一、基本信息
1.本次作业的地址: https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/ntu/Embedded_Application/homework/2088
2.项目Git的地址:https://gitee.com/ntucs/PairProg/tree/SE016_017
3.开发环境:Pycharm2018、Python3.6
4.结对成员:1613072016 高耀、1613072017 钱金
二、项目分析
1.程序运行模块(方法、函数)介绍
1.1Task1:
(1)读文件到缓冲区,统计文本行数(process_file(dst))
def process_file(dst): # 读文件到缓冲区,统计文本行数 try: # 打开 file = open(dst, 'r') # dst为文本的目录路径 except IOError as e: print(e) return None try: # 读文件到缓冲区,统计文本行数 lines = len(file.readlines()) # 关闭文件,重新打开 file.close() file = open(dst, "r") bvffer = file.read() except: print("Read File Error!") return None file.close() return bvffer, lines
(2)处理缓冲区,返回存放每个单词频率的字典word_freq,单词总数(process_buffer(bvffer))
def process_buffer(bvffer): # 处理缓冲区,返回存放每个单词频率的字典word_freq,单词总数 if bvffer: word_freq = {} # 将文本内容都小写 bvffer = bvffer.lower() # 用空格消除文本中标点符号 words = bvffer.replace(punctuation, ' ').split(' ') # 正则匹配至少以4个英文字母开头,跟上字母数字符号,单词以分隔符分割,不区分大小写 regex_word = "^[a-z]{4}(\w)*" for word in words: if re.match(regex_word, word): # 数据字典已经存在该单词,数量+1 if word in word_freq.keys(): word_freq[word] = word_freq[word] + 1 # 不存在,把单词存入字典,数量置为1 else: word_freq[word] = 1 return word_freq, len(words)
(3) 按照单词的频数排序,返回前十的单词组(output_result(word_freq))
def output_result(word_freq): # 按照单词的频数排序,返回前十的单词组 if word_freq: sorted_word_freq = sorted(word_freq.items(), key=lambda v: v[1], reverse=True) for item in sorted_word_freq[:10]: # 输出 Top 10 的单词 print('<' + str(item[0]) + '>:' + str(item[1])) return sorted_word_freq[:10]
(4)保存结果到文件result.txt(save_result(lines, words, items))
def save_result(lines, words, items): # 保存结果到文件(result.txt) try: result = open("result.txt", "w") # 以写模式打开,并清空文件内容 except Exception as e: result = open("result.txt", "x") # 文件不存在,创建文件并打开 # 写入文件result.txt result.write("lines:" + lines + "\n") result.write("words:" + words + "\n") for item in items: item = '<' + str(item[0]) + '>:' + str(item[1]) + '\n' result.write(item) print('写入result.txt已完成') result.close()
(5) 主函数入口
if __name__ == "__main__": # 命令行传递参数 parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument('dst') args = parser.parse_args() dst = args.dst bvffer, lines = process_file(dst) word_freq, words = process_buffer(bvffer) items = output_result(word_freq) # 把lines、words类型强制转化为str lines = str(lines) words = str(words) save_result(lines, words, items)
1.2Task2:
(1)停词表模块(在Task1的基础上,在process_buffer(buffer)函数内增加语句读取stopwords.txt内容并实现跳过这些单词输出)
def process_buffer(bvffer): # 处理缓冲区,返回存放每个单词频率的字典word_freq,单词总数 if bvffer: word_freq = {} # 将文本内容都小写 bvffer = bvffer.lower() # 用空格消除文本中标点符号 words = bvffer.replace(punctuation, ' ').split(' ') # 正则匹配至少以4个英文字母开头,跟上字母数字符号,单词以分隔符分割,不区分大小写 regex_word = "^[a-z]{4}(\w)*" # 停词表模块 txtWords = open("stopwords.txt", 'r').readlines() # 读取停词表文件 stopWords = [] # 存放停词表的list # 读取文本是readlines所以写入list要将换行符取代 for i in range(len(txtWords)): txtWords[i] = txtWords[i].replace('\n', '') stopWords.append(txtWords[i]) for word in words: if word not in stopWords: # 当单词不在停词表中时,使用正则表达式匹配 if re.match(regex_word, word): # 数据字典已经存在该单词,数量+1 if word in word_freq.keys(): word_freq[word] = word_freq[word] + 1 # 不存在,把单词存入字典,数量置为1 else: word_freq[word] = 1 return word_freq, len(words)
(2)高频词组模块(nltk的安装就不再赘述,使用nltk.collocations下的两个类BigramCollocationFinder、 TrigramCollocationFinder,在Task1的基础上增加def word_group(dst)函数实现对二元词组和三元词组的统计)【参考博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/no-tears-girl/p/7096519.html】
def word_group(dst): # 统计高频的二元词组、三元词组BigramCollocationFinder、 TrigramCollocationFinder str = open(dst, 'r').read() # 用空格消除文本中标点符号 wordGroup = str.lower() tokens = nltk.wordpunct_tokenize(wordGroup) # 二元词组 finder = nltk.collocations.BigramCollocationFinder.from_words(tokens) # 过滤掉符合条件fn的词组 finder.apply_word_filter(lambda x: x in [',', '.', '’', '“', '”', '\'', '"', ',"', ',”']) print("频率前五的二元词组") # 这里的key是排序依据,就是说先按t[1](词频)排序,-表示从大到小;再按照词组(t[0])排序,默认从a-z. print(sorted(finder.ngram_fd.items(), key=lambda t: (-t[1], t[0]))[:5]) # 三元词组 finder = nltk.collocations.TrigramCollocationFinder.from_words(tokens) # 过滤掉符合条件fn的词组 finder.apply_word_filter(lambda x: x in [',', '.', '’', '“', '”', '\'', '"', ',"', ',”']) print("频率前五的三元词组") print(sorted(finder.ngram_fd.items(), key=lambda t: (-t[1], t[0]))[:5])
2.程序算法的时间、空间复杂度分析
(1)以下面的代码为例进行分析
def output_result(word_freq): # 按照单词的频数排序,输出前十的单词 if word_freq: sorted_word_freq = sorted(word_freq.items(), key=lambda v: v[1], reverse=True) for item in sorted_word_freq[:10]: # 输出 Top 10 的单词 print('<' + str(item[0]) + '>:' + str(item[1])) return sorted_word_freq[:10]
时间复杂度:sort函数使用的Timsort算法,其最Best Case下时间复杂度为O(n),Average Case下时间复杂度为O(nlog2n),Worst Case下时间复杂度为O(nlog2n); for循环的时间复杂度为O(n);所以该段代码的时间复杂度:Best Case:O(n), Average Case:O(nlog2n) ,Worst Case:O(nlog2n)
空间复杂度:sort函数使用的Timsort算法空间复杂度为O(n),for循环的空间复杂度也为O(n),所以该段代码的空间复杂度为O(n)
3.程序运行案例截图
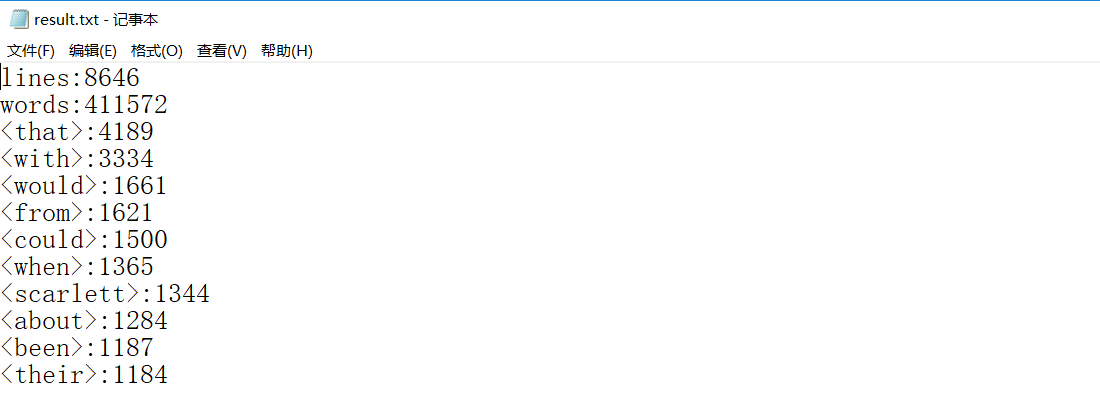
(1)Task1 基本任务:result.txt截图

(2)Task2.1 停词功能:stopwords.txt截图、result.txt截图(自定义停用词,该处为与Task1结果对比,挑选上图结果的一部分单词作为停用词)

(3)Task2.2 高频词组

三、性能分析(把主函数的语句用main()函数封装,在主函数运行性能测试代码)
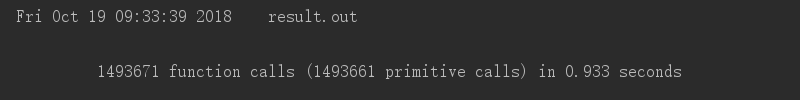
1.Task1
(1)运行时间
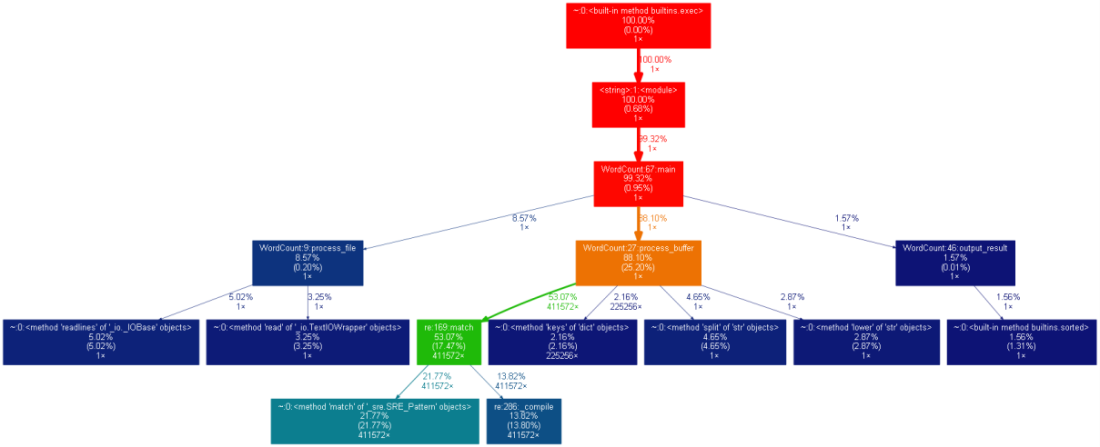
(2)性能图表(result.out->result.png)
2.Task2
(1)运行时间
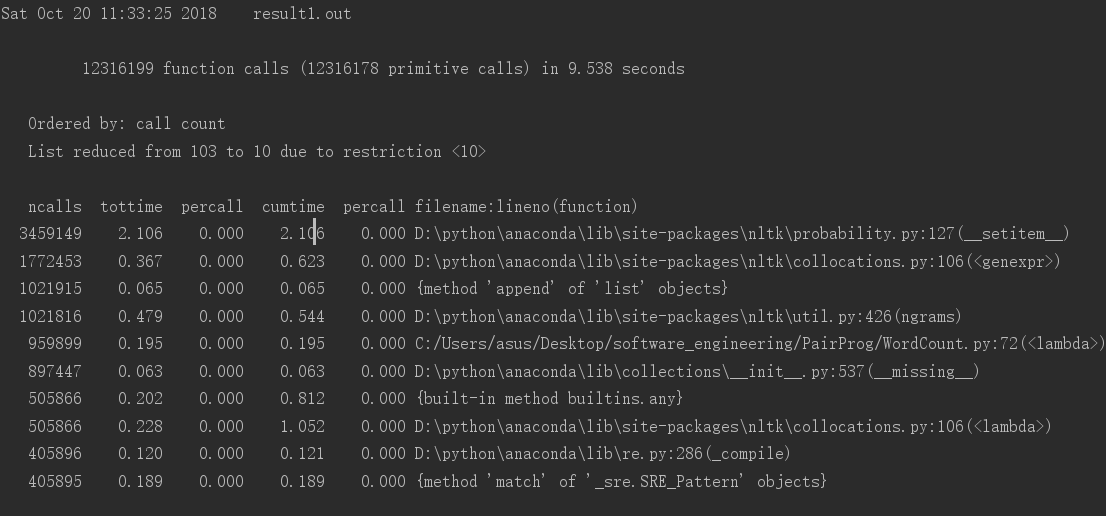
(2)性能图表(result1.out->result1.png)
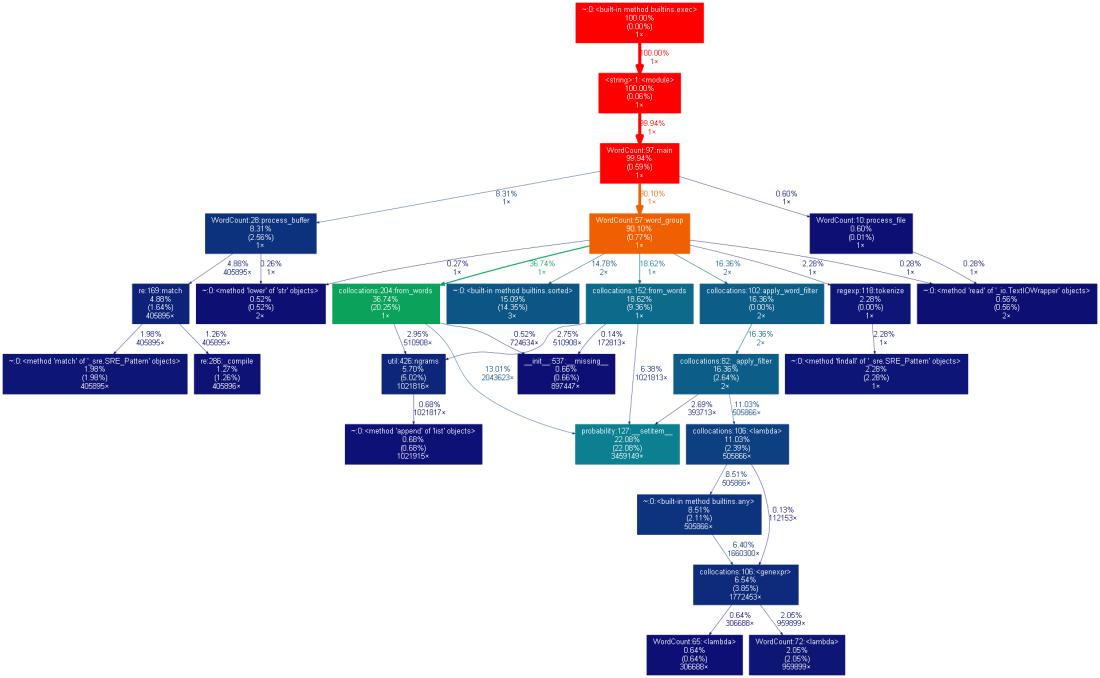
四、其他
1.结对编程时间开销
| PSP | 任务内容 | 预估耗时(min) | 实际耗时(min) |
| Planning | 计划 | 40 | 50 |
| Coding Standard | 代码规范 | 10 | 10 |
| Coding | 具体编码 | 180 | 200 |
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 30 | 25 |
| Test And Improve | 性能测试及改进 | 40 | 50 |
| Reporting | 撰写博客以及push码云 | 100 | 100 |
| Postmortem | 总结 | 10 | 15 |
| 合计 | 410 | 450 |
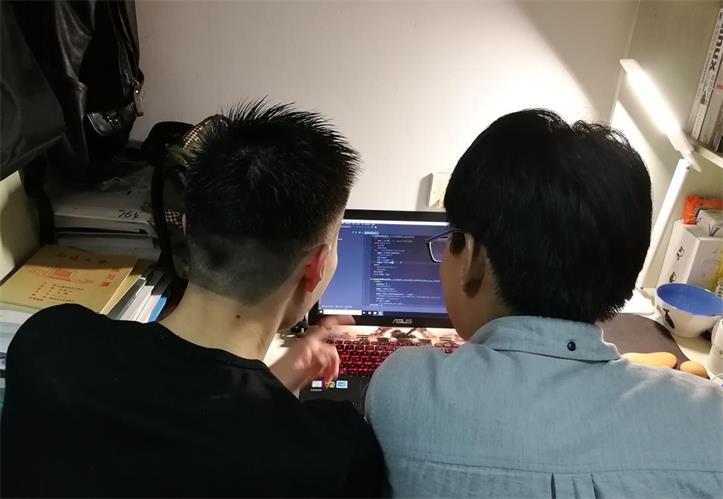
2.结对编程照片

五、事后分析与总结
1.简述关于停词表部分的决策过程
一开始准备使用nltk中的停词表,但是考虑到时间开销以及停词效果显示方面的原因,我们选择创建stopwords.txt,自定义停词内容,然后通过代码读取txt文档中停用词,在输出词频前十的过程中进行剔除停用词。
2.评价
(1)钱金评价高耀:①高耀同学学习能力强、对于不熟悉的方法上手很快。表现在:Task2中要求实现统计高频短语,高耀同学快速掌握了 nltk(Natural LanguageToolkit,自然语言处理工具包)的使用方法。②高耀同学做事认真且有条理、但是严谨性需加强。表现在:编写博客层次清晰有条理,但是对于代码的容错机制欠缺。
(2)高耀评价钱金:①钱金同学思维活跃、常常想出好的方法。表现在:Task2中要求实现统计高频短语,钱金同学想出使用正则表达式的方法来匹配短语。②钱金同学的基础代码能力欠缺,需要继续努力。
3.关于结对过程的建议
(1)可以以自由结对编程的形式开展,同学自主寻找的结对伙伴彼此比较熟悉能够更有效率地开展结对编程工作;当然,不太熟悉的人结对编程也有一定好处,如可以锻炼个人的与他人交流沟通、相处之道。
4.其他
(1)大多数人偏好 “单打独斗”,只愿一个人完成整个功能的实现,而忽视了这种做法存在的致命缺陷——主观意愿过强;而结对作业不仅提供了一个能从客观角度帮助你分析的队友,还提供了一种结对编程形式的模板——其中一人主攻编码模块,另一人则更客观提出编码意见促进编码实现,这也算是一种不可多得的编程体验吧。







 已为社区贡献11条内容
已为社区贡献11条内容

所有评论(0)