HarmonyOS鸿蒙开发常用4种布局详细说明
HarmonyOS鸿蒙开发常用4种布局详细说明1、线性布局2、层叠布局3、网格布局4、列表布局。
一直会分享,虽然鸿蒙目前来没有多大发展,但不可否然以后发展,华为的技术是一大突破,存在即合理
可以现在没有多大发展。但不可否定未来的发展。
关注’猿来编码‘,微信订阅号,回复 ’组件‘,获取
介绍一下鸿蒙开发常用4种布局
1、线性布局
2、层叠布局
3、网格布局
4、列表布局
1. 线性布局(Column/Row)
线性布局(LinearLayout)是开发中最常用的布局,通过线性容器Row(行)和Column(列)构建,它是其他布局的基础,其子元素在线性方向上(水平或垂直)依次排列,基本形式如下:
Column(列)
子元素在排列方向上的间距,可以通过组件参数space参数进行控制
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
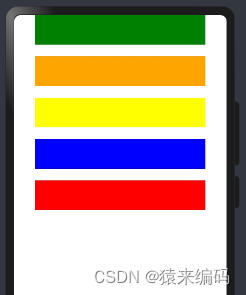
Column({space:20}) {
//一行
Row() {
}.width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor(Color.Green)
Row() {
}.width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor(Color.Orange)
Row() {
}.width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor(Color.Yellow)
Row() {
}.width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor(Color.Blue)
Row() {
}.width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor(Color.Red)
}.width('100%').alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Center)
}
}
效果:

Row(行)
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Row({space:20}) {
Column() {
}.width('15%').height(50).backgroundColor(Color.Red);
Column() {
}.width('15%').height(50).backgroundColor(Color.Orange);
Column() {
}.width('15%').height(50).backgroundColor(Color.Red);
Column() {
}.width('15%').height(50).backgroundColor(Color.Blue);
Column() {
}.width('15%').height(50).backgroundColor(Color.Pink);
}.width('100%').padding(20).backgroundColor('#ccc')
}
}

子元素排列与对齐
● 主轴:线性布局容器在布局方向上的轴线,Row容器主轴为横向,Column容器主轴为纵向。
● 交叉轴:垂直于主轴方向的轴线。Row容器交叉轴为纵向,Column容器交叉轴为横向。
子元素沿主轴方向的排列方式
可以通过justifyContent 属性进行控制,可选值如下:
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Column({space:20}) {
//一行
Row() {
}.width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor(Color.Green)
Row() {
}.width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor(Color.Red)
}.width('100%').height('100%').justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)

.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Start)

.justifyContent(FlexAlign.End)

.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceBetween)

.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceAround)

.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceEvenly)

子元素沿交叉轴方向的对齐方式
可以通过alignItems 属性进行控制,可选值如下:
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Column() {
Row() {
}.width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor(Color.Red)
Row() {
}.width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor(Color.Orange)
Row() {
}.width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor(Color.Yellow)
}.width('100%').height('100%').alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Start)
}
}
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Start)

.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Center)

.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.End)

**
2、层叠布局(Stack)
Stack布局是一种常用的布局方式,它允许将子元素沿垂直于屏幕的方向堆叠在一起,类似于图层的叠加。子元素可以按照其添加顺序依次叠加在一起,后添加的子元素会覆盖之前添加的子元素,层叠布局具有较强的页面层叠、位置定位能力,其使用场景有广告、卡片层叠效果等。
Stack容器中的子组件可通过zIndex属性设置其所在的层级,zIndex值越大,层级越高,即zIndex值大的组件会覆盖在zIndex值小的组件上方
Stack 布局通常会和 position绝对定位配合使用,设置元素左上角相对于父容器左上角偏移位置配合使用,position语法示例:.position({ x: 180, y: 130 })
@Entry
@Component
struct StackAlign {
@State alignment: Alignment = Alignment.Center;
build() {
Column() {
Stack() {
Row() {
Text('1')
}
.width(300).height(300).backgroundColor(Color.Yellow)
Row() {
Text('2')
}
.width(150).height(150).backgroundColor(Color.Red)
Row() {
Text('3')
}
.width(75).height(75).backgroundColor(Color.Green)
}
}
.width('100%')
}
}

.alignContent(Alignment.TopStart)
@Entry
@Component
struct StackAlign {
@State alignment: Alignment = Alignment.Center;
build() {
Column() {
Stack() {
Row() {
Text('1')
}
.width(300).height(300).backgroundColor(Color.Blue)
Row() {
Text('2')
}
.width(150).height(150).backgroundColor(Color.Red)
Row() {
Text('3')
}
.width(75).height(75).backgroundColor(Color.Yellow)
}
.width('100%').backgroundColor('#ccc').alignContent(Alignment.TopStart) }
.width('100%')
}
}

.alignContent(Alignment.TopEnd)

.alignContent(Alignment.Top)

.alignContent(Alignment.Start)

.alignContent(Alignment.Center)

.alignContent(Alignment.End)

.alignContent(Alignment.BottomStart)

.alignContent(Alignment.BottomEnd)

.alignContent(Alignment.Bottom)

**
3、网格布局(Grid)
**
网格布局(Grid)是一种强大的页面排版方式,通过将页面划分为行和列组成的网格,使得子组件可以在这个二维网格中自由定位。网格布局的容器组件为Grid,子组件为GridItem,如下图所示。
用1fr来表示占1个’单位‘
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Grid(){
GridItem(){}.backgroundColor(Color.Red)
GridItem(){}.backgroundColor(Color.Green)
GridItem(){}.backgroundColor(Color.Yellow)
GridItem(){}.backgroundColor(Color.Brown)
GridItem(){}.backgroundColor(Color.Orange)
GridItem(){}.backgroundColor(Color.Black)
GridItem(){}.backgroundColor(Color.Orange)
GridItem(){}.backgroundColor(Color.Gray)
GridItem(){}.backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
}.width('100%').height(400).rowsTemplate('1fr 2fr 1fr').columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr 1fr').rowsGap(10).columnsGap(10)
}
}
.rowsTemplate(‘1fr 2fr 1fr’)

.columnsTemplate(‘1fr 2fr 1fr’)

.rowStart(1).rowEnd(2)

.rowsGap(10).columnsGap(30)

当显示内容超出显示区域时,有滚动效果
4、列表布局(List)
列表(List)是一种复杂的容器组件,使用列表可以轻松高效地显示结构化、可滚动的列表信息。列表布局的容器组件为List,子组件为ListItem或者ListItemGroup,其中,ListItem表示单个列表项,ListItemGroup用于列表数据的分组展示,其子组件也是ListItem,如下图所示
.listDirection(Axis.Vertical)
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
List({space:10}) {
ListItem() {
Text('list1')
}.width('100%').backgroundColor(Color.Red)
ListItemGroup() {
ListItem() {
Text('list2')
}.width('100%')
ListItem() {
Text('list3')
}.width('100%')
}.width('100%').backgroundColor(Color.Yellow)
}.width('100%').listDirection(Axis.Vertical)
}
}

.listDirection(Axis.Horizontal)

.alignListItem(ListItemAlign.End)

.alignListItem(ListItemAlign.Start)

.alignListItem(ListItemAlign.Center)

scrollBar属性可控制滚动条样式
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State contactsGroups: object[] = [
{
title: 'A',
contacts: [
'赵云',
'李白',
'王思'
],
},
{
title: 'B',
contacts: [
'白叶',
'伯乐'
],
},
{
title: 'C',
contacts: [
'王大',
'张三'
],
},
{
title: 'D',
contacts: [
'白龙',
'小明'
],
},
{
title: 'E',
contacts: [
'盖伦',
'石头',
'光辉'
],
}
]
@Builder Header(item){
Text(item.title).fontSize(30).backgroundColor('#ccc').width('100%')
}
build() {
List(){
ForEach(this.contactsGroups,(item)=>{
ListItemGroup({header:this.Header(item)}){
ForEach(item.contacts,(user)=>{
ListItem(){
Text(user)
}.width('100%').height(50)
})
}
},item=>JSON.stringify(item));
}.width('100%').height(300).scrollBar(BarState.On)
}
}

以上就是常用布局
关注’猿来编码‘,微信订阅号,回复 ’布局‘,获取

开放原子开发者工作坊旨在鼓励更多人参与开源活动,与志同道合的开发者们相互交流开发经验、分享开发心得、获取前沿技术趋势。工作坊有多种形式的开发者活动,如meetup、训练营等,主打技术交流,干货满满,真诚地邀请各位开发者共同参与!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容





所有评论(0)