiveCount).tags(tags)
.description("The approximate number of threads that are actively executing tasks")
.baseUnit(BaseUnits.THREADS).register(registry);
Gauge.builder(metricPrefix + "executor.queued", tp, tpRef -> tpRef.getQueue().size()).tags(tags)
.description("The approximate number of tasks that are queued for execution").baseUnit(BaseUnits.TASKS)
.register(registry);
Gauge.builder(metricPrefix + "executor.queue.remaining", tp, tpRef -> tpRef.getQueue().remainingCapacity())
.tags(tags)
.description("The number of additional elements that this queue can ideally accept without blocking")
.baseUnit(BaseUnits.TASKS).register(registry);
Gauge.builder(metricPrefix + "executor.pool.size", tp, ThreadPoolExecutor::getPoolSize).tags(tags)
.description("The current number of threads in the pool").baseUnit(BaseUnits.THREADS)
.register(registry);
Gauge.builder(metricPrefix + "executor.pool.core", tp, ThreadPoolExecutor::getCorePoolSize).tags(tags)
.description("The core number of threads for the pool").baseUnit(BaseUnits.THREADS).register(registry);
Gauge.builder(metricPrefix + "executor.pool.max", tp, ThreadPoolExecutor::getMaximumPoolSize).tags(tags)
.description("The maximum allowed number of threads in the pool").baseUnit(BaseUnits.THREADS)
.register(registry);
}Nacos的线程池
/*
* Copyright 1999-2018 Alibaba Group Holding Ltd.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.alibaba.nacos.common.executor;
import com.alibaba.nacos.common.JustForTest;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* Unified thread pool creation factory, and actively create thread pool resources by ThreadPoolManager for unified life
* cycle management {@link ExecutorFactory.Managed}.
*
* <p>Unified thread pool creation factory without life cycle management {@link ExecutorFactory}.
*
* <p>two check style ignore will be removed after issue#2856 finished.
*
* @author <a href="mailto:liaochuntao@live.com">liaochuntao</a>
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"PMD.ThreadPoolCreationRule", "checkstyle:overloadmethodsdeclarationorder",
"checkstyle:missingjavadocmethod"})
public final class ExecutorFactory {
public static ExecutorService newSingleExecutorService() {
return Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
}
public static ExecutorService newSingleExecutorService(final ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1, threadFactory);
}
public static ExecutorService newFixedExecutorService(final int nThreads) {
return Executors.newFixedThreadPool(nThreads);
}
public static ExecutorService newFixedExecutorService(final int nThreads, final ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return Executors.newFixedThreadPool(nThreads, threadFactory);
}
public static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleScheduledExecutorService(final ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1, threadFactory);
}
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledExecutorService(final int nThreads,
final ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(nThreads, threadFactory);
}
public static ThreadPoolExecutor newCustomerThreadExecutor(final int coreThreads, final int maxThreads,
final long keepAliveTimeMs, final ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(coreThreads, maxThreads, keepAliveTimeMs, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(), threadFactory);
}
public static final class Managed {
private static final String DEFAULT_NAMESPACE = "nacos";
private static final ThreadPoolManager THREAD_POOL_MANAGER = ThreadPoolManager.getInstance();
/**
* Create a new single executor service with default thread factory and register to manager.
*
* @param group group name
* @return new single executor service
*/
public static ExecutorService newSingleExecutorService(final String group) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
THREAD_POOL_MANAGER.register(DEFAULT_NAMESPACE, group, executorService);
return executorService;
}
/**
* Create a new single executor service with input thread factory and register to manager.
*
* @param group group name
* @param threadFactory thread factory
* @return new single executor service
*/
public static ExecutorService newSingleExecutorService(final String group, final ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1, threadFactory);
THREAD_POOL_MANAGER.register(DEFAULT_NAMESPACE, group, executorService);
return executorService;
}
/**
* Create a new fixed executor service with default thread factory and register to manager.
*
* @param group group name
* @param nThreads thread number
* @return new fixed executor service
*/
public static ExecutorService newFixedExecutorService(final String group, final int nThreads) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(nThreads);
THREAD_POOL_MANAGER.register(DEFAULT_NAMESPACE, group, executorService);
return executorService;
}
/**
* Create a new fixed executor service with input thread factory and register to manager.
*
* @param group group name
* @param nThreads thread number
* @param threadFactory thread factory
* @return new fixed executor service
*/
public static ExecutorService newFixedExecutorService(final String group, final int nThreads,
final ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(nThreads, threadFactory);
THREAD_POOL_MANAGER.register(DEFAULT_NAMESPACE, group, executorService);
return executorService;
}
/**
* Create a new single scheduled executor service with input thread factory and register to manager.
*
* @param group group name
* @param threadFactory thread factory
* @return new single scheduled executor service
*/
public static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleScheduledExecutorService(final String group,
final ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
ScheduledExecutorService executorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1, threadFactory);
THREAD_POOL_MANAGER.register(DEFAULT_NAMESPACE, group, executorService);
return executorService;
}
/**
* Create a new scheduled executor service with input thread factory and register to manager.
*
* @param group group name
* @param nThreads thread number
* @param threadFactory thread factory
* @return new scheduled executor service
*/
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledExecutorService(final String group, final int nThreads,
final ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
ScheduledExecutorService executorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(nThreads, threadFactory);
THREAD_POOL_MANAGER.register(DEFAULT_NAMESPACE, group, executorService);
return executorService;
}
/**
* Create a new custom executor service and register to manager.
*
* @param group group name
* @param coreThreads core thread number
* @param maxThreads max thread number
* @param keepAliveTimeMs keep alive time milliseconds
* @param threadFactory thread factory
* @return new custom executor service
*/
public static ThreadPoolExecutor newCustomerThreadExecutor(final String group, final int coreThreads,
final int maxThreads, final long keepAliveTimeMs, final ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(coreThreads, maxThreads, keepAliveTimeMs,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(), threadFactory);
THREAD_POOL_MANAGER.register(DEFAULT_NAMESPACE, group, executor);
return executor;
}
@JustForTest
public static ThreadPoolManager getThreadPoolManager() {
return THREAD_POOL_MANAGER;
}
}
}
附录:死锁案例
1、线程死锁
public class DeadLock {
private static final byte[] lock1=new byte[0];
private static final byte[] lock2=new byte[0];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock1) {
System.out.println("get lock1 start");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("get lock1 end");
synchronized (lock2) {
System.out.println("get lock2 start");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("get lock2 end");
}
}
}
}, "thread1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock2) {
System.out.println("get lock2 start");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("get lock2 end");
synchronized (lock1) {
System.out.println("get lock1 start");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("get lock1 end");
}
}
}
}, "thread2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
2、 线程饥饿死锁
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
public class ExecuteLock {
private static ExecutorService single= Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
public static class NormalCallable implements Callable<String>{
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Entry NormalCallable");
return "annother success";
}
}
public static class DeadLockCallable implements Callable<String> {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Entry DeadLockCallable");
Future<String> submit = single.submit(new NormalCallable());
return "success:"+submit.get();
}
}
// 主线程在等待一个FutureTask完成,而线程池中一个线程也在等待一个FutureTask完成。
//从代码实现可以看到,主线程往线程池中扔了一个任务A,任务A又往同一个线程池中扔了一个任务B,并等待B的完成,由于线程池中只有一个线程,这将导致B会被停留在阻塞队列中,而A还得等待B的完成,这也就是互相等待导致了死锁的反生
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
DeadLockCallable task = new DeadLockCallable();
Future<String> submit = single.submit(task);
System.out.println(submit.get());
System.out.println("over");
single.shutdown();
}
}

使用jps查看


本文主要介绍Java如何自定义线程池,并介绍了一些知名中间件是如何自定义线程池使用的,方便扩展我们的视野,加深我们对线程池的理解,更好的应用到实战项目中。

开放原子开发者工作坊旨在鼓励更多人参与开源活动,与志同道合的开发者们相互交流开发经验、分享开发心得、获取前沿技术趋势。工作坊有多种形式的开发者活动,如meetup、训练营等,主打技术交流,干货满满,真诚地邀请各位开发者共同参与!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献5条内容
已为社区贡献5条内容






所有评论(0)