Spring5
Spring框架概述Spring5是轻量级的开源的javaEE框架使用基本的JavaBean代替EJB,解决企业应用开发的复杂性Spring有两个核心部分:IOC和AOPIOC(Inversion of Control 即控制反转)将对象交给容器管理,把创建对象的过程交给Spring进行管理AOP (Aspect Orient Programming),直译过来就是 面向切面编程,AOP 是一种编
·

Spring框架概述
- Spring5是轻量级的开源的javaEE框架
- 使用基本的JavaBean代替EJB,解决企业应用开发的复杂性
- Spring有两个核心部分:IOC和AOP
- IOC(Inversion of Control 即控制反转)将对象交给容器管理,把创建对象的过程交给Spring进行管理
- AOP (Aspect Orient Programming),直译过来就是 面向切面编程,AOP 是一种编程思想,是面向对象编程(OOP)的一种补充。不修改源代码的情况下,进行功能的增强
- Spring特点
- 方便解耦,简化开发
- 对Aop编程的支持
- 方便整合其它框架
- 方便程序的测试
- 减低Java EE API的开发难度,对JavaAPI进行二次封装
- 方便进行事务操作
入门案例
- spring框架jar包源连接 https://repo.spring.io/ui/native/libs-release/org/springframework/spring/
- 实现一个入门案例
- 创建JavaProject
- 导入spring5相关jar包
- 创建一个普通类和一个普通方法
- 创建JavaProject
public class User {
public void add(){
System.out.println("This is a addMethod...");
}
}
- 创建spring配置文件,在配置文件中创建对象
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--配置User对象创建-->
<bean id="user" class="com.ljz.spring5.User"></bean>
</beans>
- 编写测试代码
package com.ljz.spring5.testdemo;
import com.ljz.spring5.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestSpring5 {
@Test
public void testAdd(){
//1.加载Spring配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
//2.获取配置创建的对象
User user = context.getBean("user", User.class);
System.out.println(user);
user.add();
}
}
IOC概念和原理
1.什么是IOC
- 控制反转,Inversion of control 把对象创建和对象之间的调用过程,交给Spring进行管理
- 使用IOC的目的:为了降低耦合度
- 入门案例就是使用的IOC实现的
2.IOC底层原理
- 普通方式进行对象创建原理图

- xml解析,工厂模式,反射

3.IOC接口—BeanFactory
- IOC思想基于IOC容器完成,IOC容器底层就是对象工厂
- Spring提供IOC容器实现两种方式:(两个接口)
- BeanFactory:IOC容器基本实现,是Spring内部的使用接口,不提供开发人员使用
- 加载配置文件时,不会创建对象,在获取对象(使用)时才回去创建对象
- ApplicationContext:BeanFactory接口的子接口,提供更多更强大的功能,一般由开发人员进行使用
- 加载配置文件时就会把配置文件中的对象进行创建
- BeanFactory:IOC容器基本实现,是Spring内部的使用接口,不提供开发人员使用
- ApplicationContext接口有实现类

IOC操作Bean管理(基于XML)
1.什么是Bean管理
- Bean管理是指两个操作
- Spring创建对象
- Spring注入属性(DI)
2.Bean管理操作有两种方式
- 基于xml配置文件方式实现
- 基于注解方式实现
3.基于xml方式操作Bean管理
- 创建对象
<!--配置User对象创建-->
<bean id="user" class="com.ljz.spring5.User"></bean>
- 在配置文件中,使用bean标签,在标签中添加添加对应属性,就可以实现对象创建
- 在bean标签中的常用属性说明
| key | value |
|---|---|
| id属性 | 对象的唯一标识 |
| class属性 | 类的全路径(包类路径) |
| property标签 | 注入属性标签 |
| constructor-arg标签 | 构造器标签 |
- 创建对象时,默认执行无参构造方法完成对象创建
- 注入属性:DI,依赖注入,就是注入属性,DI是IOC的一种具体实现,注入属性需要在对象完成创建的基础上进行完成
- 注入属性:DI,依赖注入,就是注入属性,DI是IOC的一种具体实现,注入属性需要在对象完成创建的基础上进行完成
第一种注入方式:使用set方式进行注入
package com.ljz.spring5;
public class Book {
//创建属性
private String BName;
private String BAuthor;
//set方式注入
public void setBName(String BName) {
this.BName = BName;
}
public void setBAuthor(String BAuthor) {
this.BAuthor = BAuthor;
}
public void testBook(){
System.out.println(BName+"::"+BAuthor);
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--set方法注入属性-->
<bean id="book" class="com.ljz.spring5.Book">
<!--
在bean标签在使用property完成属性注入
name:类中的属性名称
value:向属性注入的值
-->
<property name="BName" value="数据结构"></property>
<property name="BAuthor" value="严蔚敏"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
@Test
public void testBook(){
//1.加载Spring配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("BookBean.xml");
//2.获取配置创建的对象
Book book = context.getBean("book", Book.class);
System.out.println(book);
book.testBook();
}
第二种注入方式:使用有参构造方法注入
package com.ljz.spring5;
/**
* 使用有参数构造注入属性
*/
public class Orders {
//定义属性
private String OName;
private String OAddress;
public Orders(String OName, String OAddress) {
this.OName = OName;
this.OAddress = OAddress;
}
public void testOrders(){
System.out.println(OName+"::"+OAddress);
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--有参数构造注入属性-->
<bean id="order" class="com.ljz.spring5.Orders">
<constructor-arg name="OName" value="电脑"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="OAddress" value="China"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
@Test
public void testOrders(){
//1.加载Spring配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("OrderBean.xml");
//2.获取配置创建的对象
Orders order = context.getBean("order", Orders.class);
System.out.println(order);
order.testOrders();
}
p名称空间注入(了解即可)
1. 使用p名称空间注入,可以简化xml配置方式
2. 第一步:添加p名称空间到配置文件中
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--p名称空间注入-->
</beans>
3. 第二步:进行属性注入,在bean标签中进行操作
<!--使用p名称空间注入的类必须包含set方法-->
<bean id="book" class="com.ljz.spring5.Book" p:BName="基础30讲" p:BAuthor="张宇">
</bean>
4. 编写测试代码
@Test
public void testBook2(){
//1.加载Spring配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("pnspace.xml");
//2.获取配置创建的对象
Book book = context.getBean("book", Book.class);
System.out.println(book);
book.testBook();
}
注入空值和特殊符号
- 字面量
- null值
<!--null值-->
<property name="address">
<null/>
</property>
- 属性值包含特殊符号
<!--
属性值包含特殊符号
1.把<>进行转义<,>
2.把带特殊符号的内容写到CDATA
-->
<property name="address">
<value><![CDATA[<<南京>>]]></value>
</property>
注入属性==外部bean
- 创建两个类service类和dao类
- 在service类中调用dao类中的方法
package com.ljz.spring5.service;
import com.ljz.spring5.dao.UserDao;
public class UserService {
//Spring注入外部bean
//1.创建UserDao属性,生成set方法
private UserDao userDao;
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void add(){
System.out.println("service add.......");
//2.调用update()方法
userDao.update();
//3.编写xml文件
/*
原始方式创建UserDao对象
UserDao userDao = new UserDaoImpl();
userDao.update();
*/
}
}
- 在Spring配置文件中进行配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--1.service和dao对象的创建-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.ljz.spring5.service.UserService">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.ljz.spring5.dao.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>
- 编写测试代码
@Test
public void testBean(){
//1.加载Spring配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("outsidebean.xml");
//2.获取配置创建的对象
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userService.add();
}
注入属性==内部bean
- 一对多关系:部门和员工
- 一个部门有多个员工,一个员工属于一个部门
- 在实体类之间表示一对多关系
//部门类
public class Dept {
private String dname;
public void setDname(String dname) {
this.dname = dname;
}
}
//员工类
public class Emp {
private String ename;
private String gender;
//员工属于某一个部门,使用对象形式表示
private Dept dept;
public void setDept(Dept dept) {
this.dept = dept;
}
public void setEname(String ename) {
this.ename = ename;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
}
- 在Spring配置文件中进行配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--内部bean-->
<bean id="emp" class="com.ljz.spring5.bean.Emp">
<!--设置两个普通属性-->
<property name="ename" value="张三"></property>
<property name="gender" value="男"></property>
<!--添加内部bean属性-->
<property name="dept">
<bean id="dept" class="com.ljz.spring5.bean.Dept">
<property name="dname" value="开发部"></property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
- 编写测试代码
@Test
public void testBean2(){
//1.加载Spring配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("insidebean.xml");
//2.获取配置创建的对象
Emp emp = context.getBean("emp", Emp.class);
System.out.println(emp.toString());
}
注入属性==级联赋值
<!--级联赋值-->
<bean id="emp" class="com.ljz.spring5.bean.Emp">
<!--设置两个普通属性-->
<property name="ename" value="李四"></property>
<property name="gender" value="女"></property>
<!--级联赋值-->
<property name="dept" ref="dept"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="dept" class="com.ljz.spring5.bean.Dept">
<property name="dname" value="财务部"></property>
</bean>
<!--级联赋值-->
<bean id="emp" class="com.ljz.spring5.bean.Emp">
<!--设置两个普通属性-->
<property name="ename" value="李四"></property>
<property name="gender" value="女"></property>
<!--级联赋值-->
<property name="dept" ref="dept"></property>
<property name="dept.dname" value="技术部"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="dept" class="com.ljz.spring5.bean.Dept">
<!-- <property name="dname" value="财务部"></property>-->
</bean>
//使用第二种级联赋值时,必须先获取对象
public Dept getDept() {
return dept;
}
@Test
public void testBean3(){
//1.加载Spring配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cascade.xml");
//2.获取配置创建的对象
Emp emp = context.getBean("emp", Emp.class);
System.out.println(emp.toString());
}
4.XML注入集合类型属性
1.注入数组类型属性
2.注入List集合类型属性
3.注入Map集合属性
4.创建学生类
package com.ljz.spring5.collectiontype;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class Stu {
//1.数组类型属性
private String[] courses;
//2.list集String
private List<String> lists;
//3.map集合类型属性
private Map<String,String> maps;
//4.set集String
private Set<String> sets;
public void setSets(Set<String> sets) {
this.sets = sets;
}
public void setCourses(String[] courses) {
this.courses = courses;
}
public void setLists(List<String> lists) {
this.lists = lists;
}
public void setMaps(Map<String, String> maps) {
this.maps = maps;
}
//编写测试方法
public void test(){
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(courses));
System.out.println(lists);
System.out.println(maps);
System.out.println(sets);
}
}
<!--1.集合类型属性注入-->
<bean id="stu" class="com.ljz.spring5.collectiontype.Stu">
<!--数组类型属性注入-->
<property name="courses">
<array>
<value>Java课程</value>
<value>数据库课程</value>
</array>
</property>
<!--list类型属性注入-->
<property name="lists">
<list>
<value>张宇</value>
<value>宇哥</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--map类型属性注入-->
<property name="maps">
<map>
<entry key="JAVA" value="java"></entry>
<entry key="PYTHON" value="python"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<!--set类型属性注入-->
<property name="sets">
<set>
<value>MySQL</value>
<value>Redis</value>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
public class TestStu {
@Test
public void testCollection(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("StuBean.xml");
Stu stu = context.getBean("stu", Stu.class);
stu.test();
}
}
5.在集合中设置对象类型值
<!--创建多个course对象-->
<bean id="course1" class="com.ljz.spring5.collectiontype.Course">
<property name="cname" value="Spring5框架"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="course2" class="com.ljz.spring5.collectiontype.Course">
<property name="cname" value="MyBatis框架"></property>
</bean>
<!--注入list集合类型,值是对象-->
<property name="courseList">
<list>
<ref bean="course1"></ref>
<ref bean="course2"></ref>
</list>
</property>
//学生所以学的多门课程
private List<Course> courseList;
public void setCourseList(List<Course> courseList) {
this.courseList = courseList;
}
//添加test方法的输出
public void test(){
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(courses));
System.out.println(lists);
System.out.println(maps);
System.out.println(sets);
System.out.println(courseList);
}
6.把集合注入部分提取出来
- 在Spring配置文件在引入命名空间util
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd">
<!--1 集合类型属性注入-->
</beans>
- 使用util标签完成list集合的注入提取
<!--1 提取list集合类型属性注入-->
<util:list id="bookList">
<value>高等数学</value>
<value>线性代数</value>
<value>数据结构</value>
</util:list>
<!--2 提取list集合类型属性注入使用-->
<bean id="book" class="com.ljz.spring5.collectiontype.Book">
<property name="list" ref="bookList"></property>
</bean>
- 编写测试代码
@Test
public void testCollection2(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("publicBean.xml");
Book book = context.getBean("book", Book.class);
System.out.println(book.toString());
}
5.IOC容器Bean管理(FactoryBean)
- 在Spring中有两种类型的bean,一种是普通bean,另外一种是工厂bean
- 普通bean:在配置文件中定义的bean类型就是返回类型
- 工厂bean:在配置文件中定义的bean类型可以和返回类型不一样
- 实现步骤
- 第一步,创建类,让这个类作为工厂bean,实现接口FactoryBean
- 第二步,实现接口中的方法,在实现的方法中定义返回的bean类型
package com.ljz.spring5.factorybean;
import com.ljz.spring5.collectiontype.Course;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
public class MyBean implements FactoryBean<Course> {
//定义返回的Bean
@Override
public Course getObject() throws Exception {
Course course = new Course();
course.setCname("Java");
return course;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return FactoryBean.super.isSingleton();
}
}
@Test
public void test3(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("MyBean.xml");
Course course = context.getBean("myBean", Course.class);
System.out.println(course);
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="myBean" class="com.ljz.spring5.factorybean.MyBean"></bean>
</beans>
6.Bean的作用域
- 在Spring中,可以设置所创建的对象是单实例还是多实例
- 在Spring中,默认创建的对象是单例对象
@Test
public void testCollection2(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("publicBean.xml");
Book book1= context.getBean("book", Book.class);
Book book2 = context.getBean("book", Book.class);
System.out.println(book1);
System.out.println(book2);
}
//=============================输出结果==========================================
com.ljz.spring5.collectiontype.Book@1dac5ef
com.ljz.spring5.collectiontype.Book@1dac5ef
//=============================修改scope为prototype==========================================
com.ljz.spring5.collectiontype.Book@5c90e579
com.ljz.spring5.collectiontype.Book@58ea606c
- 如何设置所创建的对象是多实例对象
- 在Spring配置文件中bean标签中的属性scope,用于设置多实例对象
- scope属性值
- 默认值 singleton 单实例
- prototype 多实例
- request(一次请求)
- session(一次会话)
- singleton和prototype的区别
- singleton是单实例对象,prototype是多实例对象
- 设置scope=singleton时,加载Spring配置文件时会创建单实例对象(饿汉式单例)
- 设置scope=prototype时,加载Spring配置文件不会创建对象,只有当对象在调用getBean()方法时才会创建多实例对象(懒汉式多实例)
7.Bean的生命周期
- 生命周期==>从对象创建到对象销毁的过程
- bean生命周期
- 通过构造器创建bean实例(无参构造方法)
- 为bean属性设置值和对其他bean引用(调用set方法)
- 调用bean的初始化方法(需要进行配置初始化的方法)
- bean可以使用了(对象获取到了)
- 当容器关闭的时候,调用bean销毁的方法(需要进行配置销毁方法)
package com.ljz.spring5.bean;
//bean的生命周期
public class Orders {
public Orders() {
System.out.println("第一步 执行无参数构造器创建bean实例");
}
private String oname;
public void setOname(String oname) {
this.oname = oname;
System.out.println("第二步 调用set方法设置属性值");
}
//创建执行的初始化方法
public void initMethod(){
System.out.println("第三步 执行初始化方法");
}
//创建对象执行销毁的方法
public void destroyMethod(){
System.out.println("第五步 执行对象销毁方法");
}
}
<!--bean的生命周期-->
<bean id="orders" class="com.ljz.spring5.bean.Orders" init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod">
<property name="oname" value="iphone"></property>
</bean>
@Test
public void testBean(){
// ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("OrdersBean.xml");
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("OrdersBean.xml");
Orders orders = context.getBean("orders", Orders.class);
System.out.println("第四步 获取创建的bean实例对象");
System.out.println(orders);
//手动销毁bean
context.close();
}
- bean的后置处理器
- 通过构造器创建bean实例(无参构造方法)
- 为bean属性设置值和对其他bean引用(调用set方法)
- 把bean实例传递给bean前置处理器的方法postProcessBeforeInitialization
- 调用bean的初始化方法(需要进行配置初始化的方法)
- 把bean实例传递给bean后置处理器的方法postProcessAfterInitialization
- bean可以使用了(对象获取到了)
- 当容器关闭的时候,调用bean销毁的方法(需要进行配置销毁方法)
- 演示添加后置处理器的效果
- 创建类,实现接口BeanPostProcessor,创建后置处理器
package com.ljz.spring5.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("在初始化之前执行的方法");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("在初始化之后执行的方法");
return bean;
}
}
<!--配置前后置处理器-->
<bean id="myBPP" class="com.ljz.spring5.bean.MyBeanPostProcessor"></bean>
8.xml自动装配
- 什么是自动装配
- 根据指定装配规则(属性名称或属性类型),Spring自动将匹配的属性值进行注入
- 演示过程
<!--
实现自动转配bean标签属性autowire,配置自动装配
autowire属性值常用两个值:
byName根据属性名称注入,注入值bean的id和类属性名称一致
byType根据属性类型注入
-->
<bean id="emp" class="com.ljz.spring5.autowire.Emp" autowire="byName"></bean>
<bean id="dept" class="com.ljz.spring5.autowire.Dept"></bean>
<bean id="emp" class="com.ljz.spring5.autowire.Emp" autowire="byType"></bean>
<bean id="dept" class="com.ljz.spring5.autowire.Dept"></bean>
@Test
public void test4(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("DEBean.xml");
Emp emp = context.getBean("emp", Emp.class);
System.out.println(emp);
}
9.外部属性
- 直接配置数据库信息
- 配置德鲁伊连接池
- 引入德鲁伊jar包
- 编写xml文件
- 配置德鲁伊连接池
<!--直接配置连接池-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:33068/userDb"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="abc123"></property>
</bean>
- 引入外部属性文件配置数据库连接池
- 创建外部属性文件,*.properties格式文件,写入数据库信息
- 编写properties文件
prop.driverClass = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
prop.url = jdbc.mysql://localhost:33068/userDb
prop.userName = root
prop.password = abc123
- 把外部properties文件引入到spring配置文件中
- 引入context命名空间
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-context.xsd">
2. 在spring配置文件使用标签引入外部属性文件
<!--引入外部文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!--配置连接池-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverclass}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</bean>
IOC操作Bean管理(基于注解)
1.什么是注解
- 注解是代码中的特殊标记
- 格式:@注解名称(属性名称=属性值,属性名称=属性值…)
- 使用注解,注解可以作用在类上,属性上,方法上
- 使用注解的目的:简化xml配置
2.Spring针对Bean管理中创建对象提供注解

- 上述四个注解功能是一样的,都可以用来创建bean实例
3.基于注解方式实现对象创建
- step1:引入Aop.jar
- step2:开启组件扫描
- 创建context命名空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
- 开启组件扫描
<!--
开启组件扫描
step1:创建context命名空间
step2: 开启组件扫描,单个包和多个包的写法
单个包,指定包
<context:component-scan base-package="com.ljz.spring5.dao"></context:component-scan>
多个包,两种写法
1.指定多个包
2.指定目录下所有包
指定多个包
<context:component-scan base-package="com.ljz.spring5.dao,com.ljz.spring5.service">
</context:component-scan>
-->
<!--指定目录下的所有包-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.ljz"></context:component-scan>
- 编写UserService用于测试
package com.ljz.spring5.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//在注解中的value属性值可忽略不写,默认为类名首字母小写
@Component(value = "userService")//等价于<bean id="userService" class="..."/>
public class UserService {
public void add(){
System.out.println("service add....");
}
}
- 编写测试方法
@Test
public void testService(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
System.out.println(userService);
userService.add();
}
- 运行结果

4.组件扫描配置
<!--
组件扫描配置
use-default-filters="false" 表示现在不使用默认filter,自己配置filter
context:include-filter, 设置扫描内容
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.ljz" use-default-filters="false">
<!--
示例一:
type="annotation" 根据注解进行扫描
expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" 只扫描带Controller的类
-->
<context:include-filter type="annotation"
expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
<!--
示例2
context:exclude-filter 设置指定内容不扫描
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.ljz">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation"
expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
5.基于注解方式实现属性注入
//3个最常用的属性注解
@Autowired //根据属性类型进行自动装配
@Qualifier //根据属性名称进行注入
@Resource //可以根据类型注入,可以根据名称注入
@Value //注入普通类型属性
- @Autowired实现过程
- 把service和dao对象创建,在service和dao类添加创建对象注解
public interface UserDao {
void add();
}
@Repository
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("dao add....");
}
}
- 第二步在service注入dao对象,在service类添加dao类型属性,在属性上面使用注解
@Service
public class UserService {
//定义dao类型属性,不需要添加set方法,添加注入属性注解
@Autowired //根据类型进行注入
private UserDao userDao;
public void add(){
System.out.println("service add....");
userDao.add();
}
}
- 运行结果

- @Qualified根据属性名称注入对象,当接口有多个实现类时,需要使用该注解指定实现类
- 需要和@Autowired一起使用
- @Qualifier(value=“实现类名”)
@Service
public class UserService {
//定义dao类型属性,不需要添加set方法,添加注入属性注解
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value="userDaoImpl")
private UserDao userDao;
public void add(){
System.out.println("service add....");
userDao.add();
}
}
- 运行结果

- 错误实现类
@Repository(value="userDaoImpl1")//不写value默认userDaoImpl
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("dao add....");
}
}

- @Resource既可以根据类型注入也可以根据名称注入
- @Resource是javax.annotation.Resource拓展包下的注解,不属于Spring
- JDK11以后完全移除了javax的包拓展
- spring开发中也不推荐使用了
- 根据类型注入
- @Resource是javax.annotation.Resource拓展包下的注解,不属于Spring
@Resource
private UserDao userDao;
- 根据名称注入,与@Qualifiter不同@Resource可以单独使用不需要与@Autowired联用
@Resource(value = "userDaoImpl1")
private UserDao userDao;
- @Value注入普通属性,用于替代proprietary使用
@Repository
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
@Value(value="小李")
private String name;
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("dao add...."+name);
}
}
- 运行结果

6.完全注解开发
- 创建配置类,替代xml文件
@Configuration//作为配置类替代xml文件
//包扫描注解等价于<context:component-scan base-package="com.ljz"></context:component-scan>
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.ljz"})
public class SpringConfig {
}
- 编写测试类
@Test
public void testService2(){
//加载配置类
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
System.out.println(userService);
userService.add();
}
- 基于SpringBoot开发
AOP的基本概念和原理
AOP(概念)
- 什么是AOP
- 面写切面编程(方面)
- 利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,降低业务逻辑间的耦合度
- 提高程序的可重用性,同时提高开发效率
- 通俗描述就是不通过修改源代码,在主干功能中添加新功能
- 登录例子进行说明
- 面写切面编程(方面)

- AOP底层原理
- AOP底层使用动态代理
- 两种情况动态代理
- 有接口情况,使用JDK动态代理

创建接口实现类的代理对象,增强类的方法
- 没有接口情况,使用CGLIB动态代理,创建子类代理对象,增强类方法

AOP(JDK动态代理)
- 使用JDK动态代理,使用Proxy类里面的方法创建代理对象

- 调用newProxyInstance方法

- 该方法有三个参数
- 第一个参数 loader,类加载器
- 第二个参数 增强方法所在的类,这个类实现的接口,支持多个接口
- 第三个参数,实现这个接口InvocationHandler,创建代理对象,写增强方法
- 编写JDK动态代理代码
- 创建接口,定义方法
public interface UserDao {
int add(int a,int b);
String update(String id);
}
- 创建接口实现类,实现方法
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a+b;
}
@Override
public String update(String id) {
return id;
}
}
- 使用Proxy类创建接口代理对象
package com.ljz.spring5;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class JDKProxy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建接口实现类代理对象
Class[] interfaces = {UserDao.class};
/* //匿名内部类写法
Proxy.newProxyInstance(
JDKProxy.class.getClassLoader(),
interfaces, new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
return null;
}
});*/
UserDaoImpl user Dao = new UserDaoImpl();
/*
○ 第一个参数 loader,类加载器
○ 第二个参数 增强方法所在的类,这个类实现的接口,支持多个接口
○ 第三个参数,实现这个接口InvocationHandler,创建代理对象,写增强方法
*/
UserDao dao = (UserDao)Proxy.newProxyInstance(JDKProxy.class.getClassLoader(), interfaces, new UserDaoProxy(userDao));
int add = dao.add(1, 2);
System.out.println(add);
}
}
//创建代理对象
class UserDaoProxy implements InvocationHandler{
//把创建的谁的代理对象,就把谁传递进来,使用有参构造传递
private Object obj;
public UserDaoProxy(Object obj) {
this.obj = obj;
}
//增强的逻辑
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//方法之前
System.out.println("在方法之前执行...."+method.getName()+":传递的参数..."+ Arrays.toString(args));
//被增强的方法执行
Object res = method.invoke(obj, args);
//方法之后
System.out.println("方法之后执行....."+obj);
return res;
}
}
AOP(术语)
1.连接点(理论可增强)(方法)
类的方法中那些可以被动态代理去增强的方法称为连接点
2.切入点(实际已增强)(方法)
实际开发中已增强的连接点,称为切入点
3.通知(增强)(代码段)
- 切入点中实际增强的部分逻辑(代码段),称为通知(增强)
- 通知的类型
- 前置通知
- 后置通知
- 环绕通知
- 异常通知
- 最终通知~类似于finally
4.切面~(动作)
把通知应用到切入点的过程
- 示例:将权限验证加到登录方法的过程

AOP操作
1.准备阶段
- Spring框架一般是基于AspectJ实现AOP操作
- 什么是AspectJ
- AspectJ不是Spring的组成部分,独立的AOP框架
- 一般把AspectJ和Spring框架一起使用,进行AOP操作
- 基于ApsectJ实现AOP操作
- 基于xml配置文件实现
- 基于注解方式实现(开发常用)
- 在项目工程中引入AOP相关依赖

- 切入点表达式
- 切入点表达式的作用:声明增强对象(目标类的目标方法)
- 语法结构:
execution([权限修饰符][返回类型][类全路径][方法名称]([参数列表]))- 示例一: 对com.ljz.dao.BookDao类中的add进行增强
execution(* com.ljz.dao.BookDao.add(...)) //*表示任意的访问修饰符
- 示例二: 对com.ljz.dao.BookDao类中的所有方法进行增强
execution(* com.ljz.dao.BookDao.*(...))
- 示例三: 对com.ljz.dao包中所有类,类里面的所有方法进行增强
execution(* com.;jz.dao.*.*(...))
2.AOP操作基于注解实现
- 创建类,在类中定义方法
//被增强的类
public class User {
public void add(){
System.out.println("add....");
}
}
- 创建增强类,编写增强类逻辑
- 在增强类中,创建方法,让不同的方法代表不同的通知类型
//增强的类
public class UserProxy {
//前置通知
public void before(){
System.out.println("before.....");
}
}
- 进行通知配置
- 在spring配置文件中,开启注解扫描
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--开启注解扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.ljz.spring5.aopanno"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
- 使用注解创建User和UserProxy对象
- 在User和UserProxy类上加上@Component注解
- 在增强类上添加注解@Aspect
- 在增强类上加上@Aspect注解
- 在spring配置文件中开启生成代理对象
<!--开启Aspectj生成代理对象-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
- 配置不同类型通知
- 在增强类中,在作为通知方法上面添加通知类型注解,使用切入点表达式配
//增强的类
@Component
@Aspect//生成代理对象
public class UserProxy {
//前置通知
//@Before注解表示作为前置通知
@Before(value="execution(* com.ljz.spring5.aopanno.User.add(..))")
public void before(){
System.out.println("before.....");
}
//最终通知(finally)
@After(value="execution(* com.ljz.spring5.aopanno.User.add(..))")
public void after(){
System.out.println("after......");
}
//返回通知(return)
@AfterReturning(value="execution(* com.ljz.spring5.aopanno.User.add(..))")
public void afterReturning(){
System.out.println("afterReturning......");
}
//异常通知
@AfterThrowing(value="execution(* com.ljz.spring5.aopanno.User.add(..))")
public void afterThrowing(){
int i =1/0;
System.out.println("afterThrowing......");
}
//环绕通知
@Around(value="execution(* com.ljz.spring5.aopanno.User.add(..))")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("around before....");
//被增强方法执行
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("around after.....");
}
}
- 相同切入点抽取
//相同切入点的抽取
@Pointcut(value = "execution(* com.ljz.spring5.aopanno.User.add(..))")
public void pcTest(){
}
//前置通知
//@Before注解表示作为前置通知
@Before(value="pcTest()")
public void before(){
System.out.println("before.....");
}
- 若有多个增强类对同一个方法进行增强,设置增强类优先级
- 在增强类上添加注解@Order(数字类型值),数字类型值优先级越小优先级越高
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(1)
public class PersonProxy
- 完全注解开发
- 创建配置类,不需要创建xml配置文件
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.ljz.spring5")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
public class ConfigAop {
}
3.AOP操作基于XML实现
- 创建两个类,增强类和被增强类,创建方法
//被增强类
public class Book {
//被增强方法
public void buy(){
System.out.println("buy.....");
}
}
//增强类
public class BookProxy {
public void before(){
//增强逻辑
System.out.println("before.....");
}
}
- 在Spring配置文件中创建两个类对象
<!--创建两个类的对象-->
<bean id="book" class="com.ljz.spring5.aopxml.Book"></bean>
<bean id="bookProxy" class="com.ljz.spring5.aopxml.BookProxy"></bean>
- 在Spring配置文件中配置切入点
<!--配置aop的增强-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="point" expression="execution(* com.ljz.spring5.aopxml.Book.buy(..))"/>
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:aspect ref="bookProxy">
<!--配置增强逻辑入口-->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="point"></aop:before>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
- 编写测试代码
@Test
public void testAopXml(){
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean2.xml");
Book book = context.getBean("book", Book.class);
book.buy();
}
- 运行结果

JDBC Template(概念和准备)
- 什么是JdbcTemplate
- Spring框架对JDBC进行封装,使用JdbcTemplate方便实现对数据库操作
- 准备工作
- 引入相关jar包

- 在Spring配置文件中配置数据库连接池
<!--配置数据库连接池-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://user_db"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="abc123"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
</bean>
- 配置JdbcTemplate对象,注入DataSource
<!--配置JdbcTemplate对象-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!--注入dataSource-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
- 创建service类,创建dao类,在dao注入jdbcTemplate对象
- 配置文件
<!--开启组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.ljz"></context:component-scan>
- Service
@Service
public class BookService {
//注入dao
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
}
- Dao
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao{
//注入jdbcTemplate
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
}
JDBCTemplate操作数据库
添加
- 创建数据库数据表
create database user_db character set utf8
use user_db
create table t_user(
user_id int(20) primary key,
user_name varchar(50) not null,
user_status varchar(20) not noll
)
- 创建对应数据表的实体类
package com.ljz.spring5.eneiey;
public class User {
private String userId;
private String userName;
private String userStatus;
public String getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public String getUserStatus() {
return userStatus;
}
public void setUserId(String userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public void setUserStatus(String userStatus) {
this.userStatus = userStatus;
}
}
- 编写service和dao
- 在dao进行数据库添加操作
public interface UserDao {
//添加的方法
void add(User user);
}
- 调用JdbcTemplate对象里面update方法实现添加操作
- 两个参数
- 第一个参数:sql语句
- 第二个参数:可变参数,设置sql语句值
@Repository
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
//注入jdbcTemplate
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//添加方法
@Override
public void add(User user) {
//编写sql语句
String sql = "insert into t_user values(?,?,?)";
//调用方法实现
Object [] args = {user.getUserId(), user.getUserName(), user.getUserStatus()};
int update = jdbcTemplate.update(sql,args);
System.out.println(update);
}
}
@Service
public class UserService {
//注入dao
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
//添加的方法
public void addUser(User user){
userDao.add(user);
}
}
- 编写测试语句
@Test
public void testJdbcTemplate(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
User user = new User();
user.setUserId("1");
user.setUserName("小李");
user.setUserStatus("离线");
userService.addUser(user);
}
- 测试结果


修改和删除操作
- UserDao接口
//修改的方法
void updateUser(User user);
//删除的方法
void delete(String id);
- UserDaoImpl实现类
//修改方法
@Override
public void updateUser(User user) {
//编写sql语句
sql = "update t_user set user_name=?,user_status=? where user_id =?";
args = new Object[]{user.getUserName(), user.getUserStatus(),user.getUserId()};
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,args);
}
//删除方法
@Override
public void delete(String id) {
sql = "delete from t_user where user_id = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,id);
}
- UserService业务逻辑层
- 编写测试
//修改操作
User user = new User();
user.setUserId("1");
user.setUserName("小金");
user.setUserStatus("在线");
userService.updateUser(user);
//删除操作
userService.deleteUser("1");
- 测试结果
- 修改操作


- 删除操作


查询
JdbcTemplate操作数据库(查询返回某个值)
- 查询表里有多少条记录,返回是某个值
- 使用JdbcTemplate实现查询返回某个值代码
- 两个参数:
- 第一个参数:sql
- 第二个参数返回值类型Class(对于基本数据类型则是包装类.class)
//查找表记录条数
int selectCount();
//查询表记录数
@Override
public int selectCount() {
sql = "select count(*) from t_user";
return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,Integer.class);
}
//查询表的记录数
public int findCount(){
return userDao.selectCount();
}
//查询记录
System.out.println(userService.findCount());
- 运行结果


JdbcTemplate操作数据库(查询返回某个对象)
- 场景:查询用户详情
- JdbcTemplate实现查询返回对象
- 三个参数
- 第一个参数:sql语句
- 第二个参数:RowMapper,是接口,针对返回不同类型数,使用这个接口里面实现类完成数据封装
- 第三个参数:sql语句值
@Override
public User findUserInfo(String id) {
sql = "select * from t_user where user_id = ?";
//BeanPropertyRowMapper:sping为开发封装好的RowMapper接口的实现类
User user = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<User>(User.class), id);
return user;
}
- 运行结果

JdbcTemplate操作数据库(查询返回集合)
- 场景:查询图书列分页…
- 调用jdbcTemplate方法实现查询返回集合
- 三个参数
- 第一个参数:sql语句
- 第二个参数:RowMapper,是接口,针对返回不同类型数,使用这个接口里面实现类完成数据封装
- 第三个参数:sql语句值
@Override
public List<User> findAllUser() {
sql = "select * from t_user";
return jdbcTemplate.query(sql,new BeanPropertyRowMapper<User>(User.class));
}
//查询返回集合
System.out.println(userService.findAllUser());
- 运行结果

批量操作
- 批量操作:操作表中多条记录
- JdbcTemplate实现批量添加操作
- 有两个参数
- 第一个参数:sql语句
- 第二个参数:List集合,添加多条记录数据
@Override
public void batchAddUser(List<Object[]> batchArgs) {
sql = "insert into t_user values(?,?,?)";
int[] ints = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints));
}
//批量添加
List<Object[]> batchArgs = new ArrayList<>();
Object[] o1 = {"3","小张","离线"};
Object[] o2 = {"4","小吴","离线"};
batchArgs.add(o1);
batchArgs.add(o2);
userService.batchAdd(batchArgs);
- 结果

- 对于批量修改和删除类似仅需修改sql字符串即可
//批量修改操作
@Override
public void batchUpdateUser(List<Object[]> batchArgs) {
sql = "update t_user set user_name=?,user_status=? where user_id =?";
int[] ints = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints));
}
//批量删除
@Override
public void batchDeleteUser(List<Object[]> batchArgs) {
sql = "delete from t_user where user_id = ?";
int[] ints = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints));
}
//批量修改
List<Object[]> batchArgs = new ArrayList<>();
Object[] o1 = {"小洪123","离线1","4"};
Object[] o2 = {"小吴321","离线2","5"};
batchArgs.add(o1);
batchArgs.add(o2);
userService.batchUpdate(batchArgs);
//删除
List<Object[]> batchArgs = new ArrayList<>();
Object[] o1 = {"4"};
Object[] o2 = {"5"};
batchArgs.add(o1);
batchArgs.add(o2);
userService.batchDelete(batchArgs);
事务概念
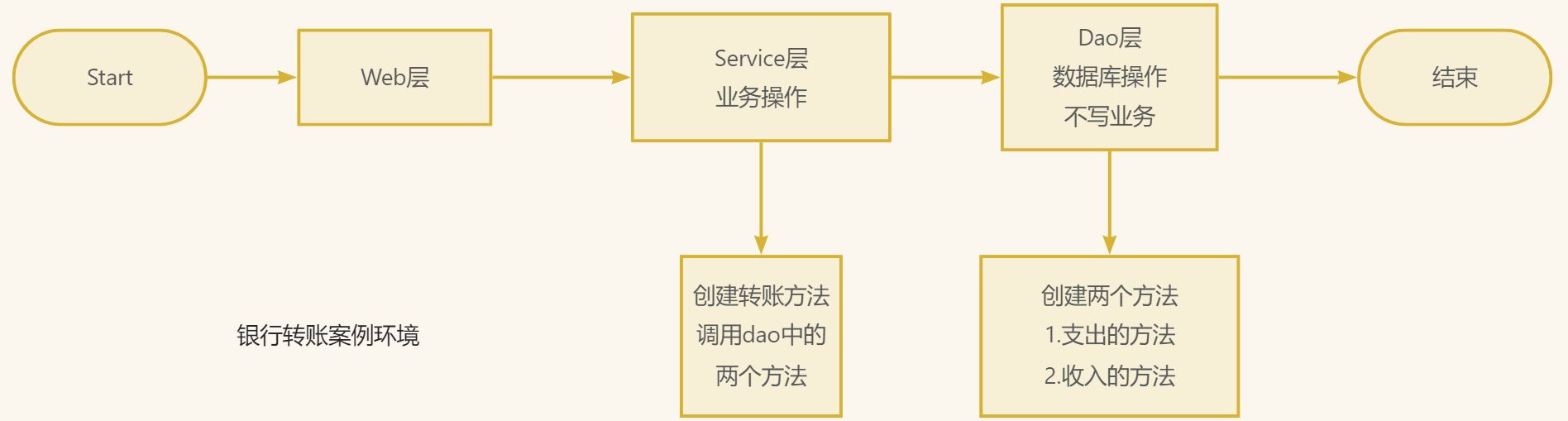
1.什么是事务
事务的数据库的操作的最基本单元,是逻辑上的一组操作,要么都成功,若有一个失败则所有操作都失败
- 经典场景:银行转账
- lucy转账100元给mary
- lucy少100元mary多100元
- 事务四个特性(ACID)
- 原子性
- 一致性
- 隔离性
- 持久性
2.搭建事务操作环境

2.1 创建数据库表,搭建dao,完成对象创建和注入
use user_db;
create table t_account(
id varchar(20) primary key ,
username varchar(50) unique not null ,
money int
);
insert into t_account(id,username,money) values('1','lucy',1000);
insert into t_account(id,username,money) values('2','mary',1000);

2.2 创建service,搭建dao,完成对象创建和注入关系
- service注入dao,在dao注入jdbcTemplate,在jdbcTemplate注入DataSource
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
}
@Repository
public class UserDaoImpl {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
}
- 在dao创建两个方法,收入和支出,在service中调用两个方法
//收入
@Override
public void addMoney() {
String sql = "update t_account set money = money+? where = username = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,100,"mary");
}
//支出
@Override
public void reduceMoney() {
//lucy转账100给mary
String sql = "update t_account set money = money-? where = username = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,100,"lucy");
}
//转账的方法
public void transferAccount(){
//lucy支出
userDao.reduceMoney();
//mary收入
userDao.addMoney();
}
- 编写测试代码
@Test
public void testJdbcTemplate(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userService.transferAccount();
}
- 上述demo正常执行时无误,若在执行过程中出现异常会有问题(模拟异常)
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
//转账的方法
public void transferAccount(){
//lucy支出
userDao.reduceMoney();
//模拟异常
int i = 10/0;
//mary收入
userDao.addMoney();
}
}

- 解决方案—数据库事务DataBases Transaction
2.3 事务操作过程
//转账的方法
public void transferAccount(){
try{
//step1 开启事务
//step2 进行业务操作
userDao.reduceMoney();//lucy支出
int i = 10/0;//模拟异常
userDao.addMoney(); //mary收入
//step3 没有发生异常,提交事务
}catch(Exception e){
//step4 出现异常,事务回滚(还原初始状态)
}
}
2.4 Spring事务管理


3.Spring注解声明式事务管理
- 在spring配置文件配置事务管理器
<!--创建事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!--注入数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
public void setDataSource(@Nullable DataSource dataSource) {
if (dataSource instanceof TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy) {
// If we got a TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy, we need to perform transactions
// for its underlying target DataSource, else data access code won't see
// properly exposed transactions (i.e. transactions for the target DataSource).
this.dataSource = ((TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy) dataSource).getTargetDataSource();
}
else {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
}
- 在Spring配置文件中,开启事务注解
- 引入命名空间tx
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
- 开启事务注解
<!--开启事务注解-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager">
</tx:annotation-driven>
- 在service类上添加事务注解(获取service类里面方法上面)
@Service
@Transactional //Spring注解声明式管理事务,该注解可用于类/方法上
public class UserService {}
- @Transactional
- 添加到类上,表示类中所有方法都添加事务
- 添加到方法上,为该方法添加事务
- 测试结果~出现异常,事务回滚

4.Spring声明式事务管理参数配置
4.1propagation:事务的传播行为
- 当一个事务方法被另一个事务方法调用时,这个事务方法如何进行
- Spring中定义了7中传播行为
- required–如果事务在运行,当前方法就在这个事务内运行,否则开启一个新事务,并在自己事务内运行

- required_new--如果当前方法必须启动新事务,并在新事务内运行,若有事务在运行,将其挂起

- supports--如果事务在运行,当前方法就在这个事务内运行,否则不能运行在事务中
- not_supports--当前方法不应该运行在事务中,运行事务时,将其挂起
- mandatory--当前方法必须在事务中运行,若没有正在运行的事务,抛出异常
- never--当前方法不应该运行在事务中,如有事务运行,抛出异常
- nested--如有事务运行,当前方法就应该在这个事务的嵌套事务中运行,否则启动一个新事务,并在自己的事务内运行
4.2 isolation:事务隔离级别
- 事务的隔离性,多个事务操作之间不会产生影响,不考虑隔离性,会产生很多问题
- 典型的3个问题
- 读脏数据–一个未提交事务读取到另一个未提交事务的数据(salary=60000)

- 不可重复读: 一个未提交的事务读取到另一个提交事务中修改的数据(salary=500)(是一种现象,允许产生)

- 虚(幻)读:一个未提交事务,读到另一个已提交事务的添加的数据
- 丢失更新
- 通过设置设置事务隔离级别,解决读问题
| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
| — | — | — | — |
| READ UNCOMMITTED (读未提交) | 有 | 有 | 有 |
| READ COMMITTED (读已提交) | 无 | 有 | 有 |
| REPEATABLE READ (可重复读)(MySQL默认) | 无 | 无 | 有 |
| SERIALIZABLE (序列化) | 无 | 无 | 无 |
@Service
//Spring注解声明式管理事务,该注解可用于类/方法上
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,isolation = Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ)
public class UserService {}
面试题:MySQL如何解决不可重复读和幻读现象?
4.3 timeout: 超时时间
- 事务需要在一定时间内进行提交,如果不提交会进行回滚
- spring中事务超时时间默认值:-1(无时间限制),设置的时间以秒为单位
4.4 readOnly: 是否只读
- 读:查询操作;写:添加,删除,修改操作
- readOnly默认值false,可读可写
- 设置readOnly=true==>只读模式==>只能执行查询操作
4.5 rollbackFor: 回滚
- 设置出现指定异常进行事务回滚
4.6 noRollbackFor: 不可回滚
- 设置出现指定异常不进行回滚
4.7 noRollbackForClassName
5.SpringXML声明式事务管理
在Spring配置文件中进行配置

<!--1.创建事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!--注入数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--2.配置通知-->
<tx:advice id="notice">
<tx:attributes>
<!--指定在那种规则的方法上添加事务-->
<tx:method name="transferAccount" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<!--<tx:method name="transfer*"/>-->
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--3.配置切入点和切面-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="pt" expression="execution(* com.ljz.spring5.service.UserService.*(..))"/>
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="notice" pointcut-ref="pt"/>
</aop:config>
6.Spring完全注解声明式事务管理
@Configuration//配置类
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.ljz")//开启主键扫描
@EnableTransactionManagement//开启事务
public class SpringTransactionConfig {
//创建数据库连接池
@Bean
public DruidDataSource getDataSource(){
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:33068/user_db?characterEncoding=utf-8");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("abc123");
return dataSource;
}
//创建jdbcTemplate对象
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource){
//在getDataSource()执行完成之后ioc容器中就存在DataSource对象,形参直接从ioc容器中获取
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
//注入DataSource
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
return jdbcTemplate;
}
//创建事务管理器对象
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager getDataSourceTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return transactionManager;
}
}
Spring5新功能…
Spring6新功能…

开放原子开发者工作坊旨在鼓励更多人参与开源活动,与志同道合的开发者们相互交流开发经验、分享开发心得、获取前沿技术趋势。工作坊有多种形式的开发者活动,如meetup、训练营等,主打技术交流,干货满满,真诚地邀请各位开发者共同参与!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容













所有评论(0)