【AI】Python 实现八数码问题
八数码问题
八数码问题
1. 题目介绍
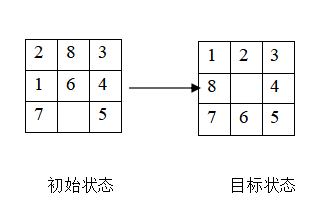
八数码问题描述为:在 3×3 组成的九宫格棋盘上,摆有 8 张牌,每张牌都刻有 1-8 中的某一个数码。棋盘中留有一个空格,允许其周围的某张牌向空格移动,这样通过移动牌就可以不断改变棋盘布局。这种游戏求解的问题是:给定一种初始的棋盘布局或结构(初始状态)和一个目标的布局(称目标状态),问如何移动牌,实现从初始状态到目标状态的转变。
例如如下的棋盘要求将初始状态移动到目标状态:

传统的解题方法包含深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索。但这会带来一个问题,即搜索是盲目的,没有根据当前棋盘的布局来动态地调整下一步搜索的策略。为此我们定义了启发式搜索算法(A* 算法),它会提取出当前棋盘的一些特征,来最优地选择下一次要搜索的方向。
对于八数码问题,其启发式方法为当前棋盘与目标棋盘的差异度,而差异度又可以通过两种方法来进行计算。
记当前棋盘为 source,目标棋盘为 target。第一种计算方法为:如果 source[i][j] != target[i][j],则差异度 += 1;第二种计算方法为:如果 source[i][j] == target[m][n],则差异度 += (abs(m - i) + abs(n - j))。
例如,对于上面的初始状态和目标状态,使用第一种计算方法,其差异度矩阵为(1 表示该位置两状态矩阵的元素不同,0 表示相同):

最终可以计算出两个矩阵的差异度为 4。
使用第二种计算方法,其差异度矩阵为(值表示 source[i][j] 的元素移动到目标位置所需的最短步数):

最终可以计算出两个矩阵的差异度为 5。
不管使用哪种办法,都能得出一个差异度,暂且记为 g。并且,解题的办法要么采用 DFS,要么采用 BFS,两种办法的搜索时间都会随着深度的增加而增加,我们的目标是尽量减少搜索的时间,也就是要想办法减少搜索深度。为了解决这个问题,记当前的搜索深度为 d,那么 d 越小越好。同时,我们又希望 g 越小越好,所以我们整体的目标就可以转化为 d + g 越小越好,这综合了 d 和 g 各自有的优势,是一个良好的 tradeoff。
因此,我们的整体目标也就转化成了:在 DFS 或 BFS 的函数中,对每一个状态都计算 f = d + g,选取 f 最小的那个结点,让它作为下次迭代的首选结点。
2. 代码演示
下面使用三种方式来评估启发式算法的性能,第一种是不使用启发式算法,第二种是使用前文提到的策略 1,第三种是使用前文提到的策略 2。
2.1 不使用启发式算法
在代码中,将变量 use_A_star 设定为 False 即指定不使用启发式算法,运行结果为:

运行 50 次求得所耗平均时间为:0.022931413650512697 s
2.2 使用启发式策略 1
在代码中,将变量 use_A_star 设定为 True,strategy 设定为 1,即指定使用启发式算法 1,运行结果为:

运行 50 次求得所耗平均时间为:0.0021903276443481444 s
2.3 使用启发式策略 2
在代码中,将变量 use_A_star 设定为 True,strategy 设定为 2,即指定使用启发式算法 2,运行结果为:

运行 50 次求得所耗平均时间为:0.002417140007019043 s
3. 结论分析
从三种方法的运行结果可以得出下列结论:使用启发式算法可以大幅度节省程序运行时间(是纯 BFS 的 1/10),启发式算法 1 比启发式算法 2 效率更高,这可能是因为算法 1 在计算矩阵差异度时只需要遍历一遍矩阵,而算法 2 需要遍历两遍矩阵。
4. 源码
import numpy as np
import time
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, source, target, strategy, cost=0, depth=0):
self.directions = ['left', 'up', 'right', 'down']
self.source = source
self.target = target
self.cost = cost
self.depth = depth
self.strategy = strategy
# 打印原始矩阵
def print_source(self):
for i in range(3):
[print(self.source[i][j], end=' ') for j in range(3)]
print()
print()
# 计算不在位的棋子个数
def num_misposition(self):
# 比较source和target,不同的地方标记为1,相同的地方标记为0
flag = np.where(self.source == self.target, 0, 1)
# 返回source与target之间不相同的数的个数
return np.sum(np.reshape(flag, (flag.size,)))
# 计算耗散值
def get_cost(self):
if self.strategy == 1:
return self.depth + self.num_misposition()
elif self.strategy == 2:
flag = np.where(self.source == self.target, 0, 1)
sum_cost = 0
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
if flag[i][j]:
for m in range(3):
for n in range(3):
if self.target[m][n] == self.source[i][j]:
dif_row, dif_col = abs(m - i), abs(n - j)
sum_cost += (dif_row + dif_col)
return sum_cost
# 将棋子0分别往四个方向移动
def move(self):
# 记录棋子0所在的行号和列号
row, col = np.where(self.source == 0)
row, col = row[0], col[0]
moved_nodes = []
for direction in self.directions:
if direction == 'left' and col > 0:
source_copy = self.source.copy()
source_copy[row, col], source_copy[row, col - 1] = source_copy[row, col - 1], source_copy[row, col]
moved_nodes.append(
Node(source_copy, target=self.target, cost=self.get_cost(), depth=self.depth + 1, strategy=self.strategy))
elif direction == 'up' and row > 0:
source_copy = self.source.copy()
source_copy[row, col], source_copy[row - 1, col] = source_copy[row - 1, col], source_copy[row, col]
moved_nodes.append(
Node(source_copy, target=self.target, cost=self.get_cost(), depth=self.depth + 1, strategy=self.strategy))
elif direction == 'right' and col < len(self.source) - 1:
source_copy = self.source.copy()
source_copy[row, col], source_copy[row, col + 1] = source_copy[row, col + 1], source_copy[row, col]
moved_nodes.append(
Node(source_copy, target=self.target, cost=self.get_cost(), depth=self.depth + 1, strategy=self.strategy))
elif direction == 'down' and row < len(self.source) - 1:
source_copy = self.source.copy()
source_copy[row, col], source_copy[row + 1, col] = source_copy[row + 1, col], source_copy[row, col]
moved_nodes.append(
Node(source_copy, target=self.target, cost=self.get_cost(), depth=self.depth + 1, strategy=self.strategy))
return moved_nodes
class EightPuzzle(object):
def __init__(self, init_node, use_A_star, strategy):
self.use_A_star = use_A_star
self.queue = []
self.closed_nodes = []
self.count = 0
self.init_node = init_node
self.time_start = 0
self.time_end = 0
self.strategy = strategy
# 判断传入的结点是否在self.closed_nodes中
def is_in_closed_nodes(self, node):
for closed_node in self.closed_nodes:
# 比较closed_node和node,不同的地方标记为1,相同的地方标记为0
flag = np.where(closed_node.source == node.source, 0, 1)
if np.sum(np.reshape(flag, (flag.size,))) == 0:
return True
return False
# 获取最小耗散值的那个结点
def get_min_cost_index(self):
min_cost = self.queue[0].cost
index = 0
for i in range(len(self.queue)):
if self.queue[i].cost < min_cost:
index = i
min_cost = self.queue[i].cost
return index
# bfs求解问题
def bfs(self):
self.time_start = time.time()
self.queue.append(self.init_node)
min_cost = self.init_node.cost
while self.queue:
if self.use_A_star:
current_node_index = self.get_min_cost_index()
current_node = self.queue.pop(current_node_index)
else:
current_node = self.queue.pop(0)
self.closed_nodes.append(current_node)
# 不在位棋子个数为0,到达终点
if current_node.num_misposition() == 0:
self.time_end = time.time()
return True, self.time_end - self.time_start, current_node
moved_nodes = current_node.move()
for next_node in moved_nodes:
if self.is_in_closed_nodes(next_node):
continue
self.queue.append(next_node)
self.count += 1
self.time_end = time.time()
return False, self.time_end - self.time_start, None
def main():
source = np.array([[2, 8, 3], [1, 6, 4], [7, 0, 5]])
target = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [8, 0, 4], [7, 6, 5]])
print('The source matrix is:\n', source)
print('The target matrix is:\n', target)
use_A_star = True
strategy = 2
init_node = Node(source, target, strategy, cost=0)
solution = EightPuzzle(init_node, use_A_star, strategy)
has_solved, time_used, result_node = solution.bfs()
if has_solved:
print('\nThis problem has been solved, using', time_used, 's.')
print('The result matrix is:')
result_node.print_source()
return time_used
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
经评论区同学指出的问题,对代码结构进行了优化,能够生成并处理更复杂的矩阵结构,算法2的效率显著优于算法1,并且优化了4层for循环提高了代码的运行速度:
import numpy as np
import sys
import time
def matrix_print(matrix):
for row in matrix:
print(' '.join(map(str, row)))
def generate_spiral_matrix(n):
if n % 2 == 0:
raise ValueError("Size must be an odd number for a zero-centered spiral matrix")
# 初始化一个n*n的矩阵
matrix = [[0]*n for _ in range(n)]
# 定义初始填充的数值
num = 1
# 定义矩阵的四个边界
left, right, top, bottom = 0, n-1, 0, n-1
while left < right and top < bottom:
# 从左到右填充上边
for i in range(left, right):
matrix[top][i] = num
num += 1
# 从上到下填充右边
for i in range(top, bottom):
matrix[i][right] = num
num += 1
# 从右到左填充下边
for i in range(right, left, -1):
matrix[bottom][i] = num
num += 1
# 从下到上填充左边
for i in range(bottom, top, -1):
matrix[i][left] = num
num += 1
left += 1
right -= 1
top += 1
bottom -= 1
# 如果n是奇数,则中心点会被最后剩下,单独设置中心点为0
if n % 2 == 1:
center = n // 2
matrix[center][center] = 0
return matrix
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, source, target, strategy, cost=0, depth=0, size=3):
self.directions = ['left', 'up', 'right', 'down']
self.source = source
self.target = target
self.cost = cost
self.depth = depth
self.strategy = strategy
self.size = size
# 打印原始矩阵
def print_source(self):
matrix_print(self.source)
# 计算不在位的棋子个数
def num_misposition(self):
# 比较source和target,不同的地方标记为1,相同的地方标记为0
flag = np.where(self.source == self.target, 0, 1)
# 返回source与target之间不相同的数的个数
return np.sum(np.reshape(flag, (flag.size,)))
# 计算耗散值
def get_cost(self):
if self.strategy == 1:
return self.depth + self.num_misposition()
elif self.strategy == 2:
# 在初始化或第一次调用 get_cost 时建立目标位置映射
if not hasattr(self, 'target_positions'):
self.target_positions = {self.target[i][j]: (i, j) for i in range(self.size) for j in range(self.size)}
sum_cost = 0
for i in range(self.size):
for j in range(self.size):
if self.source[i][j] != self.target[i][j]:
target_i, target_j = self.target_positions[self.source[i][j]]
sum_cost += abs(target_i - i) + abs(target_j - j)
return sum_cost + self.depth
# 将棋子0分别往四个方向移动
def move(self):
# 记录棋子0所在的行号和列号
row, col = np.where(self.source == 0)
row, col = row[0], col[0]
moved_nodes = []
for direction in self.directions:
if direction == 'left' and col > 0:
source_copy = np.copy(self.source)
source_copy[row, col], source_copy[row, col - 1] = source_copy[row, col - 1], source_copy[row, col]
moved_nodes.append(
Node(source_copy, target=self.target, cost=self.get_cost(), depth=self.depth + 1, strategy=self.strategy))
elif direction == 'up' and row > 0:
source_copy = np.copy(self.source)
source_copy[row, col], source_copy[row - 1, col] = source_copy[row - 1, col], source_copy[row, col]
moved_nodes.append(
Node(source_copy, target=self.target, cost=self.get_cost(), depth=self.depth + 1, strategy=self.strategy))
elif direction == 'right' and col < len(self.source) - 1:
source_copy = np.copy(self.source)
source_copy[row, col], source_copy[row, col + 1] = source_copy[row, col + 1], source_copy[row, col]
moved_nodes.append(
Node(source_copy, target=self.target, cost=self.get_cost(), depth=self.depth + 1, strategy=self.strategy))
elif direction == 'down' and row < len(self.source) - 1:
source_copy = np.copy(self.source)
source_copy[row, col], source_copy[row + 1, col] = source_copy[row + 1, col], source_copy[row, col]
moved_nodes.append(
Node(source_copy, target=self.target, cost=self.get_cost(), depth=self.depth + 1, strategy=self.strategy))
return moved_nodes
class EightPuzzle(object):
def __init__(self, init_node, use_A_star, strategy, max_iterations=100000):
self.use_A_star = use_A_star
self.queue = []
self.closed_nodes = []
self.count = 0
self.init_node = init_node
self.time_start = 0
self.time_end = 0
self.strategy = strategy
self.max_iterations = max_iterations
# 判断传入的结点是否在self.closed_nodes中
def is_in_closed_nodes(self, node):
for closed_node in self.closed_nodes:
# 比较closed_node和node,不同的地方标记为1,相同的地方标记为0
flag = np.where(closed_node.source == node.source, 0, 1)
if np.sum(np.reshape(flag, (flag.size,))) == 0:
return True
return False
# 获取最小耗散值的那个结点
def get_min_cost_index(self):
min_cost = self.queue[0].cost
index = 0
for i in range(len(self.queue)):
if self.queue[i].cost < min_cost:
index = i
min_cost = self.queue[i].cost
return index
# bfs求解问题
def bfs(self):
self.time_start = time.time()
self.queue.append(self.init_node)
while self.queue and self.count < self.max_iterations:
self.count += 1
if self.use_A_star:
current_node_index = self.get_min_cost_index()
current_node = self.queue.pop(current_node_index)
else:
current_node = self.queue.pop(0)
self.closed_nodes.append(current_node)
# 不在位棋子个数为0,到达终点
if current_node.num_misposition() == 0:
self.time_end = time.time()
return True, self.time_end - self.time_start, current_node
moved_nodes = current_node.move()
for next_node in moved_nodes:
if self.is_in_closed_nodes(next_node):
continue
self.queue.append(next_node)
self.time_end = time.time()
return False, self.time_end - self.time_start, None
def compute(size, strategy):
target = np.array(generate_spiral_matrix(size))
# 随机打乱数组
flat_target = target.flatten()
np.random.shuffle(flat_target)
source = flat_target.reshape(target.shape)
source = np.array([[2, 7, 4], [3, 8, 6], [5, 0, 1]])
target = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [8, 0, 4], [7, 6, 5]])
print('The source matrix is:')
matrix_print(source)
print('The target matrix is:')
matrix_print(target)
init_node = Node(source, target, strategy, cost=0, size=size)
solution = EightPuzzle(init_node, use_A_star=True, strategy=strategy)
has_solved, time_used, result_node = solution.bfs()
if has_solved:
print('\nThis problem has been solved, using', time_used, 's.')
print('The result matrix is:')
result_node.print_source()
return time_used
if __name__ == '__main__':
if len(sys.argv) != 2:
size = 3
else:
size = int(sys.argv[1])
strategy = 2
compute(size, strategy)

开放原子开发者工作坊旨在鼓励更多人参与开源活动,与志同道合的开发者们相互交流开发经验、分享开发心得、获取前沿技术趋势。工作坊有多种形式的开发者活动,如meetup、训练营等,主打技术交流,干货满满,真诚地邀请各位开发者共同参与!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献6条内容
已为社区贡献6条内容





所有评论(0)