Linux平台上用C++实现多线程互斥锁
在上篇用C++实现了Win32平台上的多线程互斥锁,这次写个Linux平台上的,同样参考了开源项目C++ Sockets的代码,在此对这些给开源项目做出贡献的斗士们表示感谢! 下边分别是互斥锁类和测试代码,已经在Fedora 13虚拟机上测试通过。Lock.h[cpp]view plaincopy#ifndef _Lock_H #define _Loc
·
在上篇用C++实现了Win32平台上的多线程互斥锁,这次写个Linux平台上的,同样参考了开源项目C++ Sockets的代码,在此对这些给开源项目做出贡献的斗士们表示感谢!
下边分别是互斥锁类和测试代码,已经在Fedora 13虚拟机上测试通过。
Lock.h
- #ifndef _Lock_H
- #define _Lock_H
- #include <pthread.h>
- //锁接口类
- class ILock
- {
- public:
- virtual ~ILock() {}
- virtual void Lock() const = 0;
- virtual void Unlock() const = 0;
- };
- //互斥锁类
- class CMutex : public ILock
- {
- public:
- CMutex();
- ~CMutex();
- virtual void Lock() const;
- virtual void Unlock() const;
- private:
- mutable pthread_mutex_t m_mutex;
- };
- //锁
- class CMyLock
- {
- public:
- CMyLock(const ILock&);
- ~CMyLock();
- private:
- const ILock& m_lock;
- };
- #endif
Lock.cpp
- #include "Lock.h"
- //动态方式初始化互斥锁
- CMutex::CMutex()
- {
- pthread_mutex_init(&m_mutex, NULL);
- }
- //注销互斥锁
- CMutex::~CMutex()
- {
- pthread_mutex_destroy(&m_mutex);
- }
- //确保拥有互斥锁的线程对被保护资源的独自访问
- void CMutex::Lock() const
- {
- pthread_mutex_lock(&m_mutex);
- }
- //释放当前线程拥有的锁,以使其它线程可以拥有互斥锁,对被保护资源进行访问
- void CMutex::Unlock() const
- {
- pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_mutex);
- }
- //利用C++特性,进行自动加锁
- CMyLock::CMyLock(const ILock& m) : m_lock(m)
- {
- m_lock.Lock();
- }
- //利用C++特性,进行自动解锁
- CMyLock::~CMyLock()
- {
- m_lock.Unlock();
- }
测试代码
- // pthread_mutex.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
- //
- #include <iostream>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include "Lock.h"
- using namespace std;
- //创建一个互斥锁
- CMutex g_Lock;
- //线程函数
- void * StartThread(void *pParam)
- {
- char *pMsg = (char *)pParam;
- if (!pMsg)
- {
- return (void *)1;
- }
- //对被保护资源(以下打印语句)自动加锁
- //线程函数结束前,自动解锁
- CMyLock lock(g_Lock);
- for( int i = 0; i < 5; i++ )
- {
- cout << pMsg << endl;
- sleep( 1 );
- }
- return (void *)0;
- }
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- pthread_t thread1,thread2;
- pthread_attr_t attr1,attr2;
- char *pMsg1 = "First print thread.";
- char *pMsg2 = "Second print thread.";
- //创建两个工作线程,分别打印不同的消息
- pthread_attr_init(&attr1);
- pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr1,PTHREAD_CREATE_JOINABLE);
- if (pthread_create(&thread1,&attr1, StartThread,pMsg1) == -1)
- {
- cout<<"Thread 1: create failed"<<endl;
- }
- pthread_attr_init(&attr2);
- pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr2,PTHREAD_CREATE_JOINABLE);
- if (pthread_create(&thread2,&attr2, StartThread,pMsg2) == -1)
- {
- cout<<"Thread 2: create failed"<<endl;
- }
- //等待线程结束
- void *result;
- pthread_join(thread1,&result);
- pthread_join(thread2,&result);
- //关闭线程,释放资源
- pthread_attr_destroy(&attr1);
- pthread_attr_destroy(&attr2);
- int iWait;
- cin>>iWait;
- return 0;
- }
编译成功后,运行程序
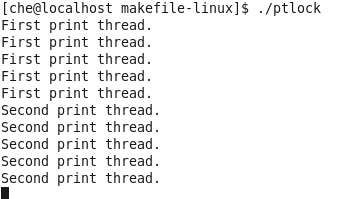
同样,若将下边代码注释掉,重新编译
- //CMyLock lock(g_Lock);
运行程序

结果显而易见。

开放原子开发者工作坊旨在鼓励更多人参与开源活动,与志同道合的开发者们相互交流开发经验、分享开发心得、获取前沿技术趋势。工作坊有多种形式的开发者活动,如meetup、训练营等,主打技术交流,干货满满,真诚地邀请各位开发者共同参与!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容





所有评论(0)