[数据结构与算法综合实验]图与景区信息管理系统
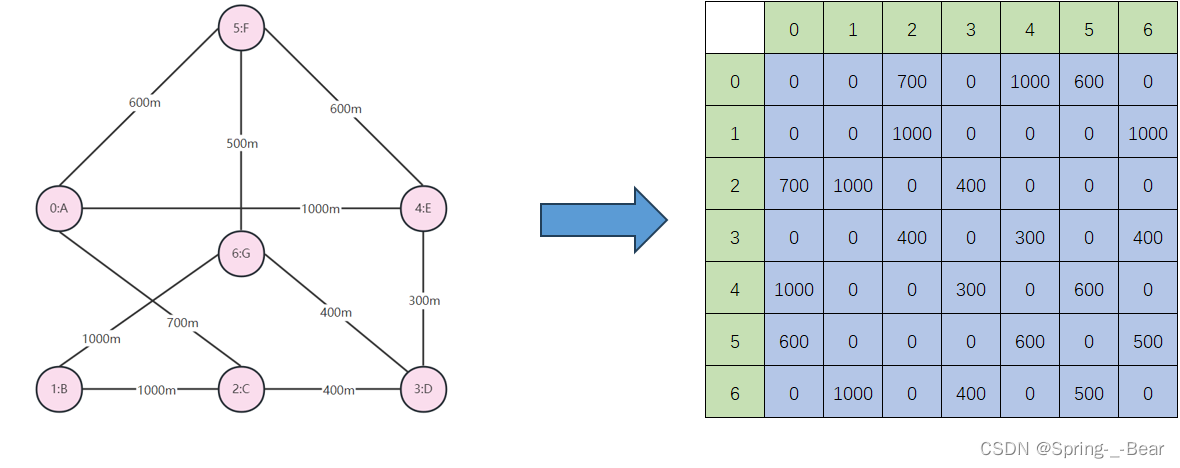
现有一个景区,景区里面有若干个景点,景点之间满足以下条件:1. 某些景点之间铺设了道路(相邻)。2. 这些道路都是可以双向行驶的(无向图)。3. 从任意一个景点出发都可以游览整个景区(连通图)。开发景区信息管理系统,对景区的信息进行管理。使用图的数据结构来保存景区景点信息,为用户提供创建图、查询景点信息、旅游景点导航、搜索最短路径、铺设电路规划等功能。
文章目录
一、实验目标
- 掌握图的定义和图的存储结构。
- 掌握图的创建方法和图的应用。
- 使用 C++ 语言,定义图的数据结构,结合迭代开发思路实现 “景区信息管理系统”。
二、实验任务
2.1 任务背景
现有一个景区,景区里面有若干个景点,景点之间满足以下条件:
- 某些景点之间铺设了道路(相邻)。
- 这些道路都是可以双向行驶的(无向图)。
- 从任意一个景点出发都可以游览整个景区(连通图)。
开发景区信息管理系统,对景区的信息进行管理。使用图的数据结构来保存景区景点信息,为用户提供创建图、查询景点信息、旅游景点导航、搜索最短路径、铺设电路规划等功能。

2.2 景点数据
景区的数据包含景点信息和景点之间的道路信息。分别由两个文本文件 Vex.txt 和 Edge.txt 存储。
2.2.1 Vex.txt
Vex.txt:存储景点信息,文件第 1 行记录景区的景点总个数。从第 2 行开始,每 3 行记录一个景点信息。 每个景点信息的记录格式为:
- 景点编号(编号从 0 开始,逐个加 1)
- 景点名字
- 景点介绍
7
0
A区
风景优美,气候宜人。门票10元。
1
B区
风景优美,气候宜人。门票20元。
2
C区
风景优美,气候宜人。门票30元。
3
D区
风景优美,气候宜人。门票40元。
4
E区
风景优美,气候宜人。门票50元。
5
F区
风景优美,气候宜人。门票60元。
6
G区
风景优美,气候宜人。门票70元。
2.2.2 Edge.txt
Edge.txt:存储道路信息,文件中每 1 行记录 1 条道路信息。格式为 “景点1的编号 景点2的编号 道路的长度”,每条记录使用空格符进行分割。 若文件中没有某两个景点的信息,就表示这两个景点之间没有直接的路径。
0 2 700
0 4 1000
0 5 600
1 2 1000
1 6 1000
2 3 400
3 4 300
3 6 400
4 5 600
5 6 500
2.3 任务要求

三、分析和设计
程序输入的数据,可从文件中直接读取,也可以从界面中输入。本程序将直接从 Vex.txt 和 Edge.txt 这两个文件中读取数据,采用图的存储结构,应用深度优先搜索算法 (DFS)、迪杰斯特拉 (Dijkstra) 算法、普里姆 (Prim) 算法等,开发景区信息管理系统。
3.1 程序设计
使用 Mircosoft Visual Studio 2019 开发工具,创建一个空的控制台工程 (Win32 Console Application)。利用图的存储结构来保存景区景点图,使用 C++ 语言开发景区信息管理系统,工程名为 GraphCPro。
- 添加 Graph.h 和 Graph.cpp 文件,用来定义图的数据结构,实现图的相关操作。
- 添加 Tourism.h 和 Tourism.cpp 文件,用来实现景区信息管理系统的相关功能。
- 添加 Main.cpp 文件,在文件中创建程序入口函数 int main(void)。
3.2 界面设计
在 int main(void) 函数中输出菜单,将系统功能列出来,供用户选择。使用 while 循环输出主菜单。使用 cin 获得用户的输入,使用 switch-case 语句判断具体是哪个功能。
| 选择 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 创建景区景点图 |
| 2 | 查询景点信息 |
| 3 | 旅游景点导航 |
| 4 | 搜索最短路径 |
| 5 | 铺设电路规划 |
| 0 | 退出 |
3.3 数据结构设计
3.3.1 图的存储
当保存图结构时,即要保存顶点信息,也要保存边。图可用数组或链表来存储。
- 数组表示,常用一维数组来保存顶点的集合,使用二维数组来保存边的集合;
- 链表表示,常用邻接表、十字链表等方式存储图的顶点和边的信息。
本程序中使用数组表示法存储图:
- 定义一维数组 Vex m_aVexs[20] 保存顶点信息,最多允许有 20 个顶点。
- 定义二维数组 (邻接矩阵) int m_AdjMatrix[20][20] 保存边的集合,数组中每个元素的值即为边的权值。
3.3.2 景区景点图
景区的地图可以看做是一个带权无向图,使用邻接矩阵来保存。
- 景区中的所有景点即为图的顶点。
- 当两个景点之间铺设的有道路时,表示两个顶点相连,为一条边。
- 两个景点之间的距离,即为边的权值。权值为 0 表示两个顶点不相连。

3.3.3 顶点和边的信息
定义 Vex 结构体,存储图的顶点信息。
struct Vex
{
int num; // 景点编号
char name[20]; // 景点名字
char desc[1024]; // 景点介绍
};
定义 Edge 结构体,存储图的边的信息。
struct Edge
{
int vex1; // 边的第一个顶点
int vex2; // 边的第二个顶点
int weight; // 权值
};
四、运行示例
4.1 系统欢迎界面

4.2 系统菜单选择

4.3 创建景区景点图

4.4 查询景点信息

4.5 旅游景点导航

4.6 搜索最短路径

4.7 铺设电路规划

4.8 退出系统

五、程序源码
注:需将 Vex.txt 和 Edge.txt 文件拷贝到源码目录下。
5.1 main.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include "Tourism.h"
#include "Graph.h"
using namespace std;
Graph m_Graph;
int main(void)
{
int choice;
// 系统界面
printf("\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\t\t\t\t\t\t");
printf("*欢迎进入景区管理系统*");
printf("\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\t\t\t\t\t\t");
system("pause");
system("cls");
do
{
// 输出系统菜单
cout << "=====景区信息管理系统=====" << endl;
cout << "* 1.创建景区景点图 *" << endl;
cout << "* 2.查询景点信息 *" << endl;
cout << "* 3.旅游景点导航 *" << endl;
cout << "* 4.搜索最短路径 *" << endl;
cout << "* 5.铺设电路规划 *" << endl;
cout << "* 0.退出 *" << endl;
cout << "==========================" << endl;
// 用户选择功能
cout << "请输入菜单项编号(0-5):";
cin >> choice;
cout << endl;
switch (choice)
{
case 1:
CreateGraph();
break;
case 2:
GetSpotInfo();
break;
case 3:
TravelPath();
break;
case 4:
FindShortPath();
break;
case 5:
DesignPath();
break;
case 0:
cout << "谢谢您使用本系统!" << endl;
break;
default:
cout << "您的输入有误!请重新输入!" << endl
<< endl;
}
} while (choice != 0);
return 0;
}
5.2 Graph.h
#pragma once
// 存储图的顶点信息
struct Vex
{
int num; // 景点编号
char name[20]; // 景点名字
char desc[1024]; // 景点介绍
};
// 存储边的信息
struct Edge
{
int vex1; // 边的第一个顶点
int vex2; // 边的第二个顶点
int weight; // 权值
};
// 顶点数组和邻接矩阵,用来保存图的信息
struct Graph
{
int m_aAdjMatrix[20][20]; // 邻接矩阵
Vex m_aVexs[20]; // 顶点信息数组
int m_nVexNum; // 当前图的顶点个数
};
// 定义链表 PathList 来保存所有路径
typedef struct Path
{
int vexs[20]; // 保存一条路径
Path *next; // 下一条路径
} *PathList;
// 初始化图
void Init(void);
// 插入顶点信息
bool InsertVex(Vex sVex);
// 插入边的信息
bool InsertEdge(Edge sEdge);
// 通过传入的顶点编号,返回对应顶点信息结构体
Vex GetVex(int v);
// 查询所有与指定顶点相连的边
int FindEdge(int v, Edge aEdge[]);
// 使用深度优先搜索算法遍历图
void DFS(int nVex, bool isVisited[], int &nIndex, PathList &pList);
// 通过调用 DFS 函数,得到深度有限搜索遍历的结果
void DFSTraverse(int nVex, PathList &pList);
// 寻找最短路径
int FindShortPath(int nVexStart, int nVexEnd, Edge aPath[]);
// 通过 Prim 算法构建最小生成树
void FindMinTree(Edge aPath[]);
5.3 Graph.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include "Graph.h"
extern Graph m_Graph;
// 函数名:Init
// 参数:void
// 返回值:void
// 功能:实现图的初始化,权值信息都初始化为0
void Init(void)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 20; j++)
{
m_Graph.m_aAdjMatrix[i][j] = 0; // 权值信息初始化为0
}
m_Graph.m_nVexNum = 0; // 景点数目初始化为0
}
}
// 函数名:InsertVex
// 参数:结构体vex
// 返回值:true:顶点未满 false:顶点已满
// 功能:通过传入结构体,将顶点的相关信息插入到顶点信息数组中
bool InsertVex(Vex sVex)
{
if (m_Graph.m_nVexNum == 20)
{
// 顶点已满
return false;
}
m_Graph.m_aVexs[m_Graph.m_nVexNum++] = sVex; // 插入顶点信息
return true;
}
// 函数名:InsertEdge
// 参数:Edge结构体
// 返回值:true:插入成功 false:下表越界
// 功能:通过传入Edge结构体,将边的相关信息插入到权值矩阵中
bool InsertEdge(Edge sEdge)
{
if (sEdge.vex1 < 0 || sEdge.vex1 >= m_Graph.m_nVexNum || sEdge.vex2 < 0 || sEdge.vex2 >= m_Graph.m_nVexNum)
{
// 下标越界
return false;
}
// 插入边的信息
m_Graph.m_aAdjMatrix[sEdge.vex1][sEdge.vex2] = sEdge.weight;
m_Graph.m_aAdjMatrix[sEdge.vex2][sEdge.vex1] = sEdge.weight;
return true;
}
// 函数名:GetVex
// 参数:输入的编号
// 返回值:对应编号的顶点信息结构体
// 功能:通过传入的顶点编号,返回对应顶点信息结构体
Vex GetVex(int v)
{
return m_Graph.m_aVexs[v];
}
// 函数名:FindEdge
// 参数:nVex:想要查询的顶点 aEdge[]:
// 返回值:边的条数
// 功能:查询与指定顶点相连的边
int FindEdge(int nVex, Edge aEdge[])
{
int k = 0;
// 遍历整个图的邻接矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
if (m_Graph.m_aAdjMatrix[nVex][i] != 0 && nVex != i)
{
// 得到边的信息
aEdge[k].vex1 = nVex;
aEdge[k].vex2 = i;
aEdge[k].weight = m_Graph.m_aAdjMatrix[nVex][i];
k++;
}
}
return k;
}
// 函数名:DFS
// 参数:int nVex:顶点编号 bVisted[]:bool类型的数组,用来记录某个顶点是否被遍历过 int &nIndex:记录遍历深度 PathList &pList:遍历得到的结果
// 返回值:void
// 功能:使用深度优先搜索算法遍历图
void DFS(int nVex, bool isVisited[], int &nIndex, PathList &pList)
{
isVisited[nVex] = true; // 修改为已访问
pList->vexs[nIndex++] = nVex; // 访问顶点nVex
int num = 0; // 被访问过的节点数
for (int i = 0; i < m_Graph.m_nVexNum; i++)
{
if (isVisited[i])
{ // 如果当前i节点被访问过,则num++
num++;
}
}
if (num == m_Graph.m_nVexNum)
{ // 如果所有节点都被访问过
// 保存一条路径
pList->next = new Path;
for (int i = 0; i < m_Graph.m_nVexNum; i++)
{
pList->next->vexs[i] = pList->vexs[i];
}
pList = pList->next;
pList->next = NULL;
}
else
{
for (int w = 0; w < m_Graph.m_nVexNum; w++)
{ // 搜索v的所有邻接点
if (m_Graph.m_aAdjMatrix[nVex][w] > 0 && !isVisited[w])
{ // 如果w是nVex的邻接点并未被访问
DFS(w, isVisited, nIndex, pList); // 递归调用DFS
isVisited[w] = false; // 改为未访问
nIndex--; // 索引值减1
}
}
}
}
// 函数名:DFSTraverse
// 参数:int nVex:顶点编号 PathList &pList:遍历得到的结果
// 返回值:void
// 功能:通过调用DFS()函数,得到深度有限搜索遍历的结果
void DFSTraverse(int nVex, PathList &pList)
{
int nIndex = 0;
bool bVisited[20] = {false};
DFS(nVex, bVisited, nIndex, pList);
}
// 函数名:FindShortPath
// 功能:寻找最短路径
// 参数:景点的起始跟目的编号;边的路径结构数组
// 返回值:nIndex
int FindShortPath(int nVexStart, int nVexEnd, Edge aPath[])
{
int nShortPath[20][20]; // 最短路径,行表示终点,列表示从起点到终点的最短路径的每一步
int nShortDistance[20]; // 保存从起点到任一顶点的最短距离
bool aVisited[20]; // 判断某点是否已在最短路径中
int v; // 每一次找到的可以加入集合的顶点
// 初始化
for (v = 0; v < m_Graph.m_nVexNum; v++)
{
aVisited[v] = false;
if (m_Graph.m_aAdjMatrix[nVexStart][v] != 0)
{
// 如果顶点v和nVexStart相连,则最短距离设置为两顶点间的距离
nShortDistance[v] = m_Graph.m_aAdjMatrix[nVexStart][v];
}
else
{
// 如果不相连,则最短距离设置为最大值
nShortDistance[v] = 0x7FFFFFFF;
}
nShortPath[v][0] = nVexStart; // 起始点为nVexStart
// 初始化最短路径
for (int w = 1; w < m_Graph.m_nVexNum; w++)
{
nShortPath[v][w] = -1;
}
}
// 初始化,将nVexStart顶点加入到集合中
aVisited[nVexStart] = true;
int min; // 暂存路径的最小值
for (int i = 1; i < m_Graph.m_nVexNum; i++)
{
min = 0x7FFFFFFF;
bool bAdd = false; // 判断是否还有顶点可以加入集合
for (int w = 0; w < m_Graph.m_nVexNum; w++)
{
if (!aVisited[w] && nShortDistance[w] < min)
{
v = w; // w顶点距离nVexStart顶点最近
min = nShortDistance[w]; // w到nVexStart的最短距离为min
bAdd = true;
}
}
// 如果没有顶点可以加入到集合,则跳出循环
if (!bAdd)
{
break;
}
aVisited[v] = true; // 将w顶点加入到集合
nShortPath[v][i] = v; // 每次找到最短路径后,就相当于从源点出发到了终点,所以nShortPath[v][i]=v
for (int w = 0; w < m_Graph.m_nVexNum; w++)
{
// 将w作为中间点计算nVexStart到所有顶点的最短距离
if (!aVisited[w] && (min + m_Graph.m_aAdjMatrix[v][w] < nShortDistance[w]) && (m_Graph.m_aAdjMatrix[v][w] > 0))
{
// 如果有新的最短距离,则更新最短路径及距离
nShortDistance[w] = min + m_Graph.m_aAdjMatrix[v][w];
for (int i = 0; i < m_Graph.m_nVexNum; i++)
{
// 如果通过w到达顶点i的距离比较短,则将w的最短路径赋值给i
nShortPath[w][i] = nShortPath[v][i];
}
}
}
}
int nIndex = 0;
int nVex1 = nVexStart;
// 将最短路径保存到边的结构体数组中
for (int i = 1; i < m_Graph.m_nVexNum; i++)
{
if (nShortPath[nVexEnd][i] != -1)
{
aPath[nIndex].vex1 = nVex1;
aPath[nIndex].vex2 = nShortPath[nVexEnd][i];
aPath[nIndex].weight = m_Graph.m_aAdjMatrix[nVex1][aPath[nIndex].vex2];
nVex1 = nShortPath[nVexEnd][i];
nIndex++;
}
}
return nIndex;
}
// 函数名:FindMinTree
// 功能:通过Prim算法构建最小生成树
// 参数:Edge aPath[]
// 返回值:void
void FindMinTree(Edge aPath[])
{
bool aVisited[20] = {false}; // 判断某顶点是否在最小生成树中
aVisited[0] = true; // 从0号顶点开始,加入到集合中
int min;
int nVex1, nVex2;
for (int k = 0; k < m_Graph.m_nVexNum - 1; k++)
{
min = 0X7FFFFFFF;
for (int i = 0; i < m_Graph.m_nVexNum; i++)
{
// 从集合中取一个顶点
if (aVisited[i])
{
for (int j = 0; j < m_Graph.m_nVexNum; j++)
{
// 从不在集合的顶点中取出一个顶点
if (!aVisited[j])
{
if ((m_Graph.m_aAdjMatrix[i][j] < min) && (m_Graph.m_aAdjMatrix[i][j] != 0))
{
nVex1 = i;
nVex2 = j;
// 找出最短边
min = m_Graph.m_aAdjMatrix[i][j];
}
}
}
}
}
// 保存最短边的两个顶点
aPath[k].vex1 = nVex1;
aPath[k].vex2 = nVex2;
aPath[k].weight = m_Graph.m_aAdjMatrix[nVex1][nVex2];
// 将两个顶点加入集合
aVisited[nVex1] = true;
aVisited[nVex2] = true;
}
}
5.4 Tourism.h
#pragma once
// 读取文件,创建景区景点图
void CreateGraph(void);
// 调用 GetVex() 函数,得到所有顶点信息并输出
void GetSpotInfo(void);
// 通过调用 DFSTraverse() 函数,实现旅游景点导航功能,将查询到的景点导航路线显示在界面上
void TravelPath();
// 调用 Graph.cpp 文件中的 FindShortPath() 函数查询两个景点间的最短路径和距离
void FindShortPath(void);
// 查询铺设电路规划图
void DesignPath();
5.5 Tourism.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "Graph.h"
using namespace std;
extern Graph m_Graph;
// 函数名:LoadVex
// 参数:void
// 返回值:void
// 功能:实现从Vex.txt文件中读取景点信息并输出
void LoadVex(void)
{
ifstream VexFile("Vex.txt");
if (!VexFile)
{
cout << "Vex.txt文件打开失败,请检查!" << endl;
return;
}
// 暂存从Vex.txt读取到的一行数据
char num[2];
char name[20];
char desc[1024];
Vex sVex;
// 逐行读取Vex.txt中的数据
VexFile.getline(num, 2); // 将第一行的数据读出丢掉
cout << "景区数目:" << atoi(num) << endl;
cout << "-----顶点-----" << endl;
// 将顶点信息保存到顶点数组中
while (VexFile.getline(num, 2))
{
sVex.num = atoi(num);
VexFile.getline(name, 20);
strcpy(sVex.name, name);
VexFile.getline(desc, 1024);
strcpy(sVex.desc, desc);
// 将顶点信息输出
cout << sVex.num << "-" << sVex.name << endl;
// 设置图的顶点
if (!InsertVex(sVex))
{
cout << "新增景点失败!" << endl;
continue;
}
}
cout << "------------" << endl;
VexFile.close();
}
// 函数名:LoadPath
// 参数:void
// 返回值:void
// 功能:实现从Edge.txt文件中读取路径信息并输出
void LoadPath()
{
ifstream EdgeFile("Edge.txt");
if (!EdgeFile)
{
cout << "Edge.txt文件打开失败,请检查!" << endl;
return;
}
Edge edge;
cout << "------边------" << endl;
while (EdgeFile)
{
EdgeFile >> edge.vex1 >> edge.vex2 >> edge.weight;
cout << "<" << edge.vex1 << "," << edge.vex2 << "> " << edge.weight << endl;
// 设置图的边
if (!InsertEdge(edge))
{
cout << "新增路径信息失败!" << endl;
continue;
}
}
cout << "-------------" << endl;
EdgeFile.close();
cout << "======================" << endl;
}
// 函数名:CreateGraph
// 参数:void
// 返回值:void
// 功能:读取文件,获取景点信息和道路信息
void CreateGraph(void)
{
cout << "\n=====创建景点景区图=====" << endl;
Init(); // 初始化图
LoadVex(); // 从Vex.txt文件中读取景点信息并输出
LoadPath(); // 从Edge.txt文件中读取路径信息并输出
cout << endl;
}
// 函数名:GetSpotInfo
// 参数:void
// 返回值:void
// 功能:调用GetVex()函数,得到所有顶点信息并输出
void GetSpotInfo(void)
{
cout << "\n=====查询景点信息=====" << endl;
int nVexNum = m_Graph.m_nVexNum;
if (nVexNum == 0)
{
cout << "请先创建图!" << endl;
return;
}
// 将景点信息罗列出来,供用户查询选择
for (int i = 0; i < m_Graph.m_nVexNum; i++)
{
Vex sVex = GetVex(i);
cout << i << "-" << sVex.name << endl;
}
cout << "====================" << endl;
// 提示用户根据编号进行查询
cout << "\n请输入想要查询的景点编号:";
int num;
cin >> num;
if (num < 0 || num >= m_Graph.m_nVexNum)
{
cout << "您的输入有误!请重新输入!" << endl;
cout << "\n请输入想要查询的景点编号:";
cin >> num;
}
else
{
Vex sVex = GetVex(num);
cout << "----------------------------" << endl;
cout << sVex.name << ":" << sVex.desc << endl;
cout << "----------------------------" << endl;
cout << "-----周边景区-----" << endl;
Edge aEdge[20];
int EdgeNum = FindEdge(num, aEdge);
for (int i = 0; i < EdgeNum; i++)
{
Vex v1 = GetVex(aEdge[i].vex1);
Vex v2 = GetVex(aEdge[i].vex2);
cout << v1.name << "->" << v2.name << " " << aEdge[i].weight << "m" << endl;
}
cout << "------------------" << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
// 函数名:TravelPath
// 参数:void
// 返回值:void
// 功能:通过调用DFSTraverse()函数,实现旅游景点导航功能,将查询到的景点导航路线显示在界面上
void TravelPath()
{
cout << "\n=======旅游景点导航======" << endl;
int nVexNum = m_Graph.m_nVexNum;
if (nVexNum == 0)
{
cout << "请先创建图!" << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < m_Graph.m_nVexNum; i++)
{
Vex sVex = GetVex(i);
cout << "*\t" << i << "-" << sVex.name << "\t\t*" << endl;
}
cout << "=========================" << endl;
// 输入景点编号
cout << "请输入想要导航的起始点编号:";
int startNum;
cin >> startNum;
if (startNum < 0 || startNum >= m_Graph.m_nVexNum)
{
cout << "您输入的编号有误!" << endl;
return;
}
// 遍历景区景点图
PathList pList = new Path;
PathList pHead = pList;
DFSTraverse(startNum, pList);
cout << endl;
// 输出遍历结果
cout << "导航路线为:" << endl;
int i = 1;
pList = pHead;
while (pList->next != NULL)
{
Vex vex = GetVex(pList->vexs[0]);
cout << "路线" << i++ << ":" << vex.name;
for (int j = 1; j < m_Graph.m_nVexNum; j++)
{
vex = GetVex(pList->vexs[j]);
cout << "->" << vex.name;
}
cout << endl;
pList = pList->next;
}
cout << endl;
delete pList;
pList = NULL;
pHead = NULL;
}
// 函数名:FindShortPath
// 功能:调用Graph.cpp文件中的FindShortPath函数查询两个景点间的最短路径和距离
// 参数:void
// 返回值:void
void FindShortPath(void)
{
cout << "\n======搜索最短路径======\n";
int nVexNum = m_Graph.m_nVexNum;
if (nVexNum == 0)
{
cout << "请先创建图!" << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < m_Graph.m_nVexNum; i++)
{
Vex sVex = GetVex(i);
cout << "*\t" << i << "-" << sVex.name << "\t\t*" << endl;
}
cout << "========================\n";
// 输入两个景点的编号
int start_place, end_place;
cout << "请输入起点的编号:";
cin >> start_place;
cout << "请输入终点的编号:";
cin >> end_place;
if (start_place < 0 || start_place >= m_Graph.m_nVexNum || end_place < 0 || end_place >= m_Graph.m_nVexNum)
{
cout << "输入错误!请重新输入!!!" << endl;
return;
}
Edge aPath[20]; // 边信息数组,依次保存最短的路径
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
// 初始化边信息数组
aPath->vex1 = -1;
aPath->vex2 = -1;
aPath->weight = -1;
}
// 搜索最短路径
int index = FindShortPath(start_place, end_place, aPath);
int length = 0; // 最短路径总长度
Vex sVex = GetVex(aPath[0].vex1);
// 得到最短路径和最短距离
cout << "\n最短路径为:" << sVex.name;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
{
sVex = GetVex(aPath[i].vex2);
cout << "->" << sVex.name;
length += aPath[i].weight;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "最短距离为:" << length << "米" << endl
<< endl;
}
// 函数名:DesignPath
// 功能:查询电路铺设规划图
// 参数:void
// 返回值:void
void DesignPath()
{
cout << "在以下两个景点之间铺设电路";
cout << "\n=======铺设电路规划=======" << endl;
Edge aPath[20];
FindMinTree(aPath); // 构建最小树
int nVexNum = m_Graph.m_nVexNum;
if (nVexNum == 0)
{
cout << "请先创建图!" << endl;
return;
}
// 输出铺设线路图
int nAllLength = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m_Graph.m_nVexNum - 1; i++)
{
Vex nVex1 = GetVex(aPath[i].vex1);
Vex nVex2 = GetVex(aPath[i].vex2);
cout << "\t" << nVex1.name << "-" << nVex2.name << ":" << aPath[i].weight << "m" << endl;
nAllLength += aPath[i].weight;
}
cout << "==========================\n";
cout << "铺设电路的总长度是:" << nAllLength << "m" << endl
<< endl;
}

开放原子开发者工作坊旨在鼓励更多人参与开源活动,与志同道合的开发者们相互交流开发经验、分享开发心得、获取前沿技术趋势。工作坊有多种形式的开发者活动,如meetup、训练营等,主打技术交流,干货满满,真诚地邀请各位开发者共同参与!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容






所有评论(0)